Ulnar Nerve: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(description of ulnar nerve) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
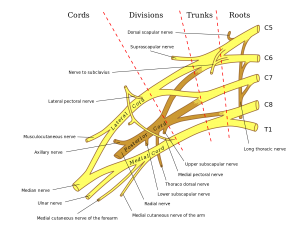
[[Image:Braplex.PNG|thumb|right|300px]] The ulnar nerve originates from C8-T1 nerve roots which form the medial cord of the brachial plexus. The ulnar nerve runs down the hand where it passes behind the medial epicondyle of the humerus at the elbow. The ulnar nerve doesn’t give branches in the axilla or in the upper arm. It starts giving muscular and cutaneous branches in the upper forearm and hand. After the ulnar nerve passes behind the medial epicondyle, it enters the forearm between the two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. The ulnar nerve may become compressed or irritated as it passes behind the medial epicondyle. The ulnar nerve travels through the cubital tunnl)that runs under the medial epicondyle. The nerve gives branches to the flexor carpi ulnaris and mmedialhalf of flexor digitorum profundus | [[Image:Braplex.PNG|thumb|right|300px]] The ulnar nerve originates from C8-T1 nerve roots which form the medial cord of the brachial plexus. The ulnar nerve runs down the hand where it passes behind the medial epicondyle of the humerus at the elbow. The ulnar nerve doesn’t give branches in the axilla or in the upper arm. It starts giving muscular and cutaneous branches in the upper forearm and hand. After the ulnar nerve passes behind the medial epicondyle, it enters the forearm between the two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. The ulnar nerve may become compressed or irritated as it passes behind the medial epicondyle. The ulnar nerve travels through the cubital tunnl)that runs under the medial epicondyle. The nerve gives branches to the flexor carpi ulnaris and mmedialhalf of flexor digitorum profundus | ||
The ulnar nerve then travels alongside the ulnar bone of the forearm into the wrist. As the nerve descends into the forearm, it stays medially above the flexor digitorium isprofundus and under the flexor carpi ulnaris giving branches to these muscles. In the lower part of the forearm, the ulnar nerve lies lateral to the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle and medial to the ulnar artery. The ulnar nerve enters the palm of the hand through the Guyon canal. The nerve and artery pass superficial to the flexor retinaculum. At the wrist, the ulnar nerve lies just lateral to the pisiform bone. The superficial branch of the ulnar nerve supplies and passes under the Palmaris brevis muscles and divides into palmar digital nerves. The deep branch of the ulnar nerve innervates the three hypothenar muscles the two medial lumbricals, the seven interrosei the adductor pollicis and the deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis.m It supplies all intrinsic hand muscles which lie medial to the flexor pollicis except the last lateral twolumbricals. s | The ulnar nerve then travels alongside the ulnar bone of the forearm into the wrist. As the nerve descends into the forearm, it stays medially above the flexor digitorium isprofundus and under the flexor carpi ulnaris giving branches to these muscles. In the lower part of the forearm, the ulnar nerve lies lateral to the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle and medial to the ulnar artery. The ulnar nerve enters the palm of the hand through the Guyon canal. The nerve and artery pass superficial to the flexor retinaculum. | ||
At the wrist, the ulnar nerve lies just lateral to the pisiform bone. The superficial branch of the ulnar nerve supplies and passes under the Palmaris brevis muscles and divides into palmar digital nerves. The deep branch of the ulnar nerve innervates the three hypothenar muscles the two medial lumbricals, the seven interrosei the adductor pollicis and the deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis.m It supplies all intrinsic hand muscles which lie medial to the flexor pollicis except the last lateral twolumbricals. s | |||
=== Root === | === Root === | ||
Revision as of 15:45, 7 June 2018
Original Editor - name here
Top Contributors - Simisola Ajeyalemi, Kim Jackson, Fasuba Ayobami, Redisha Jakibanjar and Momina Khalid
Description[edit | edit source]
The ulnar nerve originates from C8-T1 nerve roots which form the medial cord of the brachial plexus. The ulnar nerve runs down the hand where it passes behind the medial epicondyle of the humerus at the elbow. The ulnar nerve doesn’t give branches in the axilla or in the upper arm. It starts giving muscular and cutaneous branches in the upper forearm and hand. After the ulnar nerve passes behind the medial epicondyle, it enters the forearm between the two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. The ulnar nerve may become compressed or irritated as it passes behind the medial epicondyle. The ulnar nerve travels through the cubital tunnl)that runs under the medial epicondyle. The nerve gives branches to the flexor carpi ulnaris and mmedialhalf of flexor digitorum profundus
The ulnar nerve then travels alongside the ulnar bone of the forearm into the wrist. As the nerve descends into the forearm, it stays medially above the flexor digitorium isprofundus and under the flexor carpi ulnaris giving branches to these muscles. In the lower part of the forearm, the ulnar nerve lies lateral to the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle and medial to the ulnar artery. The ulnar nerve enters the palm of the hand through the Guyon canal. The nerve and artery pass superficial to the flexor retinaculum.
At the wrist, the ulnar nerve lies just lateral to the pisiform bone. The superficial branch of the ulnar nerve supplies and passes under the Palmaris brevis muscles and divides into palmar digital nerves. The deep branch of the ulnar nerve innervates the three hypothenar muscles the two medial lumbricals, the seven interrosei the adductor pollicis and the deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis.m It supplies all intrinsic hand muscles which lie medial to the flexor pollicis except the last lateral twolumbricals. s