Understanding Red Flags in Patellofemoral Pain
Top Contributors - Carin Hunter, Jess Bell and Kim Jackson
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Why do we need to know red flags?
Safety
Directing patients to the right place
If there has been trauma to the knee - always make sure the correct imaging/investigations have been done.
Non-Traumatic Masquerading Conditions[edit | edit source]
Young people[edit | edit source]
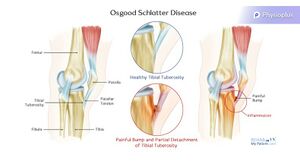
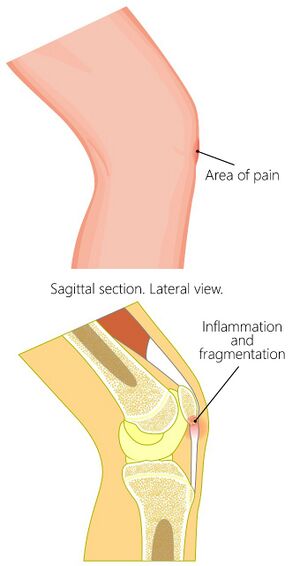
Osgood Schlatters[edit | edit source]
11-15 years olds
prevalent in kids that do lots of quads dominant sports, so running, and kicking and jumping
obvious bump at the tibial tubercle
Pain specific to tibial tubercle
inflammation and elevation of the growth plates in the tibial tuberosity, so the proximal tibia
Can be confirmed on MRI to show level of inflamation
Pain worsen to a point that it can prevent any participation in sport
Treatment:Education
Activity modification - eliminate least fav sport, change playing position to a less active one to decrease load
NSAIDS
Ice Massage(Symptomatic relief)
Address overload
extrinsic
load management of sport
footwear
landing technique
intrinsic factors
muscle length
muscle strength
Sinding-Larsen-Johansson Disease[edit | edit source]
inflammation at the growth plate of the distal pole of the patella
most likely to be seen at times of aggressive growth/growth spurts
treatment tactics that I ask parents to do is to track growth because they're more likely to manage it well at times of aggressive growth with their activity modification.
Pain worsen to a point that it can prevent any participation in sport
Treatment:activity modification
Knee Effusion[edit | edit source]
A child should not have a knee effusion
Effusion very often leads to patellofemoral pain
A knee effusion in a child should always be investigated
Possible Causes:
systemic autoimmune disease, juvenile arthritis
infective arthritis
Osteochondritis Dissecans
Osteochondritis Dissecans[edit | edit source]
cartilage and some of the subchondral bone can break off and float in the joint, which irritates the synovium, which in turn causes the effusion
autoimmune disease red flags:
Multiple joint involvement
Joint was stiff on waking
Fatigue
Infective arthritis red flags:
Temperature
Recent Illness
Osteochondral Defect[edit | edit source]
Others[edit | edit source]
Systemic Auto-Immune Disease
Slipped Epiphysis
FAI
Leukaemia
Metastatic Neuroblastoma
Primary Bone Tumour
Assessment Tools[edit | edit source]
Load Assessment Table for Growth Tracking - Track volume of exercise in a week