Flexor Hallucis Brevis: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(Unlinked incorrect page) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Description: == | == Description: == | ||
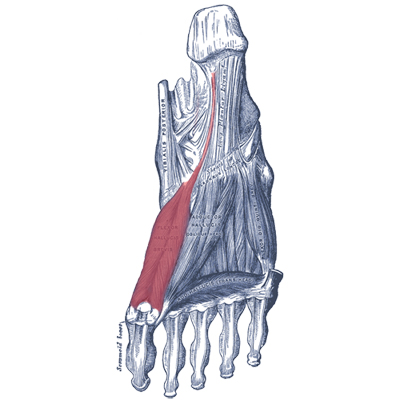
Flexor hallucis brevis is one of the third | Flexor hallucis brevis (FHB) is one of the muscles in the third layer (of four layers) of plantar muscles. It is located adjacent to the plantar surface of the 1st metatarsal and contains 2 sesamoid bones. <ref name="Fhb">Helen J.Hislop Jacqueline Montgomery,Muscle Testing,2007,8th edition.</ref>Other muscles in the third layer of plantar muscles include the [[Adductor Hallucis|adductor hallucis]] (oblique and transverse heads) and the flexor digiti minimi brevis. | ||
[[Image:Musculus flexor hallucis brevis1 (1).jpg|frame|right|50x100px]] | [[Image:Musculus flexor hallucis brevis1 (1).jpg|frame|right|50x100px]] | ||
==== Origin: ==== | ==== Origin: ==== | ||
The | The flexor hallucis brevis originates along the plantar aspect of the [[cuboid]] and [[cuneiforms]].<ref>Bartosiak K, McCormick JJ. Avascular Necrosis of the Sesamoids. Foot Ankle Clin. 2019 Mar;24(1):57-67.</ref> | ||
==== Insertion: ==== | |||
= | The medial head of the FHB is the larger head of the two. It inserts medially on the plantar plate. Also, it forms a common tendon with the [[Abductor Hallucis|abductor hallucis]] muscle before the insertion point at the base of the proximal phalanx.<ref name=":0">Hakim-Zargar M, Aronow MS, Gibson L, Obopilwe E. Implications for the anatomy of the flexor hallucis brevis insertion. Foot Ankle Int. 2010 Jan;31(1):65-8.</ref> Within this tendon sits the tibial sesamoid bone. | ||
The lateral head of the FHB inserts laterally on the plantar plate. It forms a common tendon with the [[Adductor Hallucis|adductor hallucis]] muscle before inserting on the lateral aspect of the base of the proximal phalanx.<ref name=":0" /> Within this tendon sits the fibular sesamoid bone. | |||
==== Nerve: ==== | ==== Nerve: ==== | ||
The medial and lateral head of the flexor hallucis brevis is innervated by | The medial and lateral head of the flexor hallucis brevis is innervated by the [[Medial Plantar Nerve|medial plantar nerve]]. Both heads are represented by the spinal segments S1 and S2. | ||
==== Artery: ==== | ==== Artery: ==== | ||
Supplied by branches of the posterior tibial artery | Supplied by branches of the posterior tibial artery. | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Flexion of the great toe at the | Flexion of the great toe at the [[Foot and Ankle Structure and Function|metatarsophalangeal joint]] with the assistance of the [[flexor hallucis longus]]. | ||
== Clinical Significance == | == Clinical Significance == | ||
Dysfunction of the flexor hallucis brevis will commonly present as pain in the ball of the foot when extending the big toe, difficulty and pain during gait and | Dysfunction of the flexor hallucis brevis will commonly present as pain in the ball of the foot when extending the big toe, difficulty and pain during gait, and toe deformities. This may be due to muscle injury of the FHB or [[sesamoiditis]]. | ||
Aggravation of the muscle may occur when the second toe is longer than the other toes, walking or running on uneven ground, wearing high heels or shoes that are too small. | Aggravation of the muscle may occur when the second toe is longer than the other toes, walking or running on uneven ground, wearing high heels or shoes that are too small. | ||
| Line 46: | Line 44: | ||
==== Muscle strength: ==== | ==== Muscle strength: ==== | ||
FHB strength can be measured manually by [https://www.physio-pedia.com/Category:Manual_Muscle_Testing?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=search&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal MMT] grading. Start the test by having the patient in supine/long sitting position with the foot hanging over the table. With your hand, hold the foot just below the ankle for stabilization and ask the patient to flex the big toe while you resist the movement by your fingers of the other hand. | |||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
==== | ==== Stretching: ==== | ||
Stretch the muscle by moving the big toe into hyper extension as much as possible, hold then relax. | |||
==== Strengthening ==== | |||
Pulling the towel would always be the good option for strengthening the big toe and other four toe flexors, but make sure that the patient is using the FHB muscle so she/he should flex the great toe by bending it at the MP joint. You can progress the exercise by putting a weighted object on the towel or use a resistance band. | |||
<div class="row"> | |||
<div class="col-md-6"> {{#ev:youtube|S1ngV2Or7wY|250}} <div class="text-right"><ref>Rehab My Patient. Flexor hallucis brevis strengthening. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S1ngV2Or7wY [last accessed 20/1/2022]</ref></div></div> | |||
<div class="col-md-6"> {{#ev:youtube|XtJYcL4qTUY|250}} <div class="text-right"><ref>Physiohealth01. Flexor Hallucis Brevis Strength with Theraband arch support from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XtJYcL4qTUY [last accessed 20/1/2022]</ref></div></div> | |||
</div> | |||
[[Category:Anatomy]] [[Category:Foot]] [[Category:Muscles]] [[Category:Musculoskeletal/Orthopaedics]] | == References == | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] [[Category:Foot]] [[Category:Muscles]] [[Category:Musculoskeletal/Orthopaedics]] [[Category:Foot - Anatomy]][[Category:Foot - Muscles]] | |||
<references /><br> | |||
Latest revision as of 16:30, 20 January 2022
Original Editor - name here
Top Contributors - Asma Alshehri, Patti Cavaleri, Adam Vallely Farrell, Evan Thomas, WikiSysop and Kim Jackson
Description: [edit | edit source]
Flexor hallucis brevis (FHB) is one of the muscles in the third layer (of four layers) of plantar muscles. It is located adjacent to the plantar surface of the 1st metatarsal and contains 2 sesamoid bones. [1]Other muscles in the third layer of plantar muscles include the adductor hallucis (oblique and transverse heads) and the flexor digiti minimi brevis.
Origin:[edit | edit source]
The flexor hallucis brevis originates along the plantar aspect of the cuboid and cuneiforms.[2]
Insertion:[edit | edit source]
The medial head of the FHB is the larger head of the two. It inserts medially on the plantar plate. Also, it forms a common tendon with the abductor hallucis muscle before the insertion point at the base of the proximal phalanx.[3] Within this tendon sits the tibial sesamoid bone.
The lateral head of the FHB inserts laterally on the plantar plate. It forms a common tendon with the adductor hallucis muscle before inserting on the lateral aspect of the base of the proximal phalanx.[3] Within this tendon sits the fibular sesamoid bone.
Nerve:[edit | edit source]
The medial and lateral head of the flexor hallucis brevis is innervated by the medial plantar nerve. Both heads are represented by the spinal segments S1 and S2.
Artery:[edit | edit source]
Supplied by branches of the posterior tibial artery.
Function[edit | edit source]
Flexion of the great toe at the metatarsophalangeal joint with the assistance of the flexor hallucis longus.
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
Dysfunction of the flexor hallucis brevis will commonly present as pain in the ball of the foot when extending the big toe, difficulty and pain during gait, and toe deformities. This may be due to muscle injury of the FHB or sesamoiditis.
Aggravation of the muscle may occur when the second toe is longer than the other toes, walking or running on uneven ground, wearing high heels or shoes that are too small.
Assessment[edit | edit source]
Palpation: [edit | edit source]
It is nearly impossible to palpate the FHB muscle as it is located deep in the foot. (The third layer from 4 layers of the foot muscles).
Muscle strength: [edit | edit source]
FHB strength can be measured manually by MMT grading. Start the test by having the patient in supine/long sitting position with the foot hanging over the table. With your hand, hold the foot just below the ankle for stabilization and ask the patient to flex the big toe while you resist the movement by your fingers of the other hand.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Stretching:[edit | edit source]
Stretch the muscle by moving the big toe into hyper extension as much as possible, hold then relax.
Strengthening[edit | edit source]
Pulling the towel would always be the good option for strengthening the big toe and other four toe flexors, but make sure that the patient is using the FHB muscle so she/he should flex the great toe by bending it at the MP joint. You can progress the exercise by putting a weighted object on the towel or use a resistance band.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Helen J.Hislop Jacqueline Montgomery,Muscle Testing,2007,8th edition.
- ↑ Bartosiak K, McCormick JJ. Avascular Necrosis of the Sesamoids. Foot Ankle Clin. 2019 Mar;24(1):57-67.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Hakim-Zargar M, Aronow MS, Gibson L, Obopilwe E. Implications for the anatomy of the flexor hallucis brevis insertion. Foot Ankle Int. 2010 Jan;31(1):65-8.
- ↑ Rehab My Patient. Flexor hallucis brevis strengthening. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S1ngV2Or7wY [last accessed 20/1/2022]
- ↑ Physiohealth01. Flexor Hallucis Brevis Strength with Theraband arch support from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XtJYcL4qTUY [last accessed 20/1/2022]