Ulnar Nerve: Difference between revisions
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "Category:Nerves - Wrist" to "Category:Wrist - Nerves") |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "[[/www.physio-pedia.com/" to "[[") |
||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
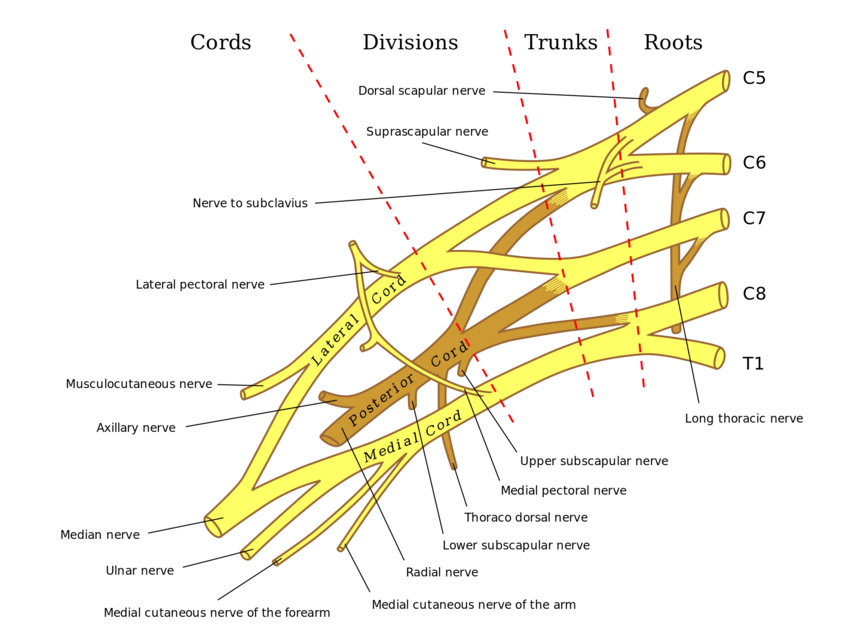
The ulnar nerve originates from C8-T1 nerve roots which form the medial cord of the [[Brachial Plexus|brachial plexus]]. | |||
[[Image:Braplex.PNG|thumb|843x843px|Brachial Plexus |center]] | |||
[[ | === Branches in the upper forearm === | ||
[[File:Nerves_of_the_left_upper_extremity.gif|right|Nerves of the upper extremity ]] | |||
The ulnar nerve runs down the hand, where it passes behind the medial epicondyle of the [[humerus]] at the elbow. The ulnar nerve doesn’t give branches in the axilla or in the upper arm. It starts with muscular and cutaneous branches in the upper forearm and hand. After the ulnar nerve passes behind the medial epicondyle, it enters the forearm between the two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. The ulnar nerve may become compressed or irritated as it passes behind the medial epicondyle. The ulnar nerve travels through the cubital tunnel that runs under the medial epicondyle. The nerve gives branches to the flexor carpi ulnaris and medial half of [[Flexor Digitorum Profundus|flexor digitorum profundus]] | |||
=== Branches in the lower forearm === | |||
The ulnar nerve then travels alongside the ulnar bone of the forearm into the wrist. As the nerve descends into the forearm, it stays medially above the flexor digitorium profundus and under the [[Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Muscle|flexor carpi ulnaris]] giving branches to these muscles. In the lower part of the forearm, the ulnar nerve lies lateral to the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle and medial to the ulnar artery. The ulnar nerve enters the palm of the hand through the Guyon canal. The nerve and artery pass superficial to the flexor retinaculum. | |||
At the wrist, the ulnar nerve lies just lateral to the pisiform bone. The superficial branch of the ulnar nerve supplies and passes under the Palmaris brevis muscles and divides into palmar digital nerves. The deep branch of the ulnar nerve innervates the three hypothenar muscles, the two medial lumbricals, the seven interrosei, the adductor pollicis and the deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis. It supplies all intrinsic hand muscles | === Branches in the wrist === | ||
At the wrist, the ulnar nerve lies just lateral to the [[pisiform]] bone. The superficial branch of the ulnar nerve supplies and passes under the Palmaris brevis muscles and divides into palmar digital nerves. The deep branch of the ulnar nerve innervates the three hypothenar muscles, the two medial lumbricals, the seven interrosei, the adductor pollicis and the deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis. It supplies all intrinsic hand muscles that lie medial to the flexor pollicis except the last two lateral lumbricals.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
=== Root === | === Root === | ||
| Line 25: | Line 31: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
==== Motor ==== | === Sensory === | ||
Anterior forearm | |||
* '''Palmar cutaneous branch:''' innervates the skin of the medial half of the hand | |||
* '''Dorsal cutaneous branch'''- innervates the skin of the medial one and a half fingers, and the associated dorsal hand area. | |||
* '''The superficial branch-''' innervates the palmar surface of the medial one and a half fingers. | |||
=== Motor === | |||
==== Anterior forearm ==== | |||
* Flexor carpi ulnaris | * Flexor carpi ulnaris | ||
* Medial half of Flexor digitorium profundus | * Medial half of Flexor digitorium profundus | ||
Hand | |||
==== Hand ==== | |||
* Hypothenar muscles | * Hypothenar muscles | ||
* Medial two lumbricals | * Medial two lumbricals | ||
| Line 36: | Line 50: | ||
* Palmaris brevis | * Palmaris brevis | ||
== | == Clinical Relevance == | ||
The ulnar nerve is most susceptible to injury at the elbow<ref>Selby, Ronald; Safran, Marc; O'brien, Stephen (2007). [http://www.msdlatinamerica.com/ebooks/PracticalOrthopaedicSportsMedicineArthrocopy/sid328804.html "Practical Orthopaedic Sports Medicine & Arthroscopy, 1st edition: Elbow Injuries"]</ref> and the wrist, resulting in varying degrees of motor and sensory loss. | |||
=== Mechanism of injury === | |||
Mechanisms of injury include: | |||
* Trauma, | |||
* Nerve impingement, | |||
* Lacerations at the wrist and , | |||
* Guyon canal cyst. | |||
== | === Characteristic signs of injury === | ||
The | The characteristic sign of injury to the ulnar nerve is the inability to grip paper between the fingers, with long-term cases resulting in ulnar claw hand deformity. | ||
[[File:Claw hand.jpg|thumb|400x400px|ulnar claw hand deformity <ref>Symptoms - Claw hand [Internet]. Adam.com. 2022 [cited 2024 Feb 11]. Available from: <nowiki>https://ssl.adam.com/content.aspx?productid=617&isarticlelink=false&pid=1&gid=003169&site=makatimed.adam.com&login=MAKA1603</nowiki> | |||
</ref>]] | |||
== Entrapment Syndromes == | |||
There are two entrapment syndromes involving the ulnar nerve or its branches: | There are two entrapment syndromes involving the ulnar nerve or its branches: | ||
* [[Cubital Tunnel Syndrome]] | * [[Cubital Tunnel Syndrome]] - when your ulnar nerve gets irritated or compressed (squeezed) at the inside of your elbow | ||
* Guyon canal syndrome | * [[Guyon Canal Syndrome|Guyon canal syndrome]]- compression of the distal [[Ulnar Nerve|ulnar nerve]] at the level of the wrist as it enters the hand through a space called ulnar tunnel or [[Guyon Canal|Guyon canal]]. <ref>Dmitri Aleksenko, Varacallo M. Guyon Canal Syndrome [Internet]. Nih.gov. StatPearls Publishing; 2023 [cited 2024 Feb 11]. Available from: <nowiki>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK431063/#:~:text=Guyon%20canal%20is%20a%20unique,known%20as%20cubital%20tunnel%20syndrome</nowiki>. | ||
</ref> | |||
== Clinical Features == | |||
The ulnar nerve injury can be characterized by the following clinical features<ref name=":0">Chaurasia BD.Human Anatomy. 6th edition.Vol1.CBS Publishers and distributors Pvt ltd.</ref>: | |||
* flattening of medial border of forearm | |||
* loss of sensation at distal interphalangeal joints of 4th and 5th digit | |||
* loss of hypothenar eminence | |||
* loss of adduction of thumb | |||
* loss of abduction of fingers | |||
* marked clawing of 4th and 5th digits | |||
* slight clawing of 4th and 5th digit | |||
* sensory, trophic and vasomotor changes | |||
== Assessment == | == Assessment == | ||
=== Neuro exam === | === Neuro exam === | ||
[[File:Cubital-Tunnel-Syndrome-Anatomy.png|thumb|776x776px|Ulnar nerve <ref>The Ulnar Tunnel - Borders - Contents - TeachMeAnatomy [Internet]. Teachmeanatomy.info. 2021 [cited 2024 Feb 11]. Available from: <nowiki>https://teachmeanatomy.info/upper-limb/areas/ulnar-tunnel/</nowiki> | |||
</ref>]] | |||
'''Weakness:''' | '''Weakness:''' | ||
* Wrist flexion | * Wrist flexion | ||
| Line 67: | Line 105: | ||
* Dorsal surface of the medial one and a half fingers | * Dorsal surface of the medial one and a half fingers | ||
== | == Neurodynamic == | ||
The upper limb neurodynamic test for the ulnar nerve(ULNT3) is performed with the patient in supine. The joints are moved sequentially | The upper limb neurodynamic test for the ulnar nerve (ULNT3) is performed with the patient in supine. The joints are moved sequentially to the end of the range or until symptoms are produced. Patients are to be instructed to report the onset of any sensation such as stretch, tingling or pain anywhere in the arm or neck. | ||
'''ULNT3 sequencing:''' | '''ULNT3 sequencing:''' | ||
* Shoulder girdle depression | * Shoulder-girdle depression | ||
* Shoulder abduction | * Shoulder abduction | ||
* Shoulder external rotation | * Shoulder external rotation | ||
| Line 78: | Line 116: | ||
* Shoulder abduction | * Shoulder abduction | ||
== Resources == | |||
== Resources | |||
{| width="100%" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" | {| width="100%" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
<div class="row"> | |||
<div class="col-md-4"> {{#ev:youtube|EoTfDy8T5vM|250}} <div class="text-right"><ref>AnatomyZone. Ulnar Nerve | 3D Anatomy Tutorial. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EoTfDy8T5vM [last accessed 24/10/2020]</ref></div></div> | |||
<div class="col-md-4"> {{#ev:youtube|GyqaKGg3HmM|250}} <div class="text-right"><ref>nabil ebraheim. Claw Hand, Ulnar Claw Hand - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim . Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GyqaKGg3HmM [last accessed 24/10/2020]</ref></div></div> | |||
<div class="col-md-4"> {{#ev:youtube|wKnpaf7OI7s|250}} <div class="text-right"><ref>Physical Therapy Nation. Upper Limb Tension Test (Ulnar Nerve Bias). Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wKnpaf7OI7s [last accessed 24/10/2020]</ref></div></div> | |||
</div> | |||
| Line 98: | Line 138: | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] [[Category:Nerves]] | [[Category:Anatomy]] [[Category:Nerves]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Hand]] | ||
[[Category:Anatomy | [[Category:Wrist]] | ||
[[Category:Wrist - Anatomy]] | |||
[[Category:Wrist - Nerves]] | [[Category:Wrist - Nerves]] | ||
[[Category:Hand - Anatomy]] | |||
[[Category:Hand - Nerves]] | [[Category:Hand - Nerves]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:04, 19 March 2024
Original Editor - Simisola Ajeyalemi
Top Contributors - Simisola Ajeyalemi, Kim Jackson, Fasuba Ayobami, Redisha Jakibanjar and Momina Khalid
Description[edit | edit source]
The ulnar nerve originates from C8-T1 nerve roots which form the medial cord of the brachial plexus.
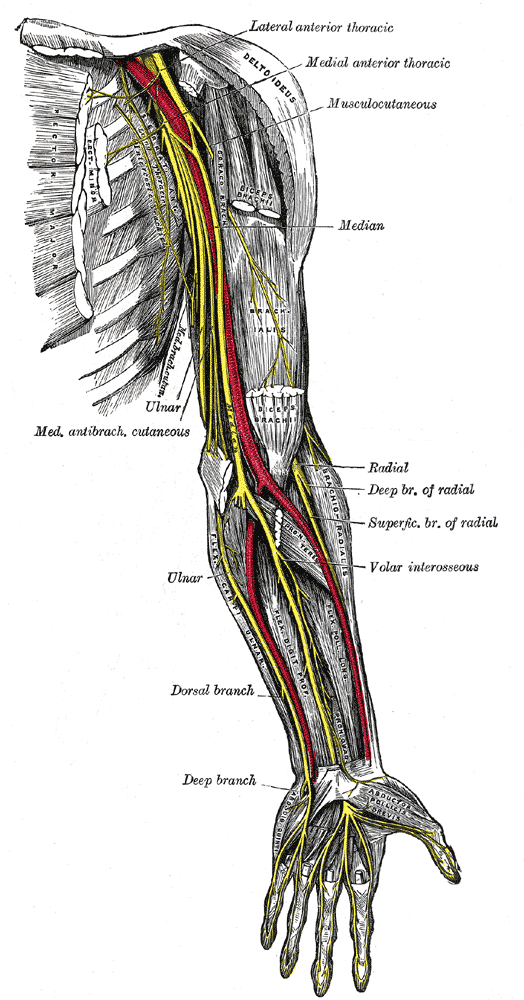
Branches in the upper forearm[edit | edit source]
The ulnar nerve runs down the hand, where it passes behind the medial epicondyle of the humerus at the elbow. The ulnar nerve doesn’t give branches in the axilla or in the upper arm. It starts with muscular and cutaneous branches in the upper forearm and hand. After the ulnar nerve passes behind the medial epicondyle, it enters the forearm between the two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. The ulnar nerve may become compressed or irritated as it passes behind the medial epicondyle. The ulnar nerve travels through the cubital tunnel that runs under the medial epicondyle. The nerve gives branches to the flexor carpi ulnaris and medial half of flexor digitorum profundus
Branches in the lower forearm[edit | edit source]
The ulnar nerve then travels alongside the ulnar bone of the forearm into the wrist. As the nerve descends into the forearm, it stays medially above the flexor digitorium profundus and under the flexor carpi ulnaris giving branches to these muscles. In the lower part of the forearm, the ulnar nerve lies lateral to the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle and medial to the ulnar artery. The ulnar nerve enters the palm of the hand through the Guyon canal. The nerve and artery pass superficial to the flexor retinaculum.
Branches in the wrist[edit | edit source]
At the wrist, the ulnar nerve lies just lateral to the pisiform bone. The superficial branch of the ulnar nerve supplies and passes under the Palmaris brevis muscles and divides into palmar digital nerves. The deep branch of the ulnar nerve innervates the three hypothenar muscles, the two medial lumbricals, the seven interrosei, the adductor pollicis and the deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis. It supplies all intrinsic hand muscles that lie medial to the flexor pollicis except the last two lateral lumbricals.[1]
Root[edit | edit source]
C8, T1
From the Medial cord of brachial plexus.
Branches[edit | edit source]
- Muscular branch
- Palmar cutaneous branch
- Dorsal cutaneous branch
Function[edit | edit source]
Sensory[edit | edit source]
- Palmar cutaneous branch: innervates the skin of the medial half of the hand
- Dorsal cutaneous branch- innervates the skin of the medial one and a half fingers, and the associated dorsal hand area.
- The superficial branch- innervates the palmar surface of the medial one and a half fingers.
Motor[edit | edit source]
Anterior forearm[edit | edit source]
- Flexor carpi ulnaris
- Medial half of Flexor digitorium profundus
Hand[edit | edit source]
- Hypothenar muscles
- Medial two lumbricals
- Adductor pollicis
- Interossei of the hand
- Palmaris brevis
Clinical Relevance[edit | edit source]
The ulnar nerve is most susceptible to injury at the elbow[2] and the wrist, resulting in varying degrees of motor and sensory loss.
Mechanism of injury[edit | edit source]
Mechanisms of injury include:
- Trauma,
- Nerve impingement,
- Lacerations at the wrist and ,
- Guyon canal cyst.
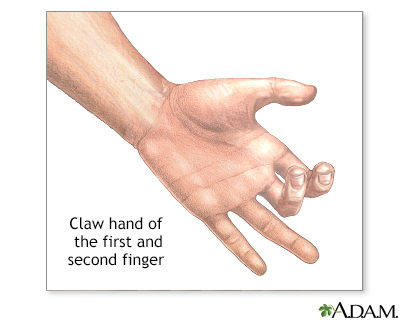
Characteristic signs of injury[edit | edit source]
The characteristic sign of injury to the ulnar nerve is the inability to grip paper between the fingers, with long-term cases resulting in ulnar claw hand deformity.
Entrapment Syndromes[edit | edit source]
There are two entrapment syndromes involving the ulnar nerve or its branches:
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome - when your ulnar nerve gets irritated or compressed (squeezed) at the inside of your elbow
- Guyon canal syndrome- compression of the distal ulnar nerve at the level of the wrist as it enters the hand through a space called ulnar tunnel or Guyon canal. [4]
Clinical Features[edit | edit source]
The ulnar nerve injury can be characterized by the following clinical features[1]:
- flattening of medial border of forearm
- loss of sensation at distal interphalangeal joints of 4th and 5th digit
- loss of hypothenar eminence
- loss of adduction of thumb
- loss of abduction of fingers
- marked clawing of 4th and 5th digits
- slight clawing of 4th and 5th digit
- sensory, trophic and vasomotor changes
Assessment[edit | edit source]
Neuro exam[edit | edit source]
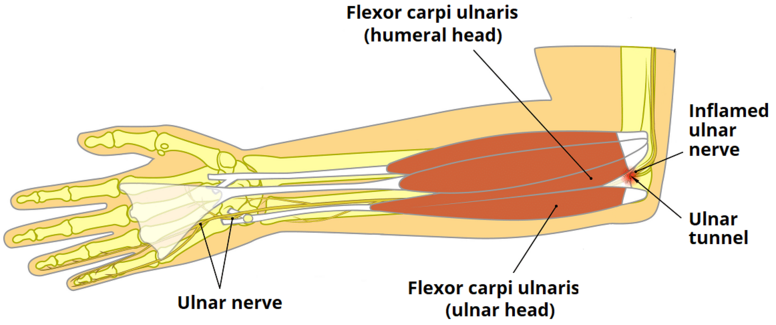
Weakness:
- Wrist flexion
- Flexion of the little finger
- Abduction of the index and little finger
- Adduction of the thumb
Diminished sensation:
- Palmar surface of the medial one and a half fingers
- Dorsal surface of the medial one and a half fingers
Neurodynamic[edit | edit source]
The upper limb neurodynamic test for the ulnar nerve (ULNT3) is performed with the patient in supine. The joints are moved sequentially to the end of the range or until symptoms are produced. Patients are to be instructed to report the onset of any sensation such as stretch, tingling or pain anywhere in the arm or neck.
ULNT3 sequencing:
- Shoulder-girdle depression
- Shoulder abduction
- Shoulder external rotation
- Wrist and Finger extension
- Elbow flexion
- Shoulder abduction
Resources[edit | edit source]
See also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Chaurasia BD.Human Anatomy. 6th edition.Vol1.CBS Publishers and distributors Pvt ltd.
- ↑ Selby, Ronald; Safran, Marc; O'brien, Stephen (2007). "Practical Orthopaedic Sports Medicine & Arthroscopy, 1st edition: Elbow Injuries"
- ↑ Symptoms - Claw hand [Internet]. Adam.com. 2022 [cited 2024 Feb 11]. Available from: https://ssl.adam.com/content.aspx?productid=617&isarticlelink=false&pid=1&gid=003169&site=makatimed.adam.com&login=MAKA1603
- ↑ Dmitri Aleksenko, Varacallo M. Guyon Canal Syndrome [Internet]. Nih.gov. StatPearls Publishing; 2023 [cited 2024 Feb 11]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK431063/#:~:text=Guyon%20canal%20is%20a%20unique,known%20as%20cubital%20tunnel%20syndrome.
- ↑ The Ulnar Tunnel - Borders - Contents - TeachMeAnatomy [Internet]. Teachmeanatomy.info. 2021 [cited 2024 Feb 11]. Available from: https://teachmeanatomy.info/upper-limb/areas/ulnar-tunnel/
- ↑ AnatomyZone. Ulnar Nerve | 3D Anatomy Tutorial. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EoTfDy8T5vM [last accessed 24/10/2020]
- ↑ nabil ebraheim. Claw Hand, Ulnar Claw Hand - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim . Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GyqaKGg3HmM [last accessed 24/10/2020]
- ↑ Physical Therapy Nation. Upper Limb Tension Test (Ulnar Nerve Bias). Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wKnpaf7OI7s [last accessed 24/10/2020]