Hernia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
* Lifting heavy objects without stabilizing the [[Abdominal Muscle Anatomy|abdominal muscles]] | * Lifting heavy objects without stabilizing the [[Abdominal Muscle Anatomy|abdominal muscles]] | ||
* [[Incontinence|Diarrhea or constipation]] | * [[Incontinence|Diarrhea or constipation]] | ||
* Family History—Although family history may not guarantee a hernia, research shows it is a reliable predictor of one occurring. | |||
* Persistent coughing or sneezing | * Persistent coughing or sneezing | ||
* [[Obesity]], poor [[nutrition]], and [[Smoking Cessation and Brief Intervention|smoking]] (all weaken muscles and make hernias more likely). | * [[Obesity]], poor [[nutrition]], and [[Smoking Cessation and Brief Intervention|smoking]] (all weaken muscles and make hernias more likely). | ||
* Pregnancy—The risk is small, but studies show that pregnancy is associated with an increase in the risk of hernia recurrence. | |||
* Injury—Most sports-related hernias occur in the groin and don’t appear as a bulge. But if left untreated, it can evolve into an inguinal hernia<ref>Utahhealth [https://healthcare.utah.edu/healthfeed/postings/2018/02/hernia.php Hernias] Available from:https://healthcare.utah.edu/healthfeed/postings/2018/02/hernia.php (last accessed 21.5.2020)</ref>. | |||
== Types == | == Types == | ||
| Line 41: | Line 44: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
== | == Prevention == | ||
Tips to Decrease the Risk of a Hernia | |||
* Maintain a healthy weight. Rapid weight loss and weight gain place pressure on the abdominal wall. | |||
* Don’t smoke. | |||
* Change lifting stance. Lift with the legs, not the back. | |||
* Change your diet to improve bowel movements.<br> | |||
== | == Treatment == | ||
If the hernia is growing larger or causing pain surgeons may decide it’s best to operate. Repair may be by sewing the hole in the abdominal wall closed during surgery. This is commonly done by patching the hole with surgical mesh. | |||
Hernias can be repaired with either open or laparoscopic surgery. | |||
* Laparoscopic surgery uses a tiny camera and miniaturized surgical equipment to repair the hernia using only a few small incisions. It’s also less damaging to the surrounding tissue. | |||
* Open surgery, the surgeon makes an incision close to the site of the hernia, and then pushes the bulging tissue back into the abdomen. They then sew the area shut, sometimes reinforcing it with surgical mesh. Finally, they close the incision. | |||
== Diagnostic Procedures == | == Diagnostic Procedures == | ||
Can include ( after medical history taken) | |||
* abdominal ultrasound - high-frequency sound waves to create an image of the structures inside the body | |||
* CT scan, which combines X-rays with computer technology to produce an image | |||
* MRI scan | |||
If a hiatal hernia is suspected other tests that allow them to assess the internal location of your stomach may be ordered: | |||
Gastrografin or barium X-ray, which is a series of X-ray pictures of your digestive tract. The pictures are recorded drinking a liquid containing diatrizoate meglumine and diatrizoate sodium (Gastrografin) or a liquid barium solution. Both show up well on the X-ray images. | |||
Endoscopy, which involves threading a small camera attached to a tube down the throat and into esophagus and stomach. | |||
== Outcome Measures == | == Outcome Measures == | ||
Revision as of 08:29, 21 May 2020
This article is currently under review and may not be up to date. Please come back soon to see the finished work! (21/05/2020)
Original Editors -
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Kim Jackson, Admin, Nehal Shah, WikiSysop and Claire Knott
Introduction[edit | edit source]
A hernia occurs when an organ or fatty tissue squeezes through a weak spot in a surrounding muscle or connective tissue called fascia.
The most common types of hernia are[1]:
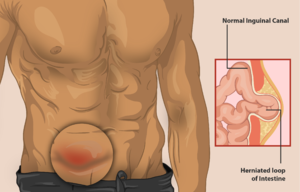
- Inguinal (inner groin) see R image
- Incisional (resulting from an incision)
- Femoral (outer groin)
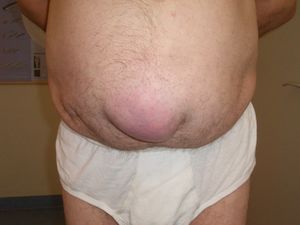
- Umbilical (belly button) see image R second down.
- Hiatal (upper stomach).
Causes[edit | edit source]
All hernias are caused by a combination of pressure and an opening/weakness of muscle or fascia; the pressure pushes an organ or tissue through the opening or weak spot. Sometimes the muscle weakness is present at birth; more often, it occurs later in life.
Anything that causes an increase in pressure in the abdomen can cause a hernia, including:
- Lifting heavy objects without stabilizing the abdominal muscles
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Family History—Although family history may not guarantee a hernia, research shows it is a reliable predictor of one occurring.
- Persistent coughing or sneezing
- Obesity, poor nutrition, and smoking (all weaken muscles and make hernias more likely).
- Pregnancy—The risk is small, but studies show that pregnancy is associated with an increase in the risk of hernia recurrence.
- Injury—Most sports-related hernias occur in the groin and don’t appear as a bulge. But if left untreated, it can evolve into an inguinal hernia[2].
Types[edit | edit source]
- Inguinal hernia - the intestine or the bladder protrudes through the abdominal wall or into the inguinal canal in the groin.
- About 96% of all groin hernias are inguinal, and most occur in men because of a natural weakness in this area.
2. Incisional hernia - the intestine pushes through the abdominal wall at the site of previous abdominal surgery.
- This type is most common in elderly or overweight people who are inactive after abdominal surgery.
3. Femoral hernia - occurs when the intestine enters the canal carrying the femoral artery into the upper thigh.
- Femoral hernias are most common in women, especially those who are pregnant or obese.
4. Umbilical hernia - part of the small intestine passes through the abdominal wall near the navel.
- Common in newborns, it also commonly afflicts obese women or those who have had many children.
5. Hiatal hernia - upper stomach squeezes through the hiatus, an opening in the diaphragm through which the esophagus passes.
Prevention[edit | edit source]
Tips to Decrease the Risk of a Hernia
- Maintain a healthy weight. Rapid weight loss and weight gain place pressure on the abdominal wall.
- Don’t smoke.
- Change lifting stance. Lift with the legs, not the back.
- Change your diet to improve bowel movements.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
If the hernia is growing larger or causing pain surgeons may decide it’s best to operate. Repair may be by sewing the hole in the abdominal wall closed during surgery. This is commonly done by patching the hole with surgical mesh.
Hernias can be repaired with either open or laparoscopic surgery.
- Laparoscopic surgery uses a tiny camera and miniaturized surgical equipment to repair the hernia using only a few small incisions. It’s also less damaging to the surrounding tissue.
- Open surgery, the surgeon makes an incision close to the site of the hernia, and then pushes the bulging tissue back into the abdomen. They then sew the area shut, sometimes reinforcing it with surgical mesh. Finally, they close the incision.
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
Can include ( after medical history taken)
- abdominal ultrasound - high-frequency sound waves to create an image of the structures inside the body
- CT scan, which combines X-rays with computer technology to produce an image
- MRI scan
If a hiatal hernia is suspected other tests that allow them to assess the internal location of your stomach may be ordered:
Gastrografin or barium X-ray, which is a series of X-ray pictures of your digestive tract. The pictures are recorded drinking a liquid containing diatrizoate meglumine and diatrizoate sodium (Gastrografin) or a liquid barium solution. Both show up well on the X-ray images.
Endoscopy, which involves threading a small camera attached to a tube down the throat and into esophagus and stomach.
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
add links to outcome measures here (also see Outcome Measures Database)
Examination[edit | edit source]
add text here related to physical examination and assessment
Medical Management[edit | edit source]
add text here
Physical Therapy Management[edit | edit source]
add text here
Key Research[edit | edit source]
add links and reviews of high quality evidence here (case studies should be added on new pages using the case study template)
Resources[edit | edit source]
add appropriate resources here
Clinical Bottom Line[edit | edit source]
add text here
References[edit | edit source]
see adding references tutorial.
- ↑ wdmed Hernias the basics Available from:https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/understanding-hernia-basics (last accessed 21.5.2020)
- ↑ Utahhealth Hernias Available from:https://healthcare.utah.edu/healthfeed/postings/2018/02/hernia.php (last accessed 21.5.2020)