Traditional Physiotherapy Interventions for Pain Conditions: Difference between revisions
(Undo revision 136108 by Kudzanayi Ronald Muzenda (talk)) |
Evan Thomas (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
'''Original Editor '''- Add a link to your Physiopedia profile here. | '''Original Editor '''- Add a link to your Physiopedia profile here. | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Traditional | |||
== Traditional Physiotherapy Modalities == | |||
=== Electrotherapy === | === Electrotherapy === | ||
The term electrotherapy and electrophyical agents have been used | The term electrotherapy and electrophyical agents have been used interchangeably to describe the modalities used in physiotherapy. Some suggest that the term electrotherapy implies modalities that use electric current only in treatment. | ||
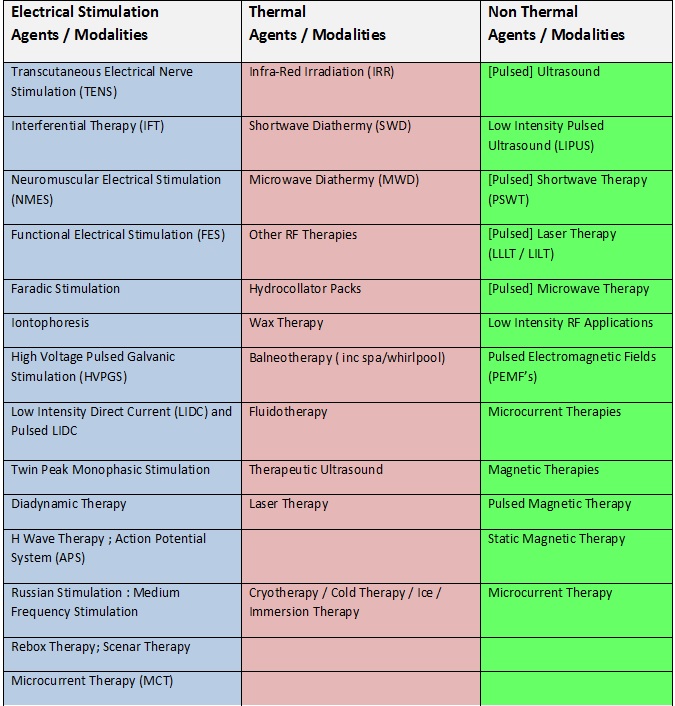
The following table | The following table categorizes various modalities into three groups, i.e. electrical stimulation agents, thermal agents, and non-thermal agents<ref>Key concepts in electrotherapy.http://www.electrotherapy.org/modality/key-concepts-in-electrotherapy.(Accessed 19 March 2016)</ref> | ||
[[Image:Electro.jpg]]<br> | [[Image:Electro.jpg]]<br> | ||
Electrical stimulation agents and thermal agents are the most used in pain management.However non thermal agents such as pulsed ultrasound | Electrical stimulation agents and thermal agents are the most used in physiotherapy pain management. However, non-thermal agents, such as pulsed ultrasound, have been reported as having an analgesic effect. | ||
==== | ==== Purported Therapeutic Effects ==== | ||
===== | ===== Electrical Stimulation ===== | ||
The exact mechanism of electrical stimulation’s beneficial effect remains controversial. Electrical stimulation is said directly block pain signals from reaching the brain so that the patient never experiences them. In addition, electrical stimulation has been shown to promote the release of endorphins which are natural painkillers produced by the body.Pain reduction occurs because the applied electrical fields act to close the body's "pain gate mechanism". | The exact mechanism of electrical stimulation’s beneficial effect remains controversial. Electrical stimulation is said directly block pain signals from reaching the brain so that the patient never experiences them. In addition, electrical stimulation has been shown to promote the release of endorphins which are natural painkillers produced by the body.Pain reduction occurs because the applied electrical fields act to close the body's "pain gate mechanism". | ||
===== Thermal | ===== Thermal Agents ===== | ||
When applied in successive fashion, heat and cold are believed to exert a physiological effect on your body's pain gate mechanism, which temporarily alters pain signals traveling to and from your brain. This temporary reduction in pain is a welcome relief for those suffering long-standing complaints of the nervous and musculoskeletal systems | When applied in successive fashion, heat and cold are believed to exert a physiological effect on your body's pain gate mechanism, which temporarily alters pain signals traveling to and from your brain. This temporary reduction in pain is a welcome relief for those suffering long-standing complaints of the nervous and musculoskeletal systems. | ||
==== | ===== Non-Thermal Agents ===== | ||
==== Current Evidence ==== | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
== Manual Therapy == | |||
=== | === Mobilization === | ||
=== Manipulation === | |||
=== | === Soft Tissue === | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
=== Purported Therapeutic Effects === | |||
=== | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
== | === Current Evidence === | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
== Additional Resources == | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 69: | Line 66: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | |||
<references /> | |||
[[Category:Pain]] [[Category:PPA_Project]] | [[Category:Pain]] [[Category:PPA_Project]] | ||
Revision as of 19:10, 16 April 2016
- Please do not edit unless you are involved in this project, but please come back in the near future to check out new information!!
- If you would like to get involved in this project and earn accreditation for your contributions, please get in touch!
Tips for writing this page:
- What is the current evidence base for the use of the following traditional therapy modalities with patients in pain? :electrotherapy/acupuncture/manipulation/massage/relaxation
- What are the proported theraputic effects?
- Should they, and how can they, be integrated with pharmacological, sociological and psychological interventions and approaches to managing pain experiences and re-integartion with function?
Original Editor - Add a link to your Physiopedia profile here.
Top Contributors - Kudzanayi Ronald Muzenda, Joanne Garvey, Kim Jackson, Evan Thomas, Lauren Lopez, Jo Etherton, WikiSysop, Simisola Ajeyalemi, Lucinda hampton, Jess Bell, Yigit Unalan and Rachael Lowe
Traditional Physiotherapy Modalities[edit | edit source]
Electrotherapy[edit | edit source]
The term electrotherapy and electrophyical agents have been used interchangeably to describe the modalities used in physiotherapy. Some suggest that the term electrotherapy implies modalities that use electric current only in treatment.
The following table categorizes various modalities into three groups, i.e. electrical stimulation agents, thermal agents, and non-thermal agents[1]
Electrical stimulation agents and thermal agents are the most used in physiotherapy pain management. However, non-thermal agents, such as pulsed ultrasound, have been reported as having an analgesic effect.
Purported Therapeutic Effects[edit | edit source]
Electrical Stimulation[edit | edit source]
The exact mechanism of electrical stimulation’s beneficial effect remains controversial. Electrical stimulation is said directly block pain signals from reaching the brain so that the patient never experiences them. In addition, electrical stimulation has been shown to promote the release of endorphins which are natural painkillers produced by the body.Pain reduction occurs because the applied electrical fields act to close the body's "pain gate mechanism".
Thermal Agents[edit | edit source]
When applied in successive fashion, heat and cold are believed to exert a physiological effect on your body's pain gate mechanism, which temporarily alters pain signals traveling to and from your brain. This temporary reduction in pain is a welcome relief for those suffering long-standing complaints of the nervous and musculoskeletal systems.
Non-Thermal Agents[edit | edit source]
Current Evidence[edit | edit source]
Manual Therapy[edit | edit source]
Mobilization[edit | edit source]
Manipulation[edit | edit source]
Soft Tissue[edit | edit source]
Purported Therapeutic Effects[edit | edit source]
Current Evidence[edit | edit source]
Additional Resources[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Key concepts in electrotherapy.http://www.electrotherapy.org/modality/key-concepts-in-electrotherapy.(Accessed 19 March 2016)