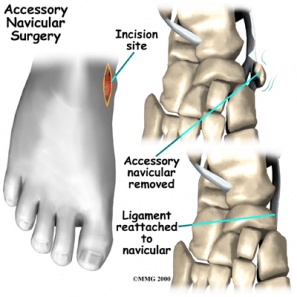
Accessory Navicular Bone
Original Editors - Carlos De Coster
Top Contributors - Aarti Sareen, Admin, Carlos De Coster, Scott Cornish, Kim Jackson, Laura Ritchie, WikiSysop, Lucinda hampton, 127.0.0.1, Evan Thomas, Tony Lowe and Oyemi Sillo
Definition/Descrition[edit | edit source]
Also known as Prehallux, Os Tibiale Externum and Navicular Secundum.
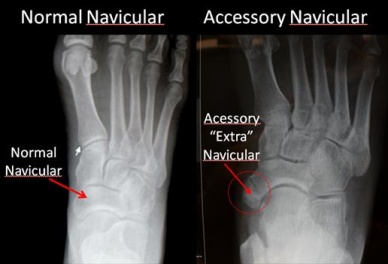
An accessory navicular bone is an accessory bone of the foot that occasionally develops abnormally causing a plantar medial enlargement of the navicular. The accssory navicular bone presents as a sesamoid in the posterior tibial tendon, in articulation with the navicularCite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title or as an enlargment of the navicular.
The Geist classification divides these into three types:
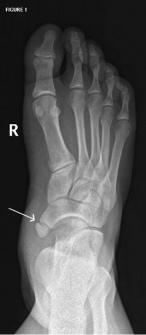
Type I: is sesamoid bone in the posterior tibialis tendon. There is a small distance (<3m) between the sesamoid and the navicular.
File:Type I AN dia.PNG File:TYPE I AN X RAY.jpg
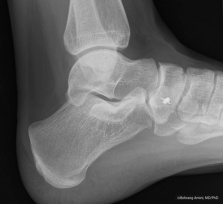
Type II: consists of an accessory bone, upto 1.2cm in diameter, in which a synchondrosis exist between it and the navicular.
File:Type II AN.PNG File:TypeIIAccessoryNavicular.jpg
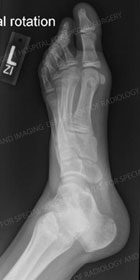
Type III: is the fused accessory navicular to the navicular resulting in large cornuate navicular.
File:TYPE III AN.PNG File:TYPE III ACCESSORY N. X RAY.PNG
Clinically Relevant Anatomy[edit | edit source]
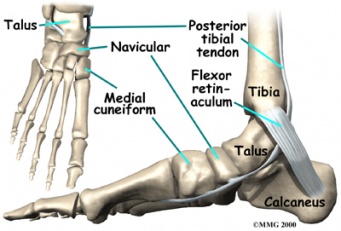 File:Foot accessory navicular clinical antomy 2.jpg
File:Foot accessory navicular clinical antomy 2.jpg
Navicular (boat shaped) is an intermediate tarsal bone on the medial side of the foot.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title It is located on the medial side of the foot, and articulates proximally with the talus. Distally it articulates with the three cuneiform bones. In some cases it articulates laterally with the cuboid. The tibialis posterior inserts to the os naviculare.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title The tibialis posterior muscle also contracts to produce inversion of the foot and assists in the plantar flexion of the foot at the ankle. Tibialis posterior also has a major role in supporting the medial arch of the foot. Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title This supports is compromised by abnormal insertion of the tendon into the accessory navicular bone when present. Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleThis lead to loss of suspension of tibialis posterior tendon and may cause peroneal spastic pes planus or simple pes planus. But, yet a cause and effect relationship between the accessory navicular and pes planus is doubtful and is yet unproved clearly.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
The presence of accessory navicular 2 or 3 is also a cause of PTT tendinopathy as the insertion of PTT on accessory navicular leads to its proximal insertion (dashed line). Here by the leverage of malleolus on the PTT is reduced and therefore stress on the tendon increase. Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
There also occurs calcaneal pitch angle lowering in patients with with symptomatic accessory navicular than in normal subjects.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Epidemiology /Etiology[edit | edit source]
The foot and ankle have numerous accessory ossification centres. But the most comman is accessory tarsal navicular bone occurring between 4-14% of population. Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleCite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleCite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
- an accessory navicular bone is present in ~10% of the population
- first appears in adolescence. In children its incidence is 4-21% of the population.Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title - more common in female patientsCite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title - reported prevalence of bilaterality is ~70% (range 50-90%)
People who have an accessory navicular often are unaware of the condition if it causes no problems. However, some people with this extra bone develop a painful condition known as accessory navicular syndrome when the bone and/or posterior tibial tendon are aggravated. This can result from any of the following:
- Trauma, as in a foot or ankle sprain
- Chronic irritation from shoes or other footwear rubbing against the extra bone
- Excessive activity or overuse
Characteristics/Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
- Typical young female (10-20 years of age) complaining of mid food/arch pain which may be insidious or post trauma.
- Difficulty with footwears.
- Prominent navicular
- Tenderness over the prominence
- Pain over the posterior tibialis tendon from a tendinitis and tightness of the tendo-achillis in long standing cases.
- Often pes planus.
- Inflamed bursa
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
- Stress fracture.
- Tendinitis
- Medial tuberosity fracture Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title - Cartilage forming bone Tumor
- Kohler’s disease. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
- Routine standing AP and lateral view are enough to look for accessory navicular but in some cases oblique view is also obtained in order to completely define the abnormality of navicular. Bilateral films may be indicated as there occurs high incidence of symmetrical abnormalities.
- On lateral weight bearing/standing film, the talonavicular cuneiform first metatarsal dorsal lalignment should be clearfully examined. “Sag” at this joint indicates structural integrity of the area.
- MRI or CT is indicated (very rare) in order to exclude tumor, fracture of medial tubersity, bone marrow edema.
AP Veiw' Lateral Veiw 'Oblique Veiw
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
add links to outcome measures here (also see Outcome Measures Database)
Examination[edit | edit source]
Patient with accessory navicular may present with complex pain patterns requiring thorough examination. Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title The examination importantly includes
- Differentiation of navicular prominence from talar head prominence in flat foot deformity by inverting and everting through the subtalar joint with a thumb over the bony prominence.Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title - Recognition of the loss of structural integrity of the longitudinal arch is important because this component of the deformity will not be corrected by surgical treatment if required. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title - Thought examination of gait.
Medical Management[edit | edit source]
CONSERVATIVE :
- Physical therapy
- Medications. Oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, may be prescribed. In some cases, oral or injected steroid medications may be used in combination with immobilization to reduce pain and inflammation. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title Corticosteroid injections can be used as a treatment modality. However, this modality should be used with caution as it may weaken the posterior tibial tendon and lead to subsequent rupture.Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleCite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleCite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleCite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleCite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleCite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleCite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleCite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleCite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleCite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleCite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleCite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleCite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
SECOND is Kindler procedure.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleCite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title In this the ossicle and navicular prominence is excised as in simple excision but along with the posterior tibial tendon advancement. Posterior tibial tendon is split and advanced along the medial side of foot to provide support to longitudinal arch.
After surgery 4 week short leg cast, well moulded into the arch with the foot plantigrade is applied. Partial weight bearing till the 8th week and later full weight bearing is allowed.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleCite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title. When the cast is being removed can start building up the ROM to counter atrophy and other physical therapy treatment which include stretching and strengthening exercises. Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
File:CAST MOULDING.jpg File:SHORT LEG CAST.jpg
Occasionally, a limited fusion of the cuneiform metatarsal or talonavicular joints also was recommended. The rationale and efficacy of this operation have been questioned.
Arthrodesis may be a reasonable treatment option in selected cases of patients with symptomatic recalcitrant Type II accessory naviculars that are large enough to accept small fragment screws.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Physical Therapy Management
[edit | edit source]
If the accessory navicular bone becomes problematic physical therapy may be prescribed.
This will include use of therapeutic modalities which relieves pain include ultrasonic therapy, TENS, massage, ROM exercises and treatments to strengthen the intrinsic foot muscles and lateral thigh rotators muscles and decrease inflammation. Often is the accessory navicular bone linked to Posterior tibial dysfunction to a pes planus. To adjust the arch of the foot, orthotic devices may be used.
- Well padded shoe orthotic should be worn for arch support. This decrease direct pressure over the navicular.
- Stretching of pernoneal and posterior tibialis along with strengthening exericises.
- Strengthening the intrinsic foot muscles and lateral thigh rotators muscles and decrease inflammation.Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title - Activity modification, such as limiting or stopping any strenuous activities that cause the Accessory Navicular bone to become symptomatic can be used for initial treatment.Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title - Gait training and Balance exercise for proper normal gait when required.
Some examples of basic and functional posterior tibialis strengthening:
| [1] | [2] |
| [3] | [4] |
Resources
[edit | edit source]
Foot health facts: http://www.footphysicians.com
http://www.aofas.org/Pages/Home.aspx
Clinical Bottom Line[edit | edit source]
Usaully the type I accessory navicular is rarely associated with symptoms and if the symptoms appears then it respond well to the conservative/ physical therapy managment. Patients with Type II accessory navicular are at the risk for disruption either from traction injury or shear forces in the region and and mostly the onset is insidious or post trauma. It fails to respond to conservative treatment when severe and fusion of the accessory navicular to the navicular may successfully relieve pain without disrupting the tibialis posterior tendon insertion.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Type III when symptomatic then excising the accessory navicular rather than excising navicular beak is more helpful.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Failed to load RSS feed from http://eutils.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=1-y-ZWVYINKeHZi7bpsugXOuniIrzEOQffwjhNAPouwaB4tkT_|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10: Error parsing XML for RSS
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ ShaychiITA. Tibialis Posterior Basic Strengthening. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zmh1FisBeeM [last accessed 24/11/12]
- ↑ ShaychiITA. Tibialis Posterior Basic Multiplanar Strengthening. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qv76eBxGQXI [last accessed 01/12/12]
- ↑ ShaychiITA. Tibialis Posterior Functional Strengthening: Full Body Weight Maintaining Supination. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1C_C5N9reB8[last accessed 01/12/12]|}
- ↑ ShaychiITA. Tibialis Posterior Functional Strengthening: Maintain Arch with Compass Squats. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TdHgyFZbOPk[last accessed 24/11/12]|}