Tularemia
Original Editors - Dana Collins from Bellarmine University's Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems project.
Lead Editors - Your name will be added here if you are a lead editor on this page. Read more.
Definition/Description[edit | edit source]
Tularemia, named after the infectious gram-negative bacterium Francisella tularensis, is a zoonotic disease. A zoonotic disease is one that is spread from animal to human. This spread may be directly i.e. handling contaminated meat or through a carrier i.e. a tick. It is also known as “Ohara’s disease”, “rabbit fever”, “deer-fly fever”,[1] “market’s men disease”, “meat-cutter’s disease”, “glandular type of tick fever”, “water rat-trappers’ disease”. It is highly infectious, <10 organisms causing severe disease in both humans and animals.[2] There are 4 sub-types of the bacterium, the most common in the United States are Type A, tularenis, and Type B, holarctica. It is on the Center for Disease Control’s list of bioterroism threats.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_detailpage&v=zUVQB39ATME
Prevalence[edit | edit source]
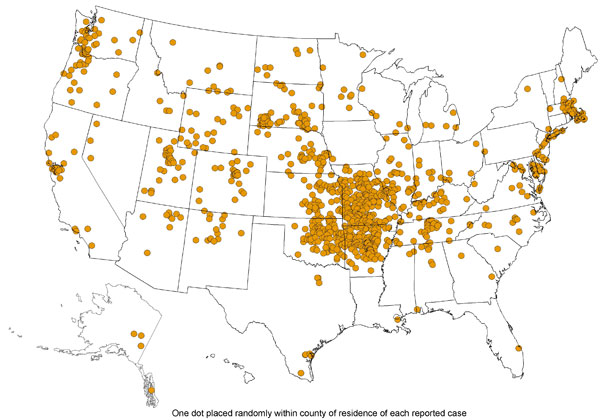
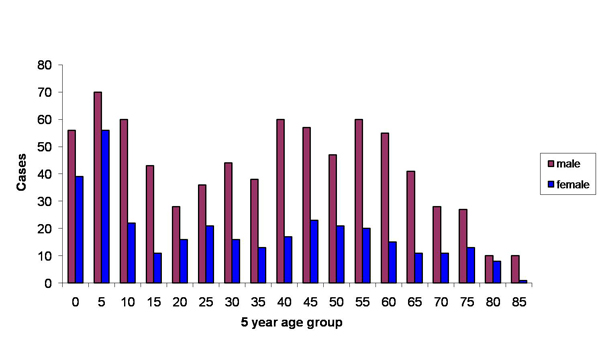
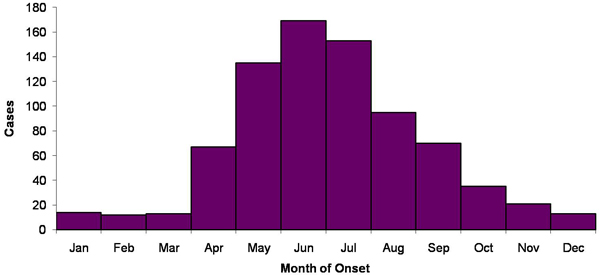
The prevalence of Tularemia in the United States depends on the geographical location and the time of year. During the spring and summer months (May-September), there is a rise in reported cases. South-Central, Pacific Northwest, and parts of the East Coast have the highest incidence of Tularemia. While the population most effected is young males 5-9 years old and those > 75 years old.[3]
The above images from: http://www.cdc.gov/tularemia/statistics/.
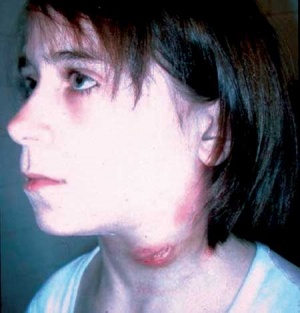
Characteristics/Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
| • Fever • Abdominal pain • Arthralgias • Shortness of breath • Malaise • Nausea/Vomiting • Sore throat |
• Chills • Prostration • Conjunctivitis • Diaphoresis • Axillary adenopathy • Cough • Hemoptysis |
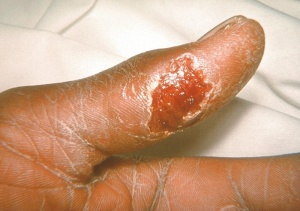
• Headache • Myalgias • Cutaneous ulcers • Weight loss • Epitrochlear adenopathy • Pleuritic chest pain, retrosternal pain |
Note: The 2 most common forms are glandular/ulcerglandular and pneumonic.
Those occurring in ≥25% of those infected with the glandular and ulceroglandular form are in bold[4]
Those occurring in ≥25% of those infected with the pneumonic form are in italics[4]
Image from
http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu
Image from:
Expectations/Prognosis[5][edit | edit source]
Untreated: Fatality ~5%
Treated: Fatality <1%
Poor outcomes have been associated with those who have underlying co-morbidities such as alcoholism or diabetes and those who delay seeking medical treatment.[4]
Medications[4][edit | edit source]
Antibiotic therapy is used to treat Tularemia. Streptomyocin and Gentamicin are usually the first administered. Ciprofloxacin along with other fluoroquinolones. Tetracycline and chloramphenicol may also be used to treat Tularemia, however they have higher relapse rates than the previously mentioned.
Resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics and azithromycin.
Diagnostic Tests/Lab Tests/Lab Values[4][5][edit | edit source]
There are numerous ways to test for F. tularensis:
• Gold Standard: Bacteriologic Culture[2]
• Most Common: Serology[2]
• PCR of sample ulcer
• Direct Stains
• Blood Culture
• Direct Fluorescent Antibody Stain
• Slide Agglutination
• Antimicrobial Susceptibility
• Biochemical Identification
• Enviornmental Specimen Evaluation
• Chest X-ray
Etiology/Causes [2][edit | edit source]
Direct transmission occurs from direct contact with the infected animal or direct contact from soil, water, or landscape. This may be from ingestion of contaminated meat (most likely rabbit), water, or inhaled dust. It can also be passed from handling or skinning contaminated animals or from a bite/scrath from a contaminated animal. Animal hosts that may spread Tularemia include lagomorphs (rabbit and hare), rodents, insectivores, carnivores, ungulates, marsupials, birds, amphibians, fish, and invertebrates. Secondary carriers include ticks, mosquitoes, biting flies or deerfly. With such a wide variety of hosts and carriers available of this disease, it is has the possibility to appear/outbreak in other regions.
Systemic Involvement [5][edit | edit source]
- Pericarditis
- Osteomyelitis
- Meningitis
- Pneumonia
Medical Management (current best evidence) [edit | edit source]
Antimicrobials are currently the best treatment option for Tularemia infections.After beginning treatment one should expect to see an improvement in symptoms and fever within 24-48 hours.[4]
- Aminoglycosides[1]
- Streptomyocin 10-14 days (1st choice)
- May also be treated with gentamicin or tetracycline for 14+ days
Tetracycline should not be used as a treatment in those whose permanent teeth have not came in.[5]
- Quinolones
- Contraindicated in those < 18 years of age
- "well tolerated, achieve adequate blood levels...and have excellent intracellular penetration"[6]
A review of 10 documented treatment cases in the United States found that those treated with Aminoglycosides have a 6-12% relapse rate of infection, while those treated with Quinolones had a 0% relapse rate.[6]
Physical Therapy Management (current best evidence)[edit | edit source]
Currently did not come across any management in regards to physical therapy.
Alternative/Holistic Management (current best evidence)[edit | edit source]
The only reported treatments for Tularemia in the literature was through antibiotics. (See above section: Medications)
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Glandular[edit | edit source]
Ulceroglandular[edit | edit source]
Glandular[edit | edit source]
Ulceroglandular[edit | edit source]
Pneumonic[edit | edit source]
Oculonglandular[edit | edit source]
Case Reports/ Case Studies[edit | edit source]
Isolation of Francisella tularensis from blood.[7]
Tularemia: Emergency department presentation of an infrequently recognized disease.[8]
Treatment of tularemia with fluoroquinolones: two cases and review.[9]
Resources
[edit | edit source]
add appropriate resources here
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
see tutorial on Adding PubMed Feed
References[edit | edit source]
see adding references tutorial.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Wilson M, Lountzis N, Ferringer T. Zoonoses of dermatologic interest. Dermatologic Therapy. 2009;22:367-378. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1529-8019.2009.01248.x/abstract. Accessed February 2011.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Petersen JM, Schriefer ME. Tularemia: emergence/re-emergence. Vet Res. 2005;36:455-467. http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1031&context=zoonoticspub&sei-redir=1#search=%22Petersen+JM,+Schriefer+ME.+Tularemia:+emergence/re-emergence.%22. Accessed February 2011.
- ↑ Hayes E, Marshall S, Dennis D. Tualremia--United States,1990-2000. www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm5109a1.htm. February 20, 2011.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 CIDRAP. Tularemia: Current, comprehensive information on pathogenesis, microbiology, epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment, and prophylaxis. http://www.cidrap.umn.edu/cidrap/content/bt/tularemia/biofacts/tularemiafactsheet.html. Updated March 16, 2010. Accessed February 2011.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Tularemia. PubMed Health. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001859/. Updated March 17,2009. Accessed February 19, 2011.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Limaye AP, Hooper CJ. Treatment of tularemia with flouroquinolones: two cases and review. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 1999;29:922-924. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10589911. Accessed February 2011.
- ↑ Provenza JM, Klotz SA, Penn RL. Isolation of francisella tularenis from blood. Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 1986;24:453-455. http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/content/short/24/3/453. Accessed February 2011.
- ↑ Harrell RE, Whitaker GR. Tularemia: Emergency department presentation of an infrequently recognized disease. Am J Emerg Med. 1985;3:415-418. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6W9K-4C4FJTF-GS&_user=10&_coverDate=09%2F30%2F1985&_rdoc=1&_fmt=high&_orig=gateway&_origin=gateway&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_rerunOrigin=google&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=8437c09158b0597f13c1896c220c972e&searchtype=a. Accessed February 2011.
- ↑ Limaye AP, Hooper CJ. Treatement of tularemia with fluoroquinolones: Two cases and review. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 1999;29:922-924.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10589911. Accessed February 2011.