Hamstrings: Difference between revisions
Shoko Otsuka (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Shoko Otsuka (talk | contribs) m (Added references) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}; | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}; | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
= Description | == Description == | ||
[[File:Hamstring tendons.png|thumb]] | [[File:Hamstring tendons.png|thumb]] | ||
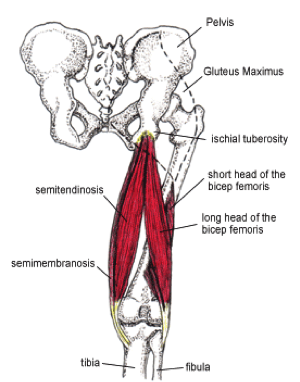
The hamstrings are a group of three muscles which predominantly act to flex the knee. Hamstrings consist of 3 muscles; | The hamstrings are a group of three muscles which predominantly act to flex the knee. Hamstrings consist of 3 muscles; | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
The muscles cross two joints and have long proximal and distal tendons with resultant long muscle tendon junctions (MTJ). MTJs extend into the muscle bellies, overlap within the muscle belly, facilitate transmission and dissipate forces across the MTJ while muscle contraction and relaxation. | The muscles cross two joints and have long proximal and distal tendons with resultant long muscle tendon junctions (MTJ). MTJs extend into the muscle bellies, overlap within the muscle belly, facilitate transmission and dissipate forces across the MTJ while muscle contraction and relaxation.<ref name=":0">Linklater JM, Hamilton B, Carmichael J, Orchard J, Wood DG. [https://www.thieme-connect.com/products/ejournals/abstract/10.1055/s-0030-1253157 Hamstring injuries: anatomy, imaging, and intervention]. InSeminars in musculoskeletal radiology 2010 Jun (Vol. 14, No. 02, pp. 131-161). © Thieme Medical Publishers.</ref> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 22: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
= Anatomy = | == Anatomy<ref>Timmins R, Woodley S, Shield A, Opar D. Anatomy of the Hamstrings. In: Thorborg K, Opar D, Shield A. (eds) [https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-31638-9_1 Prevention and Rehabilitation of Hamstring Injuries.] Springer: Cham, 2020. P1-30.</ref><ref name=":1">Palastanga N, Soames R. Anatomy and human movement, structure and function with PAGEBURST access, 6: [https://books.google.co.uk/books?hl=en&lr=&id=ySwhKi1qmlAC&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=anatomy+and+human+movement&ots=YTvZsnzCkq&sig=l5n7mQlQEKn4mq_GB3NssSIzjj0&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=anatomy%20and%20human%20movement&f=false Anatomy and Human Movement]. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2011.</ref> == | ||
==== Semimembranosus ==== | ==== Semimembranosus ==== | ||
| Line 91: | Line 92: | ||
-External rotation of lower leg when knee slightly flexed | -External rotation of lower leg when knee slightly flexed | ||
= Function of the hamstring muscle complex = | == Function of the hamstring muscle complex == | ||
The hamstrings are muscles which extend the hip and flex the knee. The hamstrings play an important part in the complex gait cycle during walking, which includes absorption of kinetic energy and protection of the knee and hip joints. During the swing phase of walking, the hamstrings decelerate the forward motion of the tibia. There is a complex interplay between hamstrings contraction and quadriceps contraction, which is an antagonist muscle of hamstrings. | The hamstrings are muscles which extend the hip and flex the knee. The hamstrings play an important part in the complex gait cycle during walking, which includes absorption of kinetic energy and protection of the knee and hip joints. During the swing phase of walking, the hamstrings decelerate the forward motion of the tibia. There is a complex interplay between hamstrings contraction and quadriceps contraction, which is an antagonist muscle of hamstrings.<ref name=":0" /><ref name=":1" /> | ||
= Resources = | == Resources == | ||
{| width="100%" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" | {| width="100%" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 115: | Line 116: | ||
|} | |} | ||
= See also | == See also == | ||
[[Hamstring_Strain|Hamstring strain]]. | [[Hamstring_Strain|Hamstring strain]]. | ||
| Line 122: | Line 123: | ||
[[ACL_Reconstruction|Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction]]. | [[ACL_Reconstruction|Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction]]. | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 12:45, 21 August 2022
Original Editor - George Prudden,
Top Contributors - George Prudden, Shoko Otsuka, Kim Jackson, Shaimaa Eldib and WikiSysop;
Description[edit | edit source]
The hamstrings are a group of three muscles which predominantly act to flex the knee. Hamstrings consist of 3 muscles;
The muscles cross two joints and have long proximal and distal tendons with resultant long muscle tendon junctions (MTJ). MTJs extend into the muscle bellies, overlap within the muscle belly, facilitate transmission and dissipate forces across the MTJ while muscle contraction and relaxation.[1]
Anatomy[2][3][edit | edit source]
Semimembranosus[edit | edit source]
Origin: The upper lateral facet on the ischial tuberosity
Insertion: A horizontal groove on the posteromedial surface of the medial tibial condyle
Nerve: Tibial division of the sciatic nerve (L5, S1 and 2)
Artery: Branches from the internal iliac, popliteal, and profunda femoris arteries
Function:
-Hip extension
-Knee flexion
-Internal rotation of lower leg when the knee is flexed
Semitendinosus[edit | edit source]
Origin: The lower medial facet of the lateral section of the ischial tuberosity
Insertion: A vertical line on the medial surface of the medial condyle of the tibia just behind the insertion of sartorius and behind and below the attachment of gracilis
Nerve: Tibial division of the sciatic nerve (L5, S1 and 2)
Artery: Branches from the internal iliac, popliteal, and profunda femoris arteries
Function:
-Hip extension
-Knee flexion
-Internal rotation of lower leg when the knee is flexed
Biceps femoris - Long head[edit | edit source]
Origin: The lower medial facet on the ischial tuberosity with the tendon of semitendinosus, spreading onto the sacrotuberous ligament
Insertion: The head of the fibular, the lateral tibial condyle and the posterior aspect of the lateral intermuscular septum
Nerve: Tibial division of the sciatic nerve (L5, S1 and 2)
Artery: Perforating branches of profunda femoris, inferior gluteal, and medial circumflex femoral arteries
Function:
-Knee flexion
-Hip extension
-External rotation of lower leg when knee slightly flexed
-Assist in external rotation of the thigh when hip extended
Biceps femoris – Short head[edit | edit source]
Origin: The lower half of the lateral lip of the linea aspera
Insertion: The head of the fibular, the lateral tibial condyle and the posterior aspect of the lateral intermuscular septum
Nerve: The common peroneal division of the sciatic nerve (L5, S1 and 2)
Artery: Perforating branches of profunda femoris, inferior gluteal, and medial circumflex femoral arteries
Function:
-Knee flexion
-External rotation of lower leg when knee slightly flexed
Function of the hamstring muscle complex[edit | edit source]
The hamstrings are muscles which extend the hip and flex the knee. The hamstrings play an important part in the complex gait cycle during walking, which includes absorption of kinetic energy and protection of the knee and hip joints. During the swing phase of walking, the hamstrings decelerate the forward motion of the tibia. There is a complex interplay between hamstrings contraction and quadriceps contraction, which is an antagonist muscle of hamstrings.[1][3]
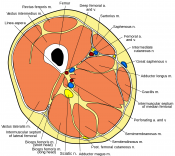
Resources[edit | edit source]
|
|
See also[edit | edit source]
Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Linklater JM, Hamilton B, Carmichael J, Orchard J, Wood DG. Hamstring injuries: anatomy, imaging, and intervention. InSeminars in musculoskeletal radiology 2010 Jun (Vol. 14, No. 02, pp. 131-161). © Thieme Medical Publishers.
- ↑ Timmins R, Woodley S, Shield A, Opar D. Anatomy of the Hamstrings. In: Thorborg K, Opar D, Shield A. (eds) Prevention and Rehabilitation of Hamstring Injuries. Springer: Cham, 2020. P1-30.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Palastanga N, Soames R. Anatomy and human movement, structure and function with PAGEBURST access, 6: Anatomy and Human Movement. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2011.