Dorsalis Pedis Artery: Difference between revisions
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
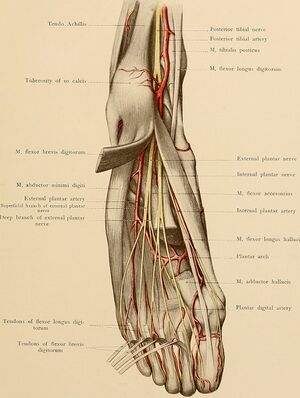
[[File: | [[File:Dorsal foot.jpeg|thumb|Dorsal foot]] | ||
The dorsalis pedis artery | The dorsalis pedis [[Arteries|artery]] is the principal dorsal artery of the [[Ankle and Foot|foot]]. It arises at the anterior aspect of the ankle joint and is a continuation of the anterior tibial artery. | ||
= | * Position: dorsal surface of the foot, running towards the first dorsal interosseous space | ||
* Origin: direct continuation of the anterior tibial artery | |||
* Termination: as the first dorsal metatarsal artery | |||
* Branches: deep plantar artery, lateral tarsal artery and arcuate artery | |||
* Relations: usually palpable between [[Extensor Hallucis Longus|extensor hallucis longus]] and [[Extensor Digitorum Longus|extensor digitorum longus]] tendons<ref name=":1">Radiopedia Dorsal pedal Artery Available:https://radiopaedia.org/articles/dorsalis-pedis-artery (accessed 9.6.2022)</ref> | |||
The dorsal | <ref>Dorsalis pedis artery (highlighted in green) - dorsal view image - © Kenhub https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/dorsalis-pedis-artery</ref> | ||
== Palpation Dorsalis Pedis Artery Pulse == | |||
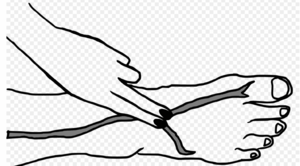
[[File:Screen Shot 2022-06-09 at 1.36.52 pm.png|thumb|Proper way to take person's pulse]] | |||
The dorsalis pedis artery pulse can be palpated lateral to the extensor hallucis longus tendon (or medially to the extensor digitorum longus tendon) on the dorsal surface of the foot, distal to the dorsal most prominence of the [[Navicular|navicular bone]] which serves as a reliable landmark for palpation. It is often examined, by physicians, when assessing whether a given patient has [[Peripheral Arterial Disease|peripheral vascular disease]]. It is absent, unilaterally or bilaterally, in 2–3% of young healthy individuals.<ref>Moore KL, Dalley AF. ''Clinically Oriented Anatomy.'' Fifth edition. Philadelphia: Lippincot Williams & Wilkins; 2006</ref> | |||
== | == Anatomy == | ||
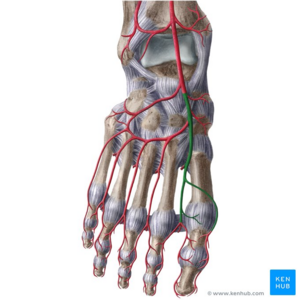
[[File:Dorsalis pedis artery - Kenhub.png|thumb|Dorsalis pedis artery]] | |||
Originates at the level of the distal [[tibia]] between the medial and lateral malleoli, continuing on from the anterior tibial artery. Runs superficially on the dorsal surface of the forefoot, over the [[talus]] and navicular towards the first dorsal interosseous space, where it continues as the first dorsal metatarsal artery.<ref name=":1" /> | |||
The branches of the dorsalis pedis artery are: | The branches of the dorsalis pedis artery are: | ||
# | # Lateral tarsal artery | ||
# | # Medial tarsal artery | ||
# | # Arcuate artery | ||
# | # First dorsal metatarsal artery | ||
# | # Deep plantar artery <ref name=":0">Gray H. ''[https://www.bartleby.com/107/161.html Anatomy of the Human Body].'' Twentieth edition. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918 Available from: https://www.bartleby.com/107/161.html [Accessed on 23 May 2019]</ref> | ||
== Size Variations == | |||
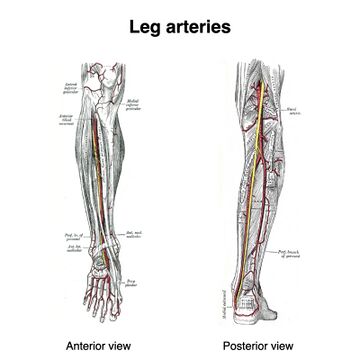
[[File:Leg-arteries-grays-illustrations.jpeg|thumb|Leg-arteries|alt=|360x360px]]The dorsal artery of the foot may be larger than usual, to compensate for a deficient plantar artery. It's terminal branches to the toes may be absent, the toes then being supplied by the medial plantar artery or its place may be taken altogether by a large perforating branch of the peroneal artery. | |||
== Significance == | == Significance == | ||
It is easy to palpate as part of an examination of the peripheral arterial system. Impalpable dorsalis pedis pulse is a sign of peripheral arterial insufficiency. Risk factors for peripheral arterial disease include [[Diabetes Mellitus Type 2|diabetes mellitus]], cigarette smoking, [[Older People Introduction|advancing age]], [[hypercholesterolemia]], [[hypertension]], overweight/[[obesity]]<ref>Radiopedia PAD Available: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/peripheral-arterial-disease?lang=us<nowiki/>(accessed 9.6.2022)</ref> <ref name=":1" />. | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 39: | Line 44: | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Anatomy Project]] | [[Category:Anatomy Project]] | ||
[[Category:Anatomical Landmarks]] | |||
Latest revision as of 06:04, 9 June 2022
Original Editor - Priyanka Chugh
Top Contributors - Priyanka Chugh, Lucinda hampton, Nina Myburg, Evan Thomas, Kim Jackson and Joao Costa
Description[edit | edit source]
The dorsalis pedis artery is the principal dorsal artery of the foot. It arises at the anterior aspect of the ankle joint and is a continuation of the anterior tibial artery.
- Position: dorsal surface of the foot, running towards the first dorsal interosseous space
- Origin: direct continuation of the anterior tibial artery
- Termination: as the first dorsal metatarsal artery
- Branches: deep plantar artery, lateral tarsal artery and arcuate artery
- Relations: usually palpable between extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus tendons[1]
Palpation Dorsalis Pedis Artery Pulse[edit | edit source]
The dorsalis pedis artery pulse can be palpated lateral to the extensor hallucis longus tendon (or medially to the extensor digitorum longus tendon) on the dorsal surface of the foot, distal to the dorsal most prominence of the navicular bone which serves as a reliable landmark for palpation. It is often examined, by physicians, when assessing whether a given patient has peripheral vascular disease. It is absent, unilaterally or bilaterally, in 2–3% of young healthy individuals.[3]
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Originates at the level of the distal tibia between the medial and lateral malleoli, continuing on from the anterior tibial artery. Runs superficially on the dorsal surface of the forefoot, over the talus and navicular towards the first dorsal interosseous space, where it continues as the first dorsal metatarsal artery.[1]
The branches of the dorsalis pedis artery are:
- Lateral tarsal artery
- Medial tarsal artery
- Arcuate artery
- First dorsal metatarsal artery
- Deep plantar artery [4]
Size Variations[edit | edit source]
The dorsal artery of the foot may be larger than usual, to compensate for a deficient plantar artery. It's terminal branches to the toes may be absent, the toes then being supplied by the medial plantar artery or its place may be taken altogether by a large perforating branch of the peroneal artery.
Significance[edit | edit source]
It is easy to palpate as part of an examination of the peripheral arterial system. Impalpable dorsalis pedis pulse is a sign of peripheral arterial insufficiency. Risk factors for peripheral arterial disease include diabetes mellitus, cigarette smoking, advancing age, hypercholesterolemia, hypertension, overweight/obesity[5] [1].
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Radiopedia Dorsal pedal Artery Available:https://radiopaedia.org/articles/dorsalis-pedis-artery (accessed 9.6.2022)
- ↑ Dorsalis pedis artery (highlighted in green) - dorsal view image - © Kenhub https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/dorsalis-pedis-artery
- ↑ Moore KL, Dalley AF. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. Fifth edition. Philadelphia: Lippincot Williams & Wilkins; 2006
- ↑ Gray H. Anatomy of the Human Body. Twentieth edition. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918 Available from: https://www.bartleby.com/107/161.html [Accessed on 23 May 2019]
- ↑ Radiopedia PAD Available: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/peripheral-arterial-disease?lang=us(accessed 9.6.2022)