Cartilage: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
== Recent Related Research (from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ Pubmed]) == | == Recent Related Research (from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ Pubmed]) == | ||
[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27828665 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27828665] | [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27828665 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27828665] | ||
<div class="researchbox"> | <div class="researchbox"> | ||
[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27785001 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27785001]<br> | [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27785001 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27785001]<br> | ||
Revision as of 20:26, 25 November 2016
Original Editor - Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page.
Top Contributors - Esraa Mohamed Abdullzaher, Lucinda hampton, Kim Jackson, George Prudden, Joao Costa and Sai Kripa
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Cartilage is a type of supporting connective tissue . It is a firm tissue but softer and more flexible than bone .
Cartilage Structure [edit | edit source]
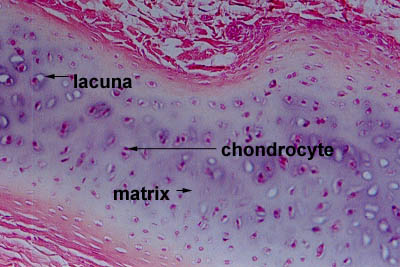
| cartilage matrix | cartilage cells |
| it is a firm gel that contain polysacchride derivaites called chondroitin sulfates which complex with protein in the ground substance forming proteoglycan . | chondrocytes are the only cells in the matrix and they occupy small chambers called lacuna . |
- Cartilage separated from the surrounding tissues by perichondrium which consist of two layers :
1- Outer Fibrous Layer : Which provide protection , mechanical support and attaches the cartilage to other structures .
2- Inner Cellular : It Is Important in the growth and maintenance of cartilage .
Cartilage types[edit | edit source]
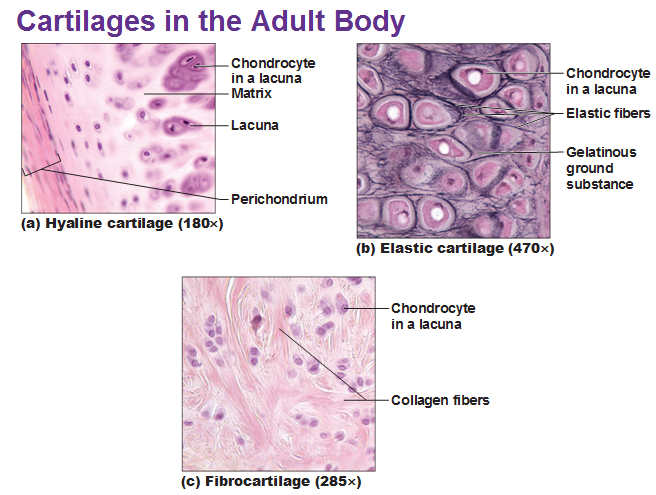
| Hyaline cartilage | fibrocartilage | elastic cartilage |
|
The matrix contain closely packed collagen fibers making it tough but slightly flexible . Example : Connection between ribs and sternum , nasal cartilage and articular cartilage ( which cover opposing bone surfaces in many joints ) . |
The matrix contain interwoven collagen fibers making it durable and tough . Example : between spinal vertebrea and around the joints . |
The matrix contain elsatic fibers making it flexible and reselient . Example : the auricle of the outer ear . |
Mechanical Behaviour of Articular Cartilage[edit | edit source]
The mechanical behaviour depend on interaction of its component : proteoglycan , collagen and interstitial fluid .
In an aqoues environment , proteogylcans are polyanionic which means the molecule has negatively charged sites that arise from sulfate and carboxyl .
In solution , the matual repulsion of these negative charges causes the aggregated proteogylcan to spread out and occupy a large volume .
Exercise and cartilage health[edit | edit source]
Participation in certain sports appear to increase risk of osteoarthritis ( result from breakdown of joint cartilage ) .
Activities that involve torsional loading , fast acceleraion and decclaration , repititive high impact and high level of participation increase risk of osteoarthritis .
Racket and soccer may increase risk of osteoarthritis but swimming and cycling are not linked with increase risk of osteoarthritis hip .
Increasing risk of osteoarthritis are related to excessive exercise or abnormal joint loading But some levels of loading and exercise are benfecial for joint health .
To Understand more about Cartilage[edit | edit source]
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27828665
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.