Tip Toe Standing Test: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Purpose == | == Purpose == | ||
The purpose of a tip toe standing test is to differentiate between the two different categories of flatfoot ([[Pes Planus|pes planus]]), namely flexible flatfoot and fixed flatfoot.<ref name=":0">Rodriguez N, Volpe RG. [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0891842209000731?via%3Dihub Clinical diagnosis and assessment of the pediatric pes planovalgus deformity]. Clinics in Podiatric Medicine and Surgery. 2010 Jan 1;27(1):43-58.</ref> It is important to differentiate flexible from fixed as the prognosis and intervention of the two presentations are vastly different. In addition, the presentation of a fixed flatfoot deformity flags possible underlying pathologies which could include cerebral palsy | The purpose of a tip toe standing test is to differentiate between the two different categories of flatfoot ([[Pes Planus|pes planus]]), namely flexible flatfoot and fixed flatfoot.<ref name=":0">Rodriguez N, Volpe RG. [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0891842209000731?via%3Dihub Clinical diagnosis and assessment of the pediatric pes planovalgus deformity]. Clinics in Podiatric Medicine and Surgery. 2010 Jan 1;27(1):43-58.</ref> It is important to differentiate flexible from fixed as the prognosis and intervention of the two presentations are vastly different. In addition, the presentation of a fixed flatfoot deformity flags possible underlying pathologies which could include cerebral palsy, other tone-influencing pathologies or tarsal coalition. | ||
This is an indirect, observational method of assessment.<ref name=":0" /> | This is an indirect, observational method of assessment.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
2. The patient is then asked to stand on tip toe. | 2. The patient is then asked to stand on tip toe. | ||
== Result == | == Result and Interpretation == | ||
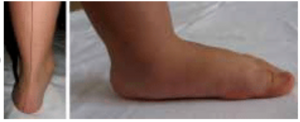
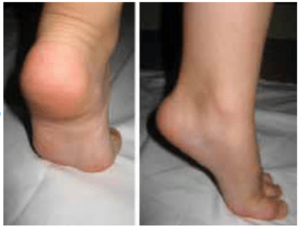
In a '''flexible flatfoot''' the heel will turn inwards (varus position) and the medial arch will become apparent. | In a '''flexible flatfoot''' the heel will turn inwards (varus position) and the medial arch will become apparent. | ||
Revision as of 21:58, 17 August 2022
Original Editor - User: Lauren Heydenrych
Top Contributors - Lauren Heydenrych
Purpose[edit | edit source]
The purpose of a tip toe standing test is to differentiate between the two different categories of flatfoot (pes planus), namely flexible flatfoot and fixed flatfoot.[1] It is important to differentiate flexible from fixed as the prognosis and intervention of the two presentations are vastly different. In addition, the presentation of a fixed flatfoot deformity flags possible underlying pathologies which could include cerebral palsy, other tone-influencing pathologies or tarsal coalition.
This is an indirect, observational method of assessment.[1]
Technique[edit | edit source]
1. The patient stands on flat ground. This can be done at a wall or other place where external support can be used.
2. The patient is then asked to stand on tip toe.
Result and Interpretation[edit | edit source]
In a flexible flatfoot the heel will turn inwards (varus position) and the medial arch will become apparent.
In fixed flatfoot, the medial longitudinal arch will remain unobservable.[2]
Performance of Tip Toe Standing Test[edit | edit source]
To further test for a flexible flatfoot, the Hubscher maneuver (or Jack's test) can also be done.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Rodriguez N, Volpe RG. Clinical diagnosis and assessment of the pediatric pes planovalgus deformity. Clinics in Podiatric Medicine and Surgery. 2010 Jan 1;27(1):43-58.
- ↑ Alazzawi S, Sukeik M, King D, Vemulapalli K. Foot and ankle history and clinical examination: A guide to everyday practice. World Journal of Orthopedics. 2017 Jan 18;8(1):21.
- ↑ Dr. Estefania Birrer Gonzalez. Toe Standing Test For Flexible Flatfoot. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nolevVWzdio [last accessed 16/07/2022]