Electrical Stimulation - Its role in upper limb recovery post-stroke: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 175: | Line 175: | ||
=== '''Shoulder Subluxation''' === | === '''Shoulder Subluxation''' === | ||
[[Image:Shoulder Subluxation This section.png]] | |||
<br> | |||
'''Overview''' Shoulder subluxation is a common problem amongst patients with extreme muscle weakness and limb inactivity. Incidence rates are reported at 17%-81% of people who suffer a stroke, with greater paralysis related to higher incidence (Manigandan et al. 2014). Weakness of the shoulder musculature can result after a stroke, often leading to subluxation due to the muscles being unable to hold the humerus within the glenohumeral fossa Shoulder subluxation is described as inferior glenohumeral joint displacement and is a very commmon secondary musculoskeletal impairment in the upper limb post stroke (Ada and Foongchomcheay 2002).<br><br> | '''Overview''' Shoulder subluxation is a common problem amongst patients with extreme muscle weakness and limb inactivity. Incidence rates are reported at 17%-81% of people who suffer a stroke, with greater paralysis related to higher incidence (Manigandan et al. 2014). Weakness of the shoulder musculature can result after a stroke, often leading to subluxation due to the muscles being unable to hold the humerus within the glenohumeral fossa Shoulder subluxation is described as inferior glenohumeral joint displacement and is a very commmon secondary musculoskeletal impairment in the upper limb post stroke (Ada and Foongchomcheay 2002).<br><br> | ||
| Line 189: | Line 190: | ||
Stimulation of the supraspinatus alone is inadequate in maintaining the humeral position of the shoulder (Kobayashi et. al. 1999). Therefore, when ES is applied to structures that aid in maintaining the position of the head of humerus in the glenoid fossa. The 2 main areas that both the guidelines and evidence strongly back are the supraspinatus and deltoid muscles (Vafadar et al. 2014, RCP 2012, NICE 2013). Although the evidence for the supraspinatus and deltoid muscles are evident, a study by Manigandan et al. (2014) reported that stimulation of the long head of biceps have also proven beneficial towards helping minimise the risk of shoulder subluxation. This could be an alternative treatment option if stimulation of the supraspinatus and deltoid muscles prove ineffective. <br> | Stimulation of the supraspinatus alone is inadequate in maintaining the humeral position of the shoulder (Kobayashi et. al. 1999). Therefore, when ES is applied to structures that aid in maintaining the position of the head of humerus in the glenoid fossa. The 2 main areas that both the guidelines and evidence strongly back are the supraspinatus and deltoid muscles (Vafadar et al. 2014, RCP 2012, NICE 2013). Although the evidence for the supraspinatus and deltoid muscles are evident, a study by Manigandan et al. (2014) reported that stimulation of the long head of biceps have also proven beneficial towards helping minimise the risk of shoulder subluxation. This could be an alternative treatment option if stimulation of the supraspinatus and deltoid muscles prove ineffective. <br> | ||
'''How do I identify a patient at risk of a shoulder subluxation?''' | '''How do I identify a patient at risk of a shoulder subluxation?''' | ||
Therefore, a criterion was developed for the assessment of patients whereby if patient’s presented with one or more of the following characteristics they would be considered as “at risk”. The characteristics are presented in the table | There is some evidence to suggest that ES could also be used as a preventative measure towards patients who maybe at risk of shoulder subluxation (EBRSR 2013, SSAF 2015). An audit by (Macdonald 2013) reported that 100% of patients who developed subluxation had low tone, further stating that patients with either flaccidity or low tone around the shoulder with reduced active ranges of motion could be considered a risk. However a caution was raised that only 50% of patients with the risk of shoulder subluxation would be suitable electrical stimulation and therapists should use their own clinical reasoning and judgment to select such eligible patients.Therefore, a criterion was developed for the assessment of patients whereby if patient’s presented with one or more of the following characteristics they would be considered as “at risk”. The characteristics are presented in the table below. | ||
Another audit by (Larkin 2014) supports the table mentioned above and further | [[Image:Table_One_Shoulder_Subluxation.png|center]]Another audit by (Larkin 2014) supports the table mentioned above and further presents a table to address some of the concerns about the suitability of ES for patients. The table below shows the suitability for ES.<br> | ||
[[Image:Table_Two_Shoulder_Subluxation.png|center]] | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 22:21, 28 January 2016
Original Editor - Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page.
Top Contributors - Rebecca Graham, Grant Burns, Craig Philip, Joshua Tan, Hannah Little, Rucha Gadgil, 127.0.0.1, Kim Jackson, Admin, Rachael Lowe, Venugopal Pawar, Dinu Dixon, Evan Thomas, Jane Hislop, Cindy John-Chu and Carina Therese Magtibay
Introduction
[edit | edit source]
Welcome to this online learning resource on the use of electrical stimulation (ES) to support recovery of upper limb following a stroke. This page has been created by a small group of final year physiotherapy students from Queen Margaret University as part of the Contemporary and Emerging Issues in Physiotherapy module.
Aims and Learning Outcomes
This resource aims to provide an interactive learning package for final year students and newly qualified physiotherapists to develop their knowledge and understanding of ES application for upper limb recovery following a stroke. A balance of theory, policy and evidence-base, as well as practical aspects for application of ES has been incorporated.
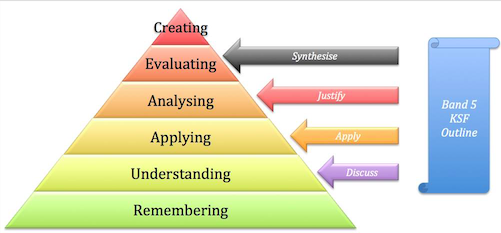
The learning outcomes have have been constructed using blooms taxonomy [1] to guide the expected level of competency, and is aligned with those expected of a newly qualified physiotherapist, described in the knowledge and skills framework KSF[2]. Link to the Physiotherapy band 5 role profile can be found in the resources section at the bottom of this page.
Table 1. below describes the intended learning outcomes
Layout and Approach
This package should take approximately ten hours to work through, however, this should be viewed as a guide only as people have varying learning styles and preferences. To support this the sections have been designed in a way which enables users to dip in and out to suit their needs. Users can choose to work on their own, or benefit from discussing and reflecting on the activities with others, such as peers, colleagues and managers. This choice is left to the user to match with their own preference and time-management. At the start of each section, a brief description of what will be covered is outlined and linked to the above learning outcomes.
This learning resource aims to be engaging and interactive. While synthesis and summary of the key information has been provided, the user will gain greater benefit by engaging with the directed reading, videos, activities, short quizzes and case studies that have been developed to support a deeper learning experience in line with adult learning theory [3]. A range of material has been incorporated in the design of this package to try and suit different learning styles. VARK Learn Ltd (http://vark-learn.com) [4]offer a tool that helps people identify their own learning preferences and maybe a helpful activity prior to commencing this resource.
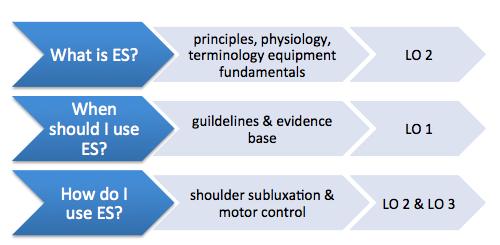
Figure 2. below outlines the content covered in the main sections of this resource
Figure 2. Outline of main sections in with mapped learning outcomes
Why this Topic?
Stroke has a large impact and burden on society [5]. It is currently the 4th largest cause of mortality in the UK [5] Although trends show decreased mortality rates over the last 20 years, it is still the leading cause of complex adult disability [5]. The UK has approximately 1.2 million stroke survivors, with half experiencing disability and 77% with upper limb difficulties [5]. In the UK the over 65’s population is estimated to rise by over 40% in the next 17 years [6], and stroke incidence is higher in this demographic. [5]. This could potentially lead to even greater numbers of stroke survivors requiring support and rehabilitation from healthcare professions such as physiotherapy. Additionally, 36% of 65+ live alone [6] underpinning the importance of successful rehabilitation of upper limb function if people are to maintain independence, due to its impact on performance of activities of daily living [7].
Physiotherapists are a core member of the multidisciplinary team required to rehabilitate stroke survivors [8]. Their main goals are to enhance people’s functional abilities, helping them improve or maintain their mobility and independence. This aligns with Scottish policy of supporting people to live independently in their homes and communities longer [9]. Physiotherapy interventions for upper limb recovery after stroke have moderate or low quality evidence, and there is insufficient data to draw comparisons as to which is most effective [7]. Therefore guidelines recommend that practice should not be limited to one approach but should be based on the need and preferences of the patient [8].
ES has a developing evidence base that supports its use for upper limb recovery after stroke [10] and the number of trials has quadrupled over the last decade [11]. However, current practice is varied and research shows that a lack of knowledge and skills are a key barrier to its use [10]. This learning package aims to addresses this contemporary issue by introducing and synthesizing key literature and translating this into practical recommendations that can support clinical practice.
What is Electrical Stimulation?[edit | edit source]
Overview
ES is an assistive technology that can be used to aid the recovery of upper limb after stroke. It uses electrical current to stimulate muscle contraction via electrodes, facilitating movement of a weakened or paralysed limb. It has been used since the mid 1960’s, traditionally to aid mobility through addressing dropped-foot, however, more recently it has been considered as a promising treatment modality for upper-limb recovery [10]. ES has also been used in the treatment of other upper motor neuron impairments including people with Cerebral Palsy, Parkinson’s Disease, Multiple Sclerosis and spinal cord injury [12].
ES Uses
Several uses and benefits have been investigated regarding ES use in stroke upper limb recovery. These include strengthening weak muscles, increasing range of motion, reducing spasticity, improving motor control, reducing shoulder subluxation, reducing pain associated with shoulder subluxation and spasticity, improving sensory and proprioceptive awareness, and improving effects of botulinum toxin for management of spasticity [13], [14]. Neuroplasticity is a key concept underpinning stroke recovery and it is the ability of the brain to adapt and form new neuroconnections [15]. By forming these new synapses, motor-skills can be relearned and concepts of sensory-motor learning are founded on this premise [16]. Following stroke there is evidence that the brain has a period of hyper-excitability within the first weeks after stroke(Butefische xxxx) and it is hypothesised that by affert stimulation central reorganisation can be enhanced by stimulation through movement which ES may be able to facilitate (Meilink 2007). Additionally there is large predictive probability (90%) of return of upper limb function decided within the first 5 weeks, indicating a critical window for influencing recovery. As will be reviewed in the following section (When should I use ES?), evidence supporting use of ES is not conclusive [10] [7] [17]. This resource focuses on two key areas; shoulder subluxation and motor control as these are the only two supported by UK guidelines [10][18][8] [19].
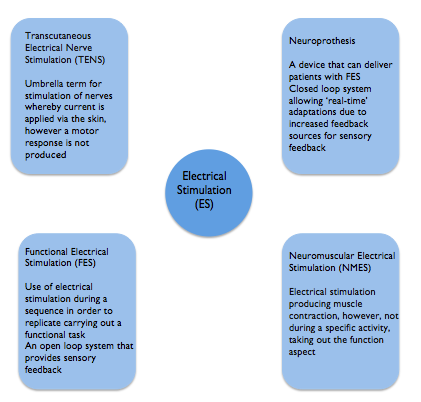
Terminology
There are various terms used within the literature for ES. Although each has a different meaning they are frequently used synonymously which can make understanding and comparing different studies challenging [8]. Highlighted below are the most common terms encountered in the literature. This learning resource has focused on ES used to support upper limb recovery which is delivered predominantly by Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES). Functional electrical stimulation (FES) and neuorprothesis are forms of NMES. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) has traditionally been used for analgesic purposes and does not elicit a motor response [20][10] although it has also been used in studies to promote sensory feedback[10].
One distinction made is the use of ES for therapeutic purposes such as to aid motor learning with the intention of a carryover effect beyond treatment. Functional electrical stimulation on the other hand is aimed at providing direct benefit to aid a task at the time of wearing and is used in an orthotic manner [11].
Physiology
ES uses electrodes to activate contraction and relaxation of muscles that have been affected by an upper motor neuron lesion. Motor-units are electrically stimulated by depolarization of motor axons, or terminal motor nerve branches. When depolarization reaches threshold, an action potential occurs due to sodium flowing from the extracellular to intracellular space. This action potential propagates along the nerve fibre axon to the muscle via the neuromuscular junction resulting in muscle contraction [21]. As an intact connection between the ventral horn and muscle is required for successful action potential propagation to reach the muscle, ES is not suitable for lower motor neuron lesions (Odstock 2015). In ES it is the nerves that are stimulated rather than muscle, as they require a lesser current of that needed to trigger muscles directly. Influencing factors include distance from electrode to nerve fibre, size of motor unit, and surrounding tissue will all impact the number and type of motor units activated[22]
ES engages the patient and delivers feedback of a sensory and visual nature, beneficial for stroke patients during their recovery and promotes motor re-learning [23] [24][17] Odstock medical 2015). Disuse atrophy is a common secondary complication of stroke and can result in muscle fibre changes [22]. ES may also be able to reverse this by bringing about muscle fibre changes over the course of treatment, with type II glycolytic fibres reverting to type I oxidative skeletal muscle fibres [22]. Type II fibres generate greater forces but fatigue more quickly, whereas type I fibres produce lesser force but are more fatigue-resistant [25]
Motor unit recruitment and Fatigue
In normal physiology, nerve fibre recruitment occurs as described by the Henneman size principle of voluntary motor unit recruitment, whereby nerves with the smallest diameter will be recruited first. When using ES, the reverse of this happens, with the largest diameter neurons being recruited first due to a lower nerve stimulus threshold [25] which can lead to fatigue. However, it has recently been established that it is in fact an uncoordinated method of recruitment, with no order, that is evident in ES [11].
One limitation of ES is that muscles can fatigue [26] and that the higher frequency selected, the quicker muscle fatigue will set in. Clinical judegement is required to determine the lowest frequency possible to achieve tonic muscle contraction[10]. Once fatigue has set in, there is argument for and against whether muscle strengthening can occur. It has been suggested that when fatigued, that no advantages can be gained from additional stimulation and therefore fatigue should be prevented if possible. Opposing arguments suggest that strengthening can only be achieved if the muscle fibre is worked to its maximum. Clarifying the cause of fatigue is important. Strengthening can occur if fatigue is within the muscle fibres due to cellular processes being activated, however if fatigue has resulted from neurotransmitter depletion or propagation failure, then the muscle will not be strengthened as the fibre is not being stimulated sufficiently [20].
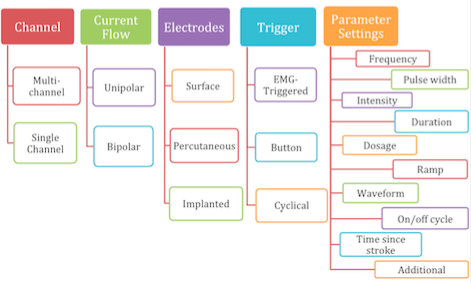
ES Devices and Parameters
ES systems include three components: the control, an electrical stimulator and electrodes which connects the ES with the nervous system [22]. There are several different ways ES devices can be configured as depicted and described below. This can vary by supplier and intended use.
Electrodes
Application of ES is done via electrodes, which generate the electrical field through either surface or percutaneous electrodes [27].ES can be provided via single channel or multichannel devices. Multichannel systems can be used when targeting multiple muscles to replicate a functional activity such as reaching and grasping, whereas a single channel device is used for less complex movements such as rectifying shoulder subluxation. Although single channel systems are mainly used for simple movements, they are potentially more portable, making them more practical for home use.
Surface electrodes are placed directly onto the skin over the nerves and are the most common [25]. As well as stimulating muscle, surface electrodes may also be used to achieve a reflex action[27]. Parameters of ES needed when using surface electrodes can differ depending on factors such as material of the electrodes, placement and surface area [25]. They are non-invasive and relatively inexpensive and are suitable for use across a wide variety of settings and by therapists and patients, promoting independence and self-management [10]. However, targeting contraction of small individual muscles can be difficult, and often activation of deeper muscles requires superficial muscles to be activated first. Surface electrodes have also been reported to cause pain for some patients when compared with percutaneous electrodes [28]. Percutaneous electrodes penetrate through the skin into the muscle via hypodermic needles or can be completely implanted whereby stimulation is received from an external unit [25]. They can address the difficulties faced with surface electrodes by being able to target deep muscles and as they use lower currents, are reported to be less painful [25]. However, factors of cost and practicality need to be taken into consideration [27]. In line with the SSAF [10] recommendations, this resource focuses on the surface mounted electrodes as they are inexpensive and most commonly used, therefore best suited to this learning resources target audience as it covers the equipment they are most likely to encounter in practice.
UniPolar vs Bipolar
Two electrodes are required (active and indifferent) to generate a flow of current, however these can be unipolar or bipolar in configuration. Unipolar is when one electrode is more active than another due to their sizes. The active electrode is typically smaller and placed near the nerve to be stimulated with the indifferent electrode placed over less excitable tissue such as fascia. In multi-channel configurations there are several active electrodes but only one indifferent electrode is required [20]. Biploar electrodes are both the same size meaning the current at each site will be equal. Both active and indifferent electrodes are placed close to the stimulated nerve and in multi-channel configurations there is an indifferent electrode for each active. Bipolar systems enable greater targeting of muscles [20].
Cyclical, button & EMG-triggered
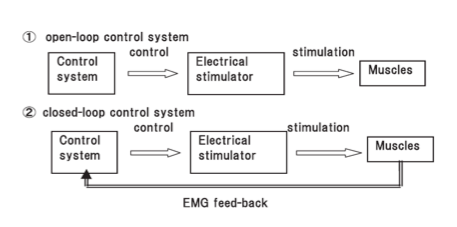
One other variable is whether the timing of when electrical stimulation is active is via a button, cyclical or EMG-triggered system. The button method is a manual form of ES and requires the user to actively press a switch to activate the stimulation. Cyclical means that the timing and sequence is predetermined by selection of an appropriate programme on the device and this is sometimes just referred to at NMES [10]. Alternatively, the EMG triggered system uses sensors built in to the active electrode to determine when voluntary muscle contraction is above a preset-threshold which then triggers the ES [10]. It has been suggested that this method promotes greater user involvement promoting neuroplastic changes [11]and leads to better outcomes [29][30]. Typically this is called EMG-triggered ES to differentiate from cyclical [10]. Cyclical or predetermined programs are considered open loop systems that rely on the user to turn-on/off whereas EMG-triggered are classified as closed-loop systems as the EMG trigger determines on/off timing.
Open and closed loop ES systems (Hara et al. 2008)
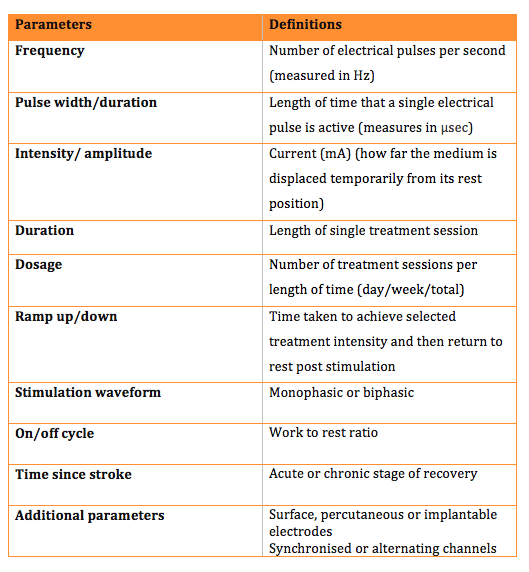
Parameters
There are various parameters that can be adjusted on ES devices to help tailor the electrical field effects to the patient and its intended application. The table below outlines each parameter and its definition. It is worth noting that not all ES devices allow individual control of all parameters and many offer a choice of pre-determined programmes.
What is Available?
Odstock medical is one of the main suppliers of ES devices, which vary in design and parameters available. They provide systems for use in the home environment, allowing regular activity and independence. The stimulators differ in the outputs they provide, including single or multichannel systems, with different outputs available.
When should I use Electrical Stimulation[edit | edit source]
Guidelines [edit | edit source]
In order to synthesise the current evidence for the use of ES for upper limb rehabilitation after stroke this section will focus on the three main guidelines used in the United Kingdom for guiding physiotherapy practice:
• SIGN Guideline 118 - Management of patients with stroke (SIGN 2010)
• NICE Clinical Guideline 162 – Stroke Rehabilitation (NICE 2013)
• Royal College of Physicians – National clinical guideline for stroke (RCP 2012)
Section 2.2:
Key intervention and treatment recommendations: “Electrical stimulation to the supraspinatus and deltoid muscles should be considered as soon as possible after stroke in patients at risk of developing shoulder subluxation. (SIGN 2010, p. 6)”. Grade A
P. 19, section 4.3.1 & 4.3.2. – Upper limb function
P. 31 & 32, section 4.9.1 & section 4.9.3 – Post-stroke spasticity
How do I use Electrical Stimulation[edit | edit source]
General Considerations[edit | edit source]
Considerations
ES can be applied by qualified health professionals; including physiotherapists and occupational therapists who are competent in its use. Although this learning package gives a theoretical overview of ES we advise that practical training is performed before applying this as a treatment [31].
The checklist below details what training is required prior to use of ES.
ES training checklist [31]
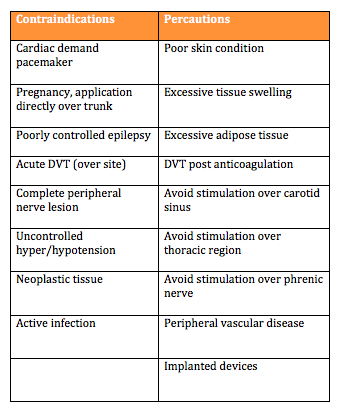
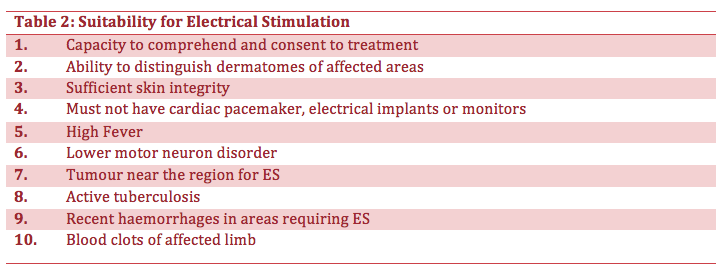
Contraindications and Precautions:
To ensure patient safety it is important to consider the contraindications and precautions before using an ES device. Understanding these will help make an informed decision regarding the use of ES as a treatment.

Page 3Using Electrical Stimulation A Guideline for Health Professionals [31]
Page 19 Scottish Stroke Allied Health Professionals Forum Use of Electrical Stimulation Following Stroke: A Consensus Statement [10]
Page 2 Referral Criteria OML Learning Through Technology [32]
The above documents highlight a variety of contraindications. Detailed below is a summary table of the main contraindications and precautions identified by the Scottish Stroke Allied Health Professionals Forum [10]
Percautions and contraindications quiz
What do Patients need to know?
Prior to commencing treatment the patient needs to give verbal consent. After they have given consent it is important to provide the patient with information regarding ES. They should be informed of the expected skin sensation and that it may uncomfortable, but they should not experience any pain. Patients should also be told what to do if they experience these sensations and how to work the ES device if a patient or carer is able to adjust it. Providing an instruction manual in lay terms may be beneficial for the patient. Contraindications and precautions should be highlighted to the patient with relevant information explained to them. After providing the patient with this information, it should be documented in the patient notes [31].
Outcome Measures: There are a variety of outcome measures that can be used in the monitoring of upper limb recovery and function post stroke, which could be used to track progress of patients using ES. Two of these outcome measures will be outlined below.
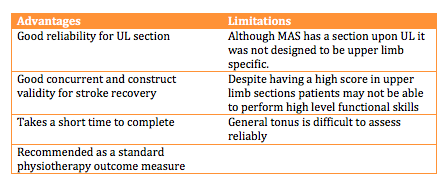
Motor Assessment Scale(MAS):
The MAS (File:Motor Assessment Scale.pdf) is an outcome measure which focuses upon functional motor activities. It has specific sections for Supine to side lying, Supine to sitting over side of bed, Balanced sitting, Sitting to standing, Walking, Upper-arm function, Hand movements, Advanced hand activities and general tonus. Each of these are scored from 0-6. A score of six is the optimal motor score in each area, with a score of 48 being available in total [33].
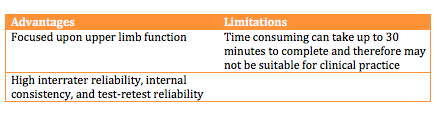
Wolf Motor Function Test:
The Wolf Motor Function Test is a timed outcome measure which aims to assess how quickly functional upper limb tasks can be performed. Patients are given 120 seconds to complete each task before the task is marked as incomplete. Each of these are scored from 0 to 5. Five is the best score achievable for each task, with 75 being the maximum score available [34].
Shoulder Subluxation[edit | edit source]
Overview Shoulder subluxation is a common problem amongst patients with extreme muscle weakness and limb inactivity. Incidence rates are reported at 17%-81% of people who suffer a stroke, with greater paralysis related to higher incidence (Manigandan et al. 2014). Weakness of the shoulder musculature can result after a stroke, often leading to subluxation due to the muscles being unable to hold the humerus within the glenohumeral fossa Shoulder subluxation is described as inferior glenohumeral joint displacement and is a very commmon secondary musculoskeletal impairment in the upper limb post stroke (Ada and Foongchomcheay 2002).
How does ES aid in Shoulder Subluxation?The National guidelines in the UK support the use of ES of the upper limb post stroke towards aiding a subluxed shoulder (NICE 2013, SIGN 2010, RCP 2012). Furthermore the evidence is strong in supporting the use of ES in clinical practice in order to treat shoulder subluxation (SSAF 2015, ADA).
The Scottish Stroke AHP forum reported that subluxation appears to arise during the flaccid period, which is the first 3 weeks post stroke and shoulder subluxation is less likely to occur if the supraspinatus has developed some movement. Furthermore (Linn et. al. 1999, Fil et. al. 2011) also stated that early application of FES preferably within the first 48 hours post stroke is vital in preventing shoulder subluxation. Therefore early application of ES is recommended and has also shown to improve function, muscle tone, joint alignments and sensory deficits (Price & Pandyan 2001).
Thus starting ES as early as possible is reiterated i.e. initiated acutely post stroke as part of best practice, as majority of patients present with a subluxation within the early stages of stroke (Ada and Foongchomcheay 2002, SIGN 2010). However there is insufficient evidence to suggest that ES makes a significance difference in a subluxed patient’s shoulder in the chronic stages of stroke (Ada and Foongchomcheay 2002). Furthermore the literature showed that there were some benefits for patients in the chronic stages of stroke but it was not statistically significant (EBRSR 2013, SSAF 2015, Paci et al. 2005). Thus further evidence is required for a definite conclusion.
Stimulation of the supraspinatus alone is inadequate in maintaining the humeral position of the shoulder (Kobayashi et. al. 1999). Therefore, when ES is applied to structures that aid in maintaining the position of the head of humerus in the glenoid fossa. The 2 main areas that both the guidelines and evidence strongly back are the supraspinatus and deltoid muscles (Vafadar et al. 2014, RCP 2012, NICE 2013). Although the evidence for the supraspinatus and deltoid muscles are evident, a study by Manigandan et al. (2014) reported that stimulation of the long head of biceps have also proven beneficial towards helping minimise the risk of shoulder subluxation. This could be an alternative treatment option if stimulation of the supraspinatus and deltoid muscles prove ineffective.
How do I identify a patient at risk of a shoulder subluxation?
There is some evidence to suggest that ES could also be used as a preventative measure towards patients who maybe at risk of shoulder subluxation (EBRSR 2013, SSAF 2015). An audit by (Macdonald 2013) reported that 100% of patients who developed subluxation had low tone, further stating that patients with either flaccidity or low tone around the shoulder with reduced active ranges of motion could be considered a risk. However a caution was raised that only 50% of patients with the risk of shoulder subluxation would be suitable electrical stimulation and therapists should use their own clinical reasoning and judgment to select such eligible patients.Therefore, a criterion was developed for the assessment of patients whereby if patient’s presented with one or more of the following characteristics they would be considered as “at risk”. The characteristics are presented in the table below.
Another audit by (Larkin 2014) supports the table mentioned above and further presents a table to address some of the concerns about the suitability of ES for patients. The table below shows the suitability for ES.
Another measure reported was the use of the motor assessment scale (MAS). Linn et al. (1999) reported that patients who scored two or more on the MAS did not develop shoulder subluxation. This could be an alternative outcome measure when assessing an ‘at risk’ patient of shoulder subluxation.
For clinicians who intend to use ES but are unfamiliar, the pathway below can be guidance towards using ES in clinical practice.
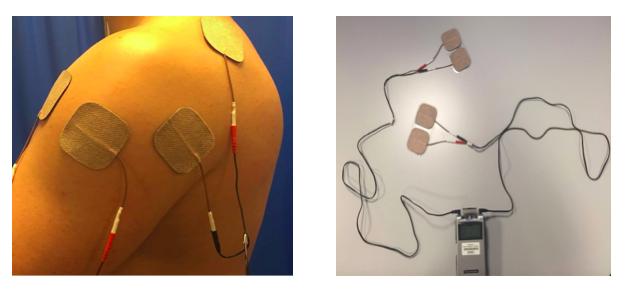
Application: Before applying ES to the upper limb to assist reduction of shoulder subluxation, you should consider the movement you wish to illicit and the structures involved in this movement. Below are pictures of ES being used to help reduce the risk of shoulder subluxation.
Reducing Shoulder Subluxation
2 pairs of electrodes required
Placement of pair 1: Supraspinatus & Middle fibres of Deltoids
Placement of pair 2: Anterior & Posterior fibres of Deltoids
A quick guide would be for all 4 electrodes fitting under the hand of the clinician over the patient’s shoulder.
When adjusting the current to relocate the position of the humerus, extensive shoulder abduction should be avoided.
Reduction of shoulder subluxation with external rotation
This is suitable for patients with significant anterior subluxation/ internal rotation of humerus.
2 pairs of electrodes required
- Placement of pair 1: Supraspinatus & Middle fibres of Deltoids
- Placement of pair 2: Teres Minor & Posterior fibres of Deltoids
You can adjust which electrodes are active or indifferent depending on your patient’s needs. This set up should relocate the humerus more posteriorly.
The current levels may be too high when the shoulder is brought into elevation and you should adjust the current where appropriate to achieve humeral relocation.
Recommendations:
If the shoulder is internally rotated, place one electrode on the posterior fibres of deltoid and the other on teres minor. If further external rotation is required, electrodes can be placed on teres minor and infraspinatus.
Recommendations:
If the shoulder is subluxed without any rotation, place the electrodes over the middle fibres of deltoid and supraspinatus
Stimulation of the supraspinatus may be challenging due to the lack of stimulation to the trapezius which would result in shoulder elevation. If that occurs, replace the electrodes over the middle and posterior deltoids.
• For Figures 1 & 2 choose which electrode to make active (Strongest effect) i.e. if active electrode over teres minor causing extensive external rotation, reverse the polarity.
• Dual channels of stimulation can be applied or alternation of electrode positions.
Dosage and Parameters:
Before commencing an FES treatment on a patient, it is important to consider the types of parameter settings available and decide upon the most appropriate setting for your patient. The different types of settings used can provoke various responses from patients.
The types of parameters to consider are recommended by the summary of evidence table below:
Summary of the main parameters outlined below:
Frequency:
Various authors have reported a diverse range of frequencies. Salisbury (2002) reported that 40hz is sufficient to elicit a contraction, however (Ada and Foongchomcheay 2002) reported that any frequency range above 30Hz would be sufficient for muscle activity. Furthermore, (Baker, Parker 1986) disputed that a range between10 – 60Hz could also be sufficient.
Therefore, there is inconclusive evidence towards a specific stimulation frequency due to different individuals requiring different frequencies and clinicians need to set the frequencies based on their own clinical judgment to achieve a tetanic contraction.
Pulse amplitude and pulse width:
Balancing frequency, pulse amplitude and width have been described as the most important factors in achieving a visible contraction. Although many trials do not state or justify their amplitude and width settings, Salisbury (2002) reports that the standard pulse width starts at 300µs. Additionally, for enhanced amplitude control, the pulse width could be reduced to 100µs. However the general consensus of various authors reports values between 100-350µs (SSAF 2014). Key factors to consider during fine tuning of pulse amplitude and width are muscle fatigue and patient comfort (Kroon et al 2005). The quality of underpinning research however is low (SSAF 2014) and therefore further research is warranted to uncover the full effects of pulse amplitude and pulse width.
Length of treatment:
The evidence aimed at the length of treatment was inconsistent due to various individual application times and overall length of treatment thus inconclusive. Ada and Foongchomcheay (2002) synthesized the evidence and recommended that ES be initially applied 1 hour per day initially and gradually increased to 6 hours per day. Moreover, patients should continue with the treatment until they have a score of more than four on MAS to reduce the recurrance of a subluxation (Ada and Foongchomcheay 2002). The literature for overall length of treatment is very varied although Chantraine et. al. (1999)reported that improvements could be seen within the first 12 months of treatment and none thereafter with only progress being maintained when remeasured at 24 months.
Waveform, ramp times and on/off cycle time:
There are no definitive guidelines or evidence justifying the specific types of waveform, ramp times and on/off cycle time when treating a subluxed shoulder. However Salisbury (2002) recommends that a slower ramp –up time of at least 2 seconds is recommended when spasticity is present as a sudden contraction would elicit a stretch reflex resulting in a reduced range of motion and add, a long ramp could also be beneficial towards reducing tone. Therefore, the general conscientious is that electrical stimulation should be considered during the acute stages, ideally the first few days post stroke in the flaccid period where there is a high risk of subluxation due to significant muscle weakness on top of conventional therapy.
In Summary:
The use of ES as a treatment for preventing shoulder subluxation and those having shoulder subluxation post stroke is advocated (Intercollegiate Stroke Working Party 2012, Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) June 2010). Furthermore, early application of ES in adjunct of traditional therapeutic treatments have proven to be more superior to conventional therapy alone. Subluxation tends to occur within the flaccid period in the first 3 weeks post stroke.
The main muscles targeted for stimulation are supraspinatus and deltoids however the evidence varies with regards to which deltoid fibers prove most beneficial. It may depend on the type of subluxation your patient may have i.e. anterior or inferior subluxation. FES should be commenced for one hour per day initially and subsequently increased to 6 hours per day (Ada and Foongchomcheay (2002).
The recommended dosage of FES is that patients should continue with the treatment until they have a score of more than four on the motor assessment scale (MAS) (Ada and Foongchomcheay (2002). However this was in adjust with improved levels of motor control. Correspondingly, patients who scored two or more on the motor assessment scale (MAS) did not develop shoulder subluxation Linn et. al. (1999). Therefore, this could be used as an outcome measure when treating patients.
There is increasingly more evidence supporting the use of FES in shoulder subluxation post stroke. Currently, there is good quality evidence to show that FES should be considered during the acute stages of stroke being it either used for the prevention or treatment of subluxation. However, further research is required regarding the device’s parameters because the variations of study designs and treatment constraints.
Mr Moses is a 70 year old retired male living with his wife. He suffered a left sided transient ischemic stroke three weeks ago and has been diagnosed with right sided hemiplegia. It was noted through an initial physiotherapy assessment that He had low tone, slight loss of sensation and a significant reduction of active shoulder movement with some internal rotation. However, upon further examination and investigation of the medical staff, the patient was shown to have a tuberculosis in the past, poor skin integrity and oedema of his left shoulder and left hand respectively.
Additionally, due to the stroke, Mr Mose’s cognition has been affected and therefore his wife now has power of attorney. A colleague has approached you to help with the diagnosis and for some advice due to the lack of improvements from conventional physiotherapy treatments.
You are the clinical specialist in treating patients with FES. Would FES be beneficial towards this patient?
Activity:
Looking back at the case study above;
1. Using the criteria above, is Mr Moses ‘at risk’ of a subluxed shoulder occuring? What are the features that deem him ‘at risk’?
Answer: Yes, Low tone, loss of sensation, reduced ROM.
2.Identify some contraindications or cautions that may affect his eligibility of ES? If so, why?
Answer: Cognition. The rest are not deemed as contraindications or cautions as they are either not on the affected area or were past conditions i.e. tuberculosis
3.Could you recommend potential electrode placements and why?
Answer: Supraspinatus, Middle or Posterior deltoid due to these muscles being the main structures in maintaining humeral position in the glenoid fossa.
4.What are the 3 main factors that need to be considered when choosing appropriate parameters?
Answer: Frequency, Pulse Amplitude and Pulse Width
8 months on, Mr Moses has made a significant recovery and is being reviewed for discharge. However, his wife is concerned about him returning home, as she is keen for him to continue progress with the use of FES as she has seen the benefits this has. She has approached you to enquire about purchasing an FES device independently to continue in Mr Mose’s rehabilitation and self management.
1. Now have a think about some of the requirements you would expect from an FES device, which would enable a patient to use at home.
Answer: Easy to use, Inexpensive, Easy to charge, Suitable for unsupervised use, Light weight and compact, Easily cleaned, Not for single person use.
2. Having read about the possible interventions and evidence, reflect upon a situation whereby, a patient has informed you that he would like to purchase an FES device for home use even though he has been using FES for more than a year. What advice would you give this patient and why?
Answer: I would advice this patient to reconsider buying an FES device as the evidence states that there is minimal to no change in improvements past the 12 month period. Therefore there would not be much benefit in buying the device due to the limited recovery of shoulder subluxation post stroke.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yWMzzY_Zrv0#t=436
Motor Control and Recovery[edit | edit source]
Overview:
It is often common for individuals to be left with a motor control deficit on their hemi-paretic side following a stroke. Many sufferers are left with controlled flexor synergy. This can cause difficulties when performing activities of daily living.
Electrical stimulation (ES) in patients with motor function impairment of the upper extremity has been employed as a rehabilitation modality for many years. In order for ES to beneficial as a treatment for motor control, it is reported that patients should have some degree of movement.
NICE (2015), suggest that patients should be able to hold a contraction but may not be able to move their arm against resistance. The proposed mechanism for upper limb motor control ES is to strengthen the elbow, wrist and finger extensor muscles, reduce the spasticity of the antagonist muscles and help to promote nueroplastic changes (Sailsbury 2002, Module 10). However, there is a limited evidence indicating that repeated muscle activation using ES may lead to improvement in voluntary motor control and providing a carry over effect (Quandt and Hummel 2014).
How does ES aid Motor control?
It is understood that when a muscle contraction is produced by electric stimulation, a whole range of sensory inputs are produced. This includes the direct sensation from the stimulation and proprioceptive feedback from joints, tendons, muscles and mechanoreceptors.
This causes a significant increase in the activity along the intact pathways to the cortex, stimulating the production of new synpatic connections (Taylor et al. 2002). The increased level of motor neuron excitation will also make it easier for weak descending inputs to activate the motor neuron and therefore help to produce a voluntary contraction (Quandt and Hummel 2014). When using ES to improve motor function it is often useful to combine muscles to produce a larger pattern of movement, similar to the combination of movements in ADL’s.
Appplication
Typically there are three main focuses of ES for upper limb:
• elbow extension
• wrist, finger and thumb extension
• reaching actions.
Overall the placement of the electrodes is key to achieving a comfortable, effective movement for the patient. It is important to ask the patient to assist with the movement, however this voluntary effort must not be so great that it causes a rise in spasticity and inhibits the desired movement. The images below indicate the electrode placement and the functional movement they help to produce.
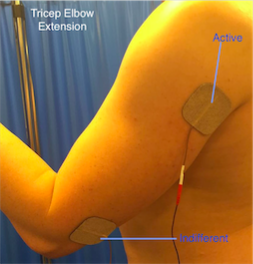
Elbow extension
• The triceps can be activated placing an active electrode over its motor point and the indifferent over the tendon at the elbow.
• Due to the size of the muscle it is useful to use larger electrodes, which may help produce a more effective movement.
• Practicing ‘table polishing’ by sliding the hand over a table using a cloth to reduce friction can be useful.
Wrist, finger and thumb extension
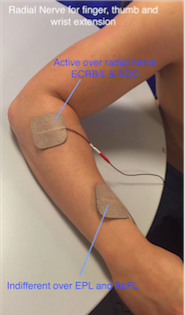
• This is best achieved by stimulation of the radial nerve, which produces an extensor pattern.
• It is often a problem to get good thumb extension so it is good practice to place the indifferent electrode over the motor points of extensor palmaris longus and abductor palmaris longus, about three fingerbreadths proximal to the wrist.
• If thumb extension is still not good, make this electrode the active, assuming this does not significantly reduce finger and wrist extension.
• Care should be taken to avoid either radial or ulna deviation of the wrist. If there is excessive ulnar deviation, move the active electrode towards the extensor carpi radialis brevis on the radial side of the arm. If radial deviation occurs, move the electrode towards the ulna side and the extensor carpi ulnaris.
Thumb abduction and opposition
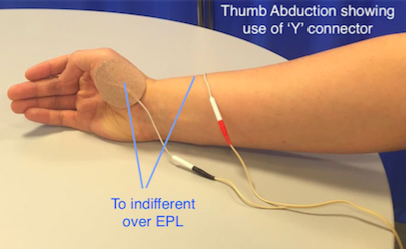
• Radial nerve stimulation can be effective at opening the hand but thumb extension alone can leave the thumb in a less than functional position.
• Abduction and opposition can be produced by stimulating the thenar eminence.
• Place the active electrode over the motor point of Abductor poliicis brevis or opponens pollicis and the indifferent over the back of the wrist. To combine this movement with a general extensor pattern it can be useful to use a ‘Y’ connector.
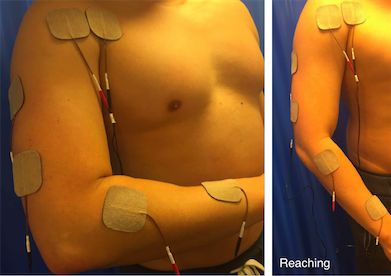
Reaching
• It is often useful to combine muscles to produce a gross pattern of movement, similar to the combination movements used in every day life. In this way it may be possible to more effectively re-train function rather than by practicing individual muscle activity.
• Reaching is where finger, thumb and wrist extension from radial nerve stimulation are combined with elbow extension and shoulder flexion by all channels on together.
Dosage and Parameters
There are a wide variety of dosage and parameters in the literature. However, the SSAHPF (2014) has been developed to provide guidance for the recommended dosage and parameters for upper limb motor control recovery after stroke. Before selecting ES as a treatment it is important that you are aware of the different dosage and parameter settings and how these will affect the treatment.
A summary of the main dosage and parameters are outlined below:
Frequency
In order to achieve a muscle contraction and minimise patient discomfort and fatigue while maximising clinical benefits has been reported as 12.5Hz (Scheffler and Chae 2007). However, it has also been reported that somewhere between 20-50Hz is appropriate (de Kroon et al. 2005, Sijuth 2008), with lower frequencies required for the upper limb (Scheffler and Chae 2007).
Pulse amplitude and pulse width
To achieve greater muscle force generation through recruitment of neurons increasingly further from the electrode, pulse amplitude and pulse width may (usually 200-400 micro sec) need to be adjusted (Scheffler and Chae 2007, Shu-Shyuan 2002). It has been suggested that the intensity frequency and pulse width of electrical current should be adjusted in order to produce a visible contraction. Although there is agreement in this area, there is still variability in application and the final decision will fall to the clinician when addressing the individual patient.
Length of treatment
Common doses and duration of treatments delivered range from 30minutes once per day to one hour three times per day for two weeks to three months (de Kroon et. Al. 2005) although this was not substantiated or justified by the original authors. Hsu (2012) randomised 95 participants to dosages of 0, 15, 30, 60 minutes of ES five times per week for four weeks and reported improved recovery in the upper limb with more intensive ES. However, de Kroon et al. (2005) suggested that the particular treatment parameters may not in fact be the critical element in the efficacy of ES within their study so it may be that individual patient treatment approaches may be sufficient.
Most evidence does not justify the choice of ramp times, stimulation wave forms or on/off cycle times so recommendations regarding these are difficult to make. However, Hsu (2012) reported cycles of 10 seconds on 10 seconds off in the first two weeks and 10 seconds on and 5 seconds off in the second two weeks.
Descriptions of the common parameters reported in literature with recommeneded ranges are synthesised in the table below:
File:ES parameter and dosage Table .pdf
While guidance has been given above in to the dosage and parameters, the clinician has to adjust these to fit the individual. It has been suggested in a review of ES, that it is the adjustment of these parameters which determines the nature of the evoked action potential response and thus impacts on the amount of muscle force generated as well as patient comfort and safety (de Kroon 2002; Ijzerman et al. 2005).
It is important to take into consideration whether the patient has any upper limb tone or spasticity. The dosage and parameters may need to be adjusted for these. Sailsbury (2002) suggested that if spasticity is present then a slower stimulation with a longer ramp time may be beneficial.
Evidence base
Currently there is a limited amount of evidence to support the use of ES for upper limb motor control. A number of articles have been synthesised and below are their detailed findings.
A systematic review by Vafander et al. (2014), found that the use of ES does not have any significant benefits over conventional treatment. A number of the articles included focused on early intervention after stroke, and concentrated on methods to measure impairments (spasticity, strength and joint motion), not function or activity. These articles showed positive benefits of ES for motor control, however it is unclear if improvements in muscle activity and joint motion can be translated to improvement in motor function. The studies that found no superiority of ES over a conventional treatment tended to be of higher quality and mostly used methods for measuring function or activity instead of impairment. A very limited number of articles concentrated on the use of ES in the later stages of recovery after stroke. Two out of the three studies found positive benefits, however once again these focused on impairments. This systematic review highlighted the need for further research into the effects of ES on upper motor function after both the early and late stages of recovery post stroke.
Although there is a lack of evidence showcasing the benefits for ES as a treatment on it’s own for upper limb motor function, one study has indicated when used in conjunction with other therapeutic techniques there is an improvement in an individuals motor control. Hara (2008) found that individuals that receive motor, proprioceptive, and cognitive inputs through the daily use of ES may demonstrate significantly greater improvements in voluntary movement and functional use of the hand and arm.
Another article by McCabe et al. (2015), suggested that for severely impaired stroke survivors with upper limb dysfunction the use of ES combined with motor learning (5 hours per day partial and whole-task practice of complex tasks) helped to improve coordination and functional task performance. However, when analysing the effectiveness of motor learning and ES, compared to motor learning alone or in conjunction with robotics there were no significant differences.
At this stage it is hard to say whether ES is an effective treatment due to the limited literature. Future research is needed with a greater consistency throughout the studies. More studies need to be undertaken with larger sample sizes, the use of ES in early and late stages of rehabilitation after stroke being explored. Furthermore, the use of standardised outcome measures for function and activity will strengthen the generalisabilty for the use of ES for upper limb recovery post stroke.
Case Study
Mrs Jones is a 62 year old women who lives alone and had a hemiplegic stroke two months ago. Following her stroke she has found activities of daily living more difficult. She is displaying a classic flexor synergy and as a result is struggling to grip, as well as extending the elbow. Mrs Jones also suffers from spasticity in her left arm. As a result she finds dressing and cooking particularly difficult. Mrs Jones was previously very active and wishes to return to higher levels of function. She has been progressing well however recently her progress has been beginning to plateau.
You have discussed with your superviosr and have agreed to trial ES to support your sessions.
Questions:
1.How do you think ES could benefit your treatment sessions and support progress towards her goals?
2.What factors would you have to take into consideration when treating Mrs Jones?
3.What electrode placements would you consider when you want to achieve: 1. elbow extension? 2. reaching? (Do you think this would best be achieved with a single or multi channel device?)
4.Using the guidelines and underpinning evidence, what considerations would you take when setting the parameters? 5. Consider how you would determine the treatment and overall dosage and intensity?
To check your decision making, refer back to the recommended reading of the SSAHPF document, linked previously.
Conclusion[edit | edit source]
Upper limb loss of function is a common consequence of stroke and reported in l significant proportion of those suffering a stroke. Recovery typically is not as good as experienced in the lower limb. Physiotherapists and other health professions can electrical stimulation as part of their treatment regimes. ES for lower limb has been widely adopted however its use for upper limb is less consistently applied.
There is robust evidence and guidelines supporting the use of electrical stimulation to prevent and treat shoulder subluxation, particularly when applied early. This may help with shoulder pain and improve function although the evidence supporting this is less robust and requires greater investigation due to conflicting and poor quality research.
The use of electrical stimulation for recovery of upper limb function and to support motor learning principles is also gaining credibility although currently the evidence based in conflicting and its practice is varied across health boards, however, there is recent promising evidence supporting its benefits with very little advsere side affects (mainly skin irritation), therefore it would be beneficial to consider its use as an adjunct modality, particularly for those who have some arm movement allowing the electrical stimulation to support greater practise.
Selection of parameters guidance has varied widely however recommendations have been suggested which is based on the most robust evidence, predominately extracted from the SSAF consensus statement (SSAF 2014). It should be noted however that appropriate tailoring will be required to achieve the optimum setting for each participant and this requires judgement of the therapist working in conjunction with the patient.
Resources
[edit | edit source]
Bellow are key resources for further information in relation to the use of electrical stimulation for upper limb after stroke.
| NICE | Clinical guideline 162 |
| Royal College of Physicians | National clinical guideline for stroke |
| SIGN | Guideline 118 - management of patients with stroke |
| SSAF | Electrical stimulation - a consensus statement |
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Feed goes here!!|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Anderson LW, Krathwohl DR. A taxonomy for learning, teaching and assessing: A revision of Bloom's Taxonomy of educational objectives. New York: Longman, 1998.
- ↑ Department of Health. The NHS knowledge and skills framework (NHS KSF) and the development review process. http://www.dh.gov.uk/ (accessed 15 April 2015).
- ↑ Biggs J, Tang C. Teaching for quality learning at university: what the students do. 4th ed. Maidenhead: Open University Press, 2011.
- ↑ Vark Learn Limited, VARK a guide to learning styles http://vark-learn.com/ (accessed 4 January 2016).
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Stroke Association. State of the Nation: Stroke statistics. https://www.stroke.org.uk/sites/default/files/stroke_statistics_2015.pdf (accessed 26 January 2016).
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Age UK. Later Life in the United Kingdom. http://www.ageuk.org.uk/Documents/EN-GB/Factsheets/Later_Life_UK_factsheet.pdf?dtrk=true (accessed 8 January 2016).
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Pollock A, Farmer SE, Brady MC, Langhorne P, Mead GE, Mehrholz J, van Wijck F. Interventions for improving upper limb function after stroke (Review). http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD010820.pub2/abstract (accessed 8 January 2016).
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. SIGN 118 Management of Patients with stroke: Rehabilitation, Prevention and Management of Complications and Discharge Planning. A national clinical guideline. http://www.sign.ac.uk/pdf/sign118.pdf (accessed 24 January 2016).
- ↑ The Scottish Government. The Healthcare Quality Strategy for NHS Scotland. http://www.gov.scot/resource/doc/311667/0098354.pdf (accessed 8 January 2016).
- ↑ 10.00 10.01 10.02 10.03 10.04 10.05 10.06 10.07 10.08 10.09 10.10 10.11 10.12 10.13 10.14 Scottish Stroke AHP Forum. Use of Electrical Stimulation Following Stoke: A Consensus Statement. http://www.chss.org.uk/documents/2014/10/electrical-stimulation-consensus-statement-ssahpf-pdf.pdf (accessed 5 January 2016).
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Quandt F, Hummel F. The Influence of Functional Electrical Stimulation on Hand Motor Recovery in Stroke Patients: A Review. Experimental and Translational Stroke Medicine 2014; 6:9. http://www.etsmjournal.com/content/6/1/9 (accessed 18 December 2015).
- ↑ Odstock Medical. Who Can Benefit from FES? http://www.odstockmedical.com/who-can-benefit-fes (accessed 23 October 2015).
- ↑ Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. SIGN 118 Management of Patients with stroke: Rehabilitation, Prevention and Management of Complications and Discharge Planning. A national clinical guideline. http://www.sign.ac.uk/pdf/sign118.pdf (accessed 24 January 2016).
- ↑ Foley N, Mehta S, Jutai J, Staines E, Teasell R. Upper Extremity Interventions. http://www.ebrsr.com/sites/default/files/module-10-upper-extremity_final_16ed.pdf (accessed 8 January 2016).
- ↑ Van Wijck F, McBean D, The brain-behaviour relationship: an introduction. In: Applied Neuroscience for the Allied Health Professions. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier, 2013. P33-52.
- ↑ Schmidt R, Lee T. Motor control and learning : a behavioral emphasis. Champaign, IL : Human Kinetics, 2011.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Howlett OA, Lannin, NA, Ada, L, Mckinstry, C. Functional Electrical Stimulation Improves Activity After Stroke: A Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2015; 96 (5):1-9. http://www.archives-pmr.org/article/S0003-9993(15)00044-1/abstract (accessed 8 January 2016).
- ↑ National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Stroke and transient ischaemic attack in over 16s: diagnosis and initial management. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg68 (accessed 19 December 2015).
- ↑ Intercollegiate Stroke Working Party. National Clinical Guideline for Stroke Fourth Edition. Homepage of Royal College of Physicians. 2012. https://www.rcplondon.ac.uk/guidelines-policy/stroke-guidelines (accessed 24 January 2016).
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 Robertson V, Ward A, Low J, Reed A. 4th ed. Electrotherapy Explained – Principles and Practice. Edinburgh: Butterworth Heinemann Elsevier. 2006.
- ↑ Neo Stroke Network. Funcitonal Electrical Stimualtion: “To stim or not to stim”. https://www.neostrokenetwork.com/newportal/Portals/0/Education%20Documents/Everything%20Stroke/Rehabilitation/09-Related%20Presentations/Functional%20Electrical%20Stimulation_a%20discussion%20paper%20by%20L%20Taipalus.pdf (accessed 5 January 2016).
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 22.3 Gorman PH, Peckham PH, Functional electrical stimulation in neurorehabilitation. In: Selzer ME, Clarke S, Cohen LG, Miller RH editors. Textbook of Neural Repair and Rehabilitation. United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press, 2014, pp. 120-134.
- ↑ Dobkins BH, Dorsch A. New Evidence for Therapies in Stroke Rehabilitation. Current Atherosclerosis Reports 2013; 15 (6): 1-9. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3679365/ (accessed 5 January 2016).
- ↑ Kawashima N, Popovic MR, Zivanovic V. Effect of Intensive Functional Electrical Stimulation Therapy on Upper-Limb Motor Recovery after Stroke: Case Study of a Patient with Chronic Stroke. Physiotherapy Canada 2013; 65 (1): 20-28. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3563372/ (accessed 8 January 2016).
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 25.3 25.4 25.5 Sheffler LR, Chae J. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation in neurorehabilitation. Muscle and Nerve 2007; 35(5): 562-590. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/mus.20758/abstract;jsessionid=33B6E38FCCF503F611C557F5541E8788.f03t01 (accessed 4 January 2016).
- ↑ Thrasher A, Graham GM, Popovic MR. Reducing muscle fatigue due to functional electrical stimulation using random modulation of stimulation parameters. Artificial Organs 2005; 29 (6): 453-458. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1525-1594.2005.29076.x/abstract (accessed 17 December 2015).
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 27.2 Ewins D, Durham S, Functional Electrical Stimualtion. In: Watson T editor. Electrotherapy: evidence based practice. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 2008, pp. 317-326.
- ↑ Popavic DB. Neural Prostheses for Movement Restoration. In: Moore J, Zouridakis G editors. Biomedical Technology and Devices Handbook. United States of America: CRC Press, 2003. p 9-16.
- ↑ De Kroon JR, Ijzerman MJ, Chae J, Lankhorst GJ, Zilvold G. Relation between stimulation characteristics and clinical outcome in studies using electrical stimulation to improve motor control of the upper extremity in stroke. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2005;37(2): 65-74. http://www.medicaljournals.se/jrm/content/?doi=10.1080/16501970410024190 (accessed 24 January 2016).
- ↑ Hara Y. Neurorehabilitation with new functional electrical stimulation for hemiparetic upper extremity in stroke patients. Journal of Nippon Medical School 2008; 75(1): 4-14. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/5492468_Neurorehabilitation_with_New_Functional_Electrical_Stimulation_for_Hemiparetic_Upper_Extremity_in_Stroke_Patients (accessed 14 December 2016).
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 31.3 Allan K, Goodman C. Using Electrical Stimulation A Guideline for Health Professionals. http://www.aci.health.nsw.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0004/211819/Using-Electrical-Stimulation-January-2014.pdf (accessed 7 January 2016).
- ↑ Taylor P. Referral Criteria OML Learning Through Technology Precautions.fckLRhttp://www.odstockmedical.com/sites/default/files/referral-criteria_0.pdf (accessed 7 January 2016).
- ↑ Carr J, Shepherd RB and Nordholm L nvestigation of a new motor assessment scale for stroke patients. Physical Therapy 1985 65:175-180. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3809245 (accessed 7 January 2016)
- ↑ Wolf SL, Thompson PA, Morris DM, Rose DK, Winstein CJ, Taub E, Giuliani C and Pearson SL. Wolf Motor Function Test in Subacute Stroke The EXCITE Trial: Attributes of the Wolf Motor Function Test in Patients with Subacute Stroke Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2005; 19 (3):194-205. http://nnr.sagepub.com/content/19/3/194.long?hwshib2=authn%3A1453766034%3A20160124%253Adbcb3854-3ac8-458b-a4c3-0ae27a7bf028%3A0%3A0%3A0%3AVr%2B4aUt5CRoWfs4DNZJ3Tw%3D%3D (accessed 7 January 2016).