Hernia
This article is currently under review and may not be up to date. Please come back soon to see the finished work! (21/05/2020)
Original Editors -
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Kim Jackson, Admin, Nehal Shah, WikiSysop and Claire Knott
Introduction[edit | edit source]
A hernia occurs when an organ or fatty tissue squeezes through a weak spot in a surrounding muscle or connective tissue called fascia.
The most common types of hernia are[1]:
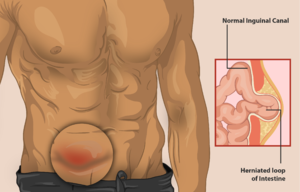
- Inguinal (inner groin) see R image
- Incisional (resulting from an incision)
- Femoral (outer groin)
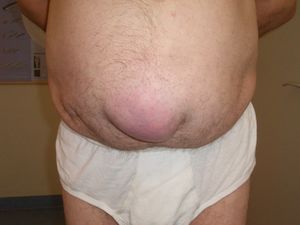
- Umbilical (belly button) see image R second down.
- Hiatal (upper stomach).
Causes[edit | edit source]
All hernias are caused by a combination of pressure and an opening/weakness of muscle or fascia; the pressure pushes an organ or tissue through the opening or weak spot. Sometimes the muscle weakness is present at birth; more often, it occurs later in life.
Anything that causes an increase in pressure in the abdomen can cause a hernia, including:
- Lifting heavy objects without stabilizing the abdominal muscles
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Persistent coughing or sneezing
- Obesity, poor nutrition, and smoking (all weaken muscles and make hernias more likely).
Types[edit | edit source]
- Inguinal hernia - the intestine or the bladder protrudes through the abdominal wall or into the inguinal canal in the groin.
- About 96% of all groin hernias are inguinal, and most occur in men because of a natural weakness in this area.
2. Incisional hernia - the intestine pushes through the abdominal wall at the site of previous abdominal surgery.
- This type is most common in elderly or overweight people who are inactive after abdominal surgery.
3. Femoral hernia - occurs when the intestine enters the canal carrying the femoral artery into the upper thigh.
- Femoral hernias are most common in women, especially those who are pregnant or obese.
4. Umbilical hernia - part of the small intestine passes through the abdominal wall near the navel.
- Common in newborns, it also commonly afflicts obese women or those who have had many children.
5. Hiatal hernia - upper stomach squeezes through the hiatus, an opening in the diaphragm through which the esophagus passes.
Characteristics/Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
add text here
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
add text here
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
add text here related to medical diagnostic procedures
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
add links to outcome measures here (also see Outcome Measures Database)
Examination[edit | edit source]
add text here related to physical examination and assessment
Medical Management[edit | edit source]
add text here
Physical Therapy Management[edit | edit source]
add text here
Key Research[edit | edit source]
add links and reviews of high quality evidence here (case studies should be added on new pages using the case study template)
Resources[edit | edit source]
add appropriate resources here
Clinical Bottom Line[edit | edit source]
add text here
References[edit | edit source]
see adding references tutorial.
- ↑ wdmed Hernias the basics Available from:https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/understanding-hernia-basics (last accessed 21.5.2020)