Finkelstein Test: Difference between revisions
Venus Pagare (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Joao Costa (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (38 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | <div class="editorbox"> | ||
'''Original Editor '''- [[User:Tracy Hall|Tracy Hall]] | '''Original Editor ''' - [[User:Tracy Hall|Tracy Hall]] | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
<br> | Finkelstein’s test is the classic provocative test for diagnosis of De Quervain’s disease. Finkelstein hypothesized that the entry of the muscle bellies of the extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) and abductor pollicis longus (APL) tendons into the first extensor compartment was responsible for the findings observed in his now eponymous test.<br> | ||
== Clinically Relevant Anatomy == | |||
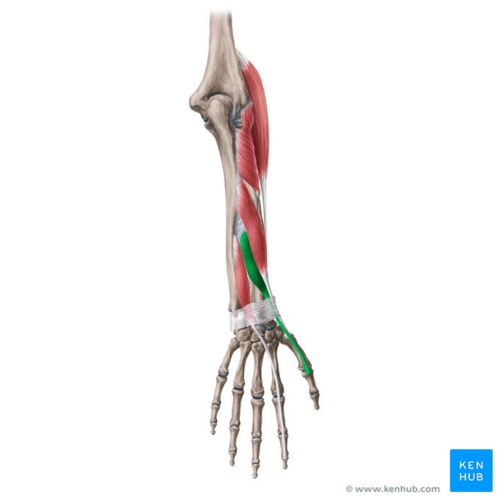
[[File:Extensor pollicis brevis muscle - Kenhub.png|alt=Extensor pollicis brevis muscle (highlighted in green) - posterior view|right|frameless|500x500px|Extensor pollicis brevis muscle (highlighted in green) - posterior view]] | |||
'''Extensor Pollicis Brevis (EPB)''' | |||
*Radial abduction of wrist (0-25°) | |||
*Thumb extension (90°) | |||
Image: Extensor pollicis brevis muscle (highlighted in green) - posterior view<ref >Extensor pollicis brevis muscle (highlighted in green) - posterior view image - © Kenhub https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/extensor-pollicis-brevis-muscle</ref><br> | |||
'''Abductor Pollicis Longus (APL)''' | |||
*Wrist radial abduction (0- 25°) | |||
*Thumb abduction (70°- 80°) | |||
<br> | |||
< | This 2 minute video is a good summary of the abductor pollicis longus.<ref >Abductor pollicis longus muscle video - © Kenhub https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/abductor-pollicis-longus-muscle</ref> | ||
{{#ev:youtube|Hoc7Hc_6u0A}} | |||
== Purpose of Testing == | |||
The Finkelstein test is used in the diagnosis of [[De Quervain's Tenosynovitis|De Quervain's]] syndrome. This fact implies a tenovaginitis and tenosynovitis of the M. extensor pollicis brevis and M. abductor pollicis longus. Finkelstein maneuver is a helpful test to diagnose De Quervain's Tendonitis or first dorsal compartment tendonitis named after the Swiss surgeon Fritz de Quervain. This is a condition brought on by irritation or inflammation of the wrist tendons at the base of the thumb. The inflammation causes the compartment (a tunnel or a sheath) around the tendon to swell and enlarge, making thumb and wrist movement painful. | |||
== Testing Position == | |||
== Testing Position | |||
Sitting or standing. | Sitting or standing. | ||
== Technique | == Technique == | ||
To begin, the patient must sit comfortable and relaxed on the examination table. Next, examine the patients hand in the air, while the other hand rests just beside the body. The therapist then asks the patient to make a fist around a thumb and to perform a ulnar deviation. | |||
< | A modified version of the test is that the patient must sit comfortable and relaxed on the examination table. The patient must hold his afflicted hand in the air, while the other hand should be resting against his/ her body. The therapist grasps the afflicted hand of the patient and rotates it in ulnar deviation. He pulls the patient’s thumb across the palm of his/ her hand. This causes additional stress on the extensor tendons of the thumb. <ref name="Day">Richard Day, John Fox; Neuro- musculoskeletal clinical tests; Churchill Livingstone Elsevier 2009- page 113 (Level of evidence = E)</ref><ref>Javier González-Iglesias, Peter Huijbregts, César Fernández-de-las-Peñas, Joshua A. Cleland; Differential Diagnosis and Physical Therapy Management of a Patient With Radial Wrist Pain of 6 Months’ Duration: A Case Report; journal of orthopaedic sports physical therapy: volume 40,number 6, June 2010. (level of evidence = C)</ref> | ||
The patient actively (or active assistive) flexes thumb maximally and wraps fingers over thumb, making a fist. The patient then ulnarly deviates his/her wrist to stretch the muscles of the 1st extensor compartment. The test is positive if the patient complains of pain over the 1st extensor compartment of the wrist. | The patient actively (or active assistive) flexes thumb maximally and wraps fingers over thumb, making a fist. The patient then ulnarly deviates his/her wrist to stretch the muscles of the 1st extensor compartment. The test is positive if the patient complains of pain over the 1st extensor compartment of the wrist. | ||
< | <clinicallyrelevant id="84104022" title="Finkelstein Test" /> | ||
== Interpretation == | |||
*<u>Negative result</u>: The patient doesn’t feel any pain radiating up the inside of his/ her arm from the thumb. <ref | *<u>Negative result</u>: The patient doesn’t feel any pain radiating up the inside of his/ her arm from the thumb. <ref name="Day" /> | ||
*<u>Positive result</u>: Ask the patient if he or she feels pain radiating up the inside of his or her arm from the thumb. If the patient reports noticeable pain then, the Finkelstein's test is positive, what indicates De | *<u>Positive result</u>: Ask the patient if he or she feels pain radiating up the inside of his or her arm from the thumb. If the patient reports noticeable pain then, the Finkelstein's test is positive, what indicates De Quervain's syndrome. <ref name="Day" />[http://www.ehow.com/how_2212413_perform-finkelsteins-test-hand.html <ref>How to Perform a Finkelstein's Test of the Hand (level of evidence = E)</ref>][[Finkelstein Test#cite%20note-3|<span class="mw-reflink-text">[3]</span>]][[Finkelstein Test|<span class="mw-reflink-text">[3]</span>]][[Finkelstein Test|<span class="mw-reflink-text">[3]</span>]]<span class="mw-reflink-text">[4]</span> | ||
== Importance of Test == | == Importance of Test == | ||
The muscles that cross the wrist are separated into compartments by the extensor retinaculum. In the first compartment, the tendons of the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus pass through to attach distally. According to Neumann, the extensor pollicis brevis attaches distally to the dorsal side of the proximal phalanx and extensor mechanism of the thumb, while the abductor pollicis longus attaches distally to the radial-dorsal side of the 1st metacarpal. The combination of maximum finger flexion and wrist ulnar deviation elongates these tendons and produces pain in symptomatic individuals.<ref>Neumann, Donald. Kinesiology of the Musculoskeletal System: Foundations for Rehabilitation. 2nd edition. St. Louis, MO: Mosby Elsevier, 2010. 303.</ref> | The muscles that cross the wrist are separated into compartments by the extensor retinaculum. In the first compartment, the tendons of the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus pass through to attach distally. According to Neumann, the extensor pollicis brevis attaches distally to the dorsal side of the proximal phalanx and extensor mechanism of the thumb, while the abductor pollicis longus attaches distally to the radial-dorsal side of the 1st metacarpal. The combination of maximum finger flexion and wrist ulnar deviation elongates these tendons and produces pain in symptomatic individuals.<ref>Neumann, Donald. Kinesiology of the Musculoskeletal System: Foundations for Rehabilitation. 2nd edition. St. Louis, MO: Mosby Elsevier, 2010. 303.</ref><br> | ||
<br> | |||
== Reliability == | |||
*Investigation into the validity of tests are important to know whether our tests are reliable or not.<br> | |||
< | *Studies that test the reliability of the Finkelstein test are very limited. One research shows that the Finkelstein test has a high reliability <ref>Javier González-Iglesias, Peter Huijbregts, César Fernández-de-las-Peñas, Joshua A. Cleland; Differential Diagnosis and Physical Therapy Management of a Patient With Radial Wrist Pain of 6 Months’ Duration: A Case Report; journal of orthopaedic; sports physical therapy: volume 40, number 6, June 2010.(level of evidence = C)</ref>, but further research is still required.<br> | ||
</ | |||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
[[Category:Assessment]] [[Category: | [[Category:Assessment]] | ||
[[Category:Wrist - Assessment and Examination]] | |||
[[Category:Hand - Assessment and Examination]] | |||
[[Category:Special Tests]] | |||
[[Category:Wrist]] | |||
[[Category:Hand]] | |||
[[Category:Tendons]] | |||
[[Category:Musculoskeletal/Orthopaedics]] | |||
[[Category:EIM_Residency_Project]] | |||
[[Category:Primary Contact]] | |||
[[Category:Sports Medicine]] | |||
[[Category:Sports Injuries]] | |||
[[Category:Athlete Assessment]] | |||
[[Category:Wrist - Special Tests]] | |||
[[Category:Hand - Special Tests]] | |||
Latest revision as of 04:33, 31 March 2022
Original Editor - Tracy Hall
Top Contributors - Aurelie Canas Perez, Admin, Kim Jackson, Venus Pagare, Rachael Lowe, Tracy Hall, Evan Thomas, Kai A. Sigel, Joao Costa, Tarina van der Stockt, WikiSysop, Laura Ritchie, Claire Knott, Wanda van Niekerk, Jennifer Chew and Tony Lowe
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Finkelstein’s test is the classic provocative test for diagnosis of De Quervain’s disease. Finkelstein hypothesized that the entry of the muscle bellies of the extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) and abductor pollicis longus (APL) tendons into the first extensor compartment was responsible for the findings observed in his now eponymous test.
Clinically Relevant Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Extensor Pollicis Brevis (EPB)
- Radial abduction of wrist (0-25°)
- Thumb extension (90°)
Image: Extensor pollicis brevis muscle (highlighted in green) - posterior view[1]
Abductor Pollicis Longus (APL)
- Wrist radial abduction (0- 25°)
- Thumb abduction (70°- 80°)
This 2 minute video is a good summary of the abductor pollicis longus.[2]
Purpose of Testing[edit | edit source]
The Finkelstein test is used in the diagnosis of De Quervain's syndrome. This fact implies a tenovaginitis and tenosynovitis of the M. extensor pollicis brevis and M. abductor pollicis longus. Finkelstein maneuver is a helpful test to diagnose De Quervain's Tendonitis or first dorsal compartment tendonitis named after the Swiss surgeon Fritz de Quervain. This is a condition brought on by irritation or inflammation of the wrist tendons at the base of the thumb. The inflammation causes the compartment (a tunnel or a sheath) around the tendon to swell and enlarge, making thumb and wrist movement painful.
Testing Position[edit | edit source]
Sitting or standing.
Technique[edit | edit source]
To begin, the patient must sit comfortable and relaxed on the examination table. Next, examine the patients hand in the air, while the other hand rests just beside the body. The therapist then asks the patient to make a fist around a thumb and to perform a ulnar deviation.
A modified version of the test is that the patient must sit comfortable and relaxed on the examination table. The patient must hold his afflicted hand in the air, while the other hand should be resting against his/ her body. The therapist grasps the afflicted hand of the patient and rotates it in ulnar deviation. He pulls the patient’s thumb across the palm of his/ her hand. This causes additional stress on the extensor tendons of the thumb. [3][4]
The patient actively (or active assistive) flexes thumb maximally and wraps fingers over thumb, making a fist. The patient then ulnarly deviates his/her wrist to stretch the muscles of the 1st extensor compartment. The test is positive if the patient complains of pain over the 1st extensor compartment of the wrist.
Finkelstein Test video provided by Clinically Relevant
Interpretation[edit | edit source]
- Negative result: The patient doesn’t feel any pain radiating up the inside of his/ her arm from the thumb. [3]
- Positive result: Ask the patient if he or she feels pain radiating up the inside of his or her arm from the thumb. If the patient reports noticeable pain then, the Finkelstein's test is positive, what indicates De Quervain's syndrome. [3][5][3][3][3][4]
Importance of Test[edit | edit source]
The muscles that cross the wrist are separated into compartments by the extensor retinaculum. In the first compartment, the tendons of the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus pass through to attach distally. According to Neumann, the extensor pollicis brevis attaches distally to the dorsal side of the proximal phalanx and extensor mechanism of the thumb, while the abductor pollicis longus attaches distally to the radial-dorsal side of the 1st metacarpal. The combination of maximum finger flexion and wrist ulnar deviation elongates these tendons and produces pain in symptomatic individuals.[6]
Reliability[edit | edit source]
- Investigation into the validity of tests are important to know whether our tests are reliable or not.
- Studies that test the reliability of the Finkelstein test are very limited. One research shows that the Finkelstein test has a high reliability [7], but further research is still required.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Extensor pollicis brevis muscle (highlighted in green) - posterior view image - © Kenhub https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/extensor-pollicis-brevis-muscle
- ↑ Abductor pollicis longus muscle video - © Kenhub https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/abductor-pollicis-longus-muscle
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Richard Day, John Fox; Neuro- musculoskeletal clinical tests; Churchill Livingstone Elsevier 2009- page 113 (Level of evidence = E)
- ↑ Javier González-Iglesias, Peter Huijbregts, César Fernández-de-las-Peñas, Joshua A. Cleland; Differential Diagnosis and Physical Therapy Management of a Patient With Radial Wrist Pain of 6 Months’ Duration: A Case Report; journal of orthopaedic sports physical therapy: volume 40,number 6, June 2010. (level of evidence = C)
- ↑ How to Perform a Finkelstein's Test of the Hand (level of evidence = E)
- ↑ Neumann, Donald. Kinesiology of the Musculoskeletal System: Foundations for Rehabilitation. 2nd edition. St. Louis, MO: Mosby Elsevier, 2010. 303.
- ↑ Javier González-Iglesias, Peter Huijbregts, César Fernández-de-las-Peñas, Joshua A. Cleland; Differential Diagnosis and Physical Therapy Management of a Patient With Radial Wrist Pain of 6 Months’ Duration: A Case Report; journal of orthopaedic; sports physical therapy: volume 40, number 6, June 2010.(level of evidence = C)