Cartilage: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
[[Image:Hyalinelabel.jpg]] | [[Image:Hyalinelabel.jpg]] | ||
- Cartilage separated from the surrounding tissues by perichondrium which consist of two layers :<br>1- Outer Fibrous Layer : Which provide protection , mechanical support and attaches the cartilage to other structures .<br>2- Inner Cellular : It Is Important in the growth and maintenance of cartilage . | - Cartilage separated from the surrounding tissues by perichondrium which consist of two layers :<br>1- Outer Fibrous Layer : Which provide protection , mechanical support and attaches the cartilage to other structures .<br>2- Inner Cellular : It Is Important in the growth and maintenance of cartilage . | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
== | == Cartilage types == | ||
{| width="500" border="1" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" | {| width="500" border="1" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Hyaline cartilage | | Hyaline cartilage | ||
| fibrocartilage | | fibrocartilage | ||
| elastic cartilage | | elastic cartilage | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
The matrix contain closely packed collagen fibers making it tough but slightly flexible . | The matrix contain closely packed collagen fibers making it tough but slightly flexible . | ||
Example : Connection between ribs and sternum , nasal cartilage and articular cartilage ( which cover opposing bone surfaces in many joints ) . | Example : Connection between ribs and sternum , nasal cartilage and articular cartilage ( which cover opposing bone surfaces in many joints ) . | ||
| The matrix contain interwoven collagen fibers making it durable and tough .<br><br>Example : between spinal vertebrea and around the joints . <br> | | The matrix contain interwoven collagen fibers making it durable and tough .<br><br>Example : between spinal vertebrea and around the joints . <br> | ||
| The matrix contain elsatic fibers making it flexible and reselient .<br>Example : the auricle of the outer ear . | | The matrix contain elsatic fibers making it flexible and reselient .<br>Example : the auricle of the outer ear . | ||
|} | |} | ||
<span style="font-size: 16.6px;">[[Image:Three-types-of-cartilage-hyaline-elastic-and-fibrocartilage.png]] </span> | <span style="font-size: 16.6px;">[[Image:Three-types-of-cartilage-hyaline-elastic-and-fibrocartilage.png]] </span> | ||
<span style="font-size: 16.6px;" /> | |||
== Recent Related Research (from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ Pubmed]) == | == Recent Related Research (from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ Pubmed]) == | ||
Revision as of 18:57, 25 November 2016
Original Editor - Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page.
Top Contributors - Esraa Mohamed Abdullzaher, Lucinda hampton, Kim Jackson, George Prudden, Joao Costa and Sai Kripa
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Cartilage is a type of supporting connective tissue . It is a firm tissue but softer and more flexible than bone .
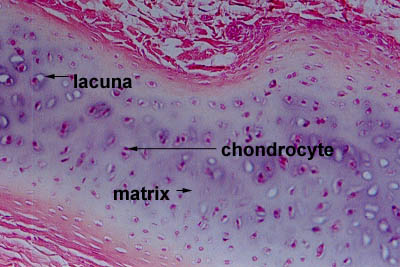
Cartilage Structure [edit | edit source]
| cartilage matrix | cartilage cells |
| it is a firm gel that contain polysacchride derivaites called chondroitin sulfates which complex with protein in the ground substance forming proteoglycan . | chondrocytes are the only cells in the matrix and they occupy small chambers called lacuna . |
- Cartilage separated from the surrounding tissues by perichondrium which consist of two layers :
1- Outer Fibrous Layer : Which provide protection , mechanical support and attaches the cartilage to other structures .
2- Inner Cellular : It Is Important in the growth and maintenance of cartilage .
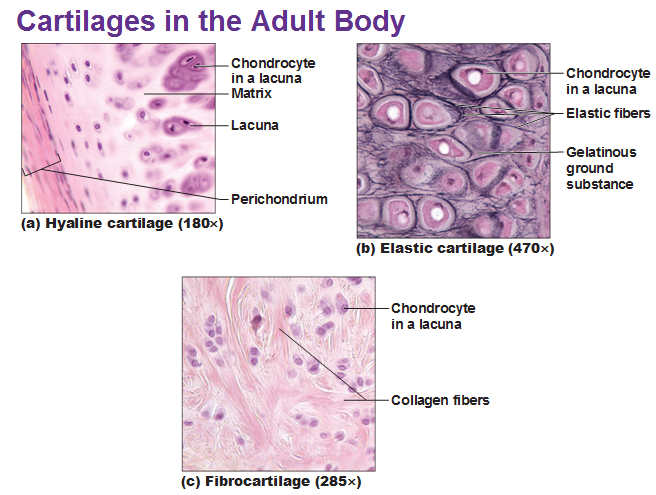
Cartilage types[edit | edit source]
| Hyaline cartilage | fibrocartilage | elastic cartilage |
|
The matrix contain closely packed collagen fibers making it tough but slightly flexible . Example : Connection between ribs and sternum , nasal cartilage and articular cartilage ( which cover opposing bone surfaces in many joints ) . |
The matrix contain interwoven collagen fibers making it durable and tough . Example : between spinal vertebrea and around the joints . |
The matrix contain elsatic fibers making it flexible and reselient . Example : the auricle of the outer ear . |
<span style="font-size: 16.6px;" />
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Extension:RSS -- Error: Not a valid URL: Feed goes here!!|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.