Thenar and Hypothenar Muscles Of The Hand: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
=== Hypothenar Eminence (HE) Muscles === | === Hypothenar Eminence (HE) Muscles === | ||
The HE muscles are<ref name=":1" /> - | |||
* '''Opponens Digiti Minimi''' | |||
'''Origin''' - the hook of hamate and associated transverse carpal ligament | |||
'''Insertion''' - lateral aspect of the proximal phalanx of the thumb. | |||
'''Nerve''' - Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8, T1) | |||
'''Artery''' - Ulnar artery | |||
'''Function''' - flex and laterally rotate the 5th metacarpal about the 5th carpometacarpal joint. | |||
* '''Abductor digiti minimi''' | |||
'''Origin''' - pisiform bone and the tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris | |||
'''Insertion''' - the ulnar base of the proximal phalanx of the small finger | |||
'''Nerve''' - Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8, T1) | |||
'''Artery''' - Ulnar artery | |||
'''Function''' - abduction of the 5th finger, as well as flexion of its proximal phalanx | |||
* '''Flexor digiti minimi brevis''' | |||
'''Origin''' - the hook of hamate and associated transverse carpal ligament | |||
'''Insertion''' - the base of the proximal phalanx of the small finger | |||
'''Nerve''' - Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8, T1) | |||
'''Artery''' - Ulnar artery | |||
'''Function''' - flexes the little finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint | |||
* '''Palmaris brevis''' | |||
'''Origin''' - the transverse carpal ligament | |||
'''Insertion''' - on the skin of the medial palm | |||
'''Nerve''' - Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8, T1) | |||
'''Artery''' - Ulnar artery | |||
'''Function''' - tenses the skin of the palm on the ulnar side during a grip action and deepens the hollow of the palm. | |||
== Clinical relevance == | == Clinical relevance == | ||
Revision as of 21:23, 19 September 2020
Original Editor - User Name
Top Contributors - Saumya Srivastava, Kim Jackson, Leana Louw, Amanda Ager and Ahmed M Diab
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The complex integrity of the human hand is one of the factors that set our spices apart from the primates. The movement of opposition played an important role in the human evolution and this was made possible as more muscles go to the thumb in modern humans than our ancestral primates[1]. Although the muscles of the human hand and forearm are found in one or more extant non –human primates, it is the combination of such what makes up for the uniqueness[1].
In this article, Thenar and Hypothenar muscles of the hands will be discussed.
Description[edit | edit source]
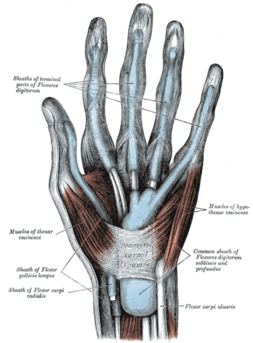
When the human hand is viewed from the palmar side, 2 'fleshy' mounds can be noted[2].
- Thenar eminence - fleshy part at the base of the thumb, made of 3 muscles which control the thumb movements.
- Hypothenar eminence - fleshy part at the base of the fifth digit (little finger), made of 4 muscles which contract to manifest motion through the little finger.
The muscles of the thenar and the hypothenar eminence along with the addcutor compartment make up the intrinsic muscles of the hands as their origin and insertion is within the carpal and metacarpal bones, ligaments, and fascia of the hand. They help with fine motor movements of the hands.[3]
The extrinsic muscles of the hand originate outside the hand, commonly the forearm, and insert into hand structures.
Thenar Eminence (TE) Muscles[edit | edit source]
The muscles of the TE are -[3]
- Opponens Pollicis the largest of the 3 muscles
Origin - at the tubercle of the trapezium
Insertion - lateral margin of the metacarpal of the thumb
Nerve - recurrent branch of the median nerve.
Artery - Superficial palmar arch from the radial artery
Function - perform opposition by flexing and medially rotating the metacarpal on the axis of the trapezium.
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis positioned anteriorly to the opponens pollicis
Origin - tubercles of the scaphoid and trapezium
Insertion - lateral aspect of the proximal phalanx of the thumb.
Nerve - recurrent branch of the median nerve.
Artery - Superficial palmar arch from the radial artery
Function - primary muscle providing opposition. Also leads to abduction of the thumb which is drawing the thumb away from the midline
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis
Origin - tubercle of the trapezium via the deep head, and the associated flexor retinaculum via the superficial head
Insertion - lateral aspect of the proximal phalanx of the thumb.
Nerve - dual innervation with fibers from both the median ( superficial head) and ulnar ( deep head) nerves
Artery - branches of the radial artery; superficial palmar artery, branches of the princeps pollicis artery and radialis indicis artery.
Function - flexion at the metacarpophalangeal and carpometacarpal joints leading to opposition of the thumb and, if continued, produces the medial rotation of thumb.
Hypothenar Eminence (HE) Muscles[edit | edit source]
The HE muscles are[3] -
- Opponens Digiti Minimi
Origin - the hook of hamate and associated transverse carpal ligament
Insertion - lateral aspect of the proximal phalanx of the thumb.
Nerve - Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8, T1)
Artery - Ulnar artery
Function - flex and laterally rotate the 5th metacarpal about the 5th carpometacarpal joint.
- Abductor digiti minimi
Origin - pisiform bone and the tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris
Insertion - the ulnar base of the proximal phalanx of the small finger
Nerve - Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8, T1)
Artery - Ulnar artery
Function - abduction of the 5th finger, as well as flexion of its proximal phalanx
- Flexor digiti minimi brevis
Origin - the hook of hamate and associated transverse carpal ligament
Insertion - the base of the proximal phalanx of the small finger
Nerve - Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8, T1)
Artery - Ulnar artery
Function - flexes the little finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint
- Palmaris brevis
Origin - the transverse carpal ligament
Insertion - on the skin of the medial palm
Nerve - Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8, T1)
Artery - Ulnar artery
Function - tenses the skin of the palm on the ulnar side during a grip action and deepens the hollow of the palm.
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
Assessment[edit | edit source]
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Diogo R, Richmond BG, Wood B. Evolution and homologies of primate and modern human hand and forearm muscles, with notes on thumb movements and tool use. J Hum Evol. 2012;63(1):64-78. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2012.04.001
- ↑ Nguyen J, Duong H. Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Hand Hypothenar Eminence. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; August 13, 2020.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Okwumabua E, Sinkler MA, Bordoni B. Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Hand Muscles. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; July 31, 2020.