Teres Major: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
== '''Function''' == | == '''Function''' == | ||
The teres major (TM) muscle acts as a function as a unit with the latissimus dorsi (LD), where it acts in synergy to extend, adduct and internally rotate the shoulder. eg The TM and LD muscles act in the acceleration and follow through phases of the throwing motion in pitchering in baseball.<ref>Fitzpatrick D, Cagle P, Flatow E. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4861626/ Isolated Teres Major Rupture: A case report with a suggested dedicated imaging protocol and review of the literature]. Journal of radiology case reports. 2016 Apr;10(4):31. Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4861626/<nowiki/>(accessed 13.1.2022)</ref>; assists the latissimus dorsi in eg rock climbing, tennis, wood-chopping, swimming, rowing.<ref name="Travell" /><ref>Ehealth star Teres Major Muscle Available:https://www.ehealthstar.com/anatomy/teres-major-muscle (accessed 13.1.2022)</ref><ref name=":0" /> | The teres major (TM) muscle acts as a function as a unit with the latissimus dorsi (LD), where it acts in synergy to extend, adduct and internally rotate the shoulder. eg The TM and LD muscles act in the acceleration and follow through phases of the throwing motion in pitchering in baseball.<ref>Fitzpatrick D, Cagle P, Flatow E. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4861626/ Isolated Teres Major Rupture: A case report with a suggested dedicated imaging protocol and review of the literature]. Journal of radiology case reports. 2016 Apr;10(4):31. Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4861626/<nowiki/>(accessed 13.1.2022)</ref>; assists the latissimus dorsi in eg rock climbing, tennis, wood-chopping, swimming, rowing.<ref name="Travell">Travell JG, Simons DG, Simons LS (1998). Travell and Simons' Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: The Trigger Point Manual, Volume 2: The Upper Half of Body (2nd ed). Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins.</ref><ref name=":1">Ehealth star Teres Major Muscle Available:https://www.ehealthstar.com/anatomy/teres-major-muscle (accessed 13.1.2022)</ref><ref name=":0" /> | ||
This 2.23 minute video is on Teres Major{{#ev:youtube|1Z-A-Cqsw54}} | |||
== Physiotherapy == | |||
Teres Major Tear | |||
[ | Teres major tear is common in sports with frequent shoulder movements: pitching in baseball, rowing, swimming, rock climbing, tennis, golf and water skiing [3]. | ||
= | The main symptom of a teres major tear is a sudden sharp pain in the shoulder, upper arm and armpit [3]. The area near the bottom of the shoulder blade can become swollen.<ref name=":1" /> | ||
=== Palpation<ref name="Biel">Biel A (2005). [https://booksofdiscovery.com/for-instructors/trail-guide-to-the-body/#TGBNEW Trail Guide to the Body] (2nd ed). Boulder, CO: Books of Discovery.</ref> | === Palpation<ref name="Biel">Biel A (2005). [https://booksofdiscovery.com/for-instructors/trail-guide-to-the-body/#TGBNEW Trail Guide to the Body] (2nd ed). Boulder, CO: Books of Discovery.</ref>=== | ||
*With the patient in prone and arm off the side of the table, grasp latissimus dorsi between your fingers and thumb | *With the patient in prone and arm off the side of the table, grasp latissimus dorsi between your fingers and thumb | ||
*Move your fingers and thumb medially to the lateral boarder of the scapula | *Move your fingers and thumb medially to the lateral boarder of the scapula | ||
*Teres major muscle fibers lie medial to the latissimus and attach to the lateral boarder of the scapula | *Teres major muscle fibers lie medial to the latissimus and attach to the lateral boarder of the scapula | ||
*Follow these fibers up towards the axilla where they blend with latissimus dorsi | *Follow these fibers up towards the axilla where they blend with latissimus dorsi | ||
=== Length Tension Testing / Stretching<ref>Sanzo P, MacHutchon M (2015). Length Tension Testing Book 2, Upper Quadrant: A Workbook of Manual Therapy Techniques (2nd ed). Canada: Brush Education.</ref> | === Length Tension Testing / Stretching<ref>Sanzo P, MacHutchon M (2015). Length Tension Testing Book 2, Upper Quadrant: A Workbook of Manual Therapy Techniques (2nd ed). Canada: Brush Education.</ref>=== | ||
*With the patient in supine, flex the patient's shoulder to 180deg with one hand by holding on the forearm | *With the patient in supine, flex the patient's shoulder to 180deg with one hand by holding on the forearm | ||
*Stabilize the scapula along the lateral boarder with the other hand | *Stabilize the scapula along the lateral boarder with the other hand | ||
*With the hand holding the forearm, externally rotate the arm | *With the hand holding the forearm, externally rotate the arm | ||
*Both the moving hand and the hand stabilizing the scapula are used to sense the amount of muscle tension and barrier | *Both the moving hand and the hand stabilizing the scapula are used to sense the amount of muscle tension and barrier | ||
Trigger Point Referral Pattern | |||
TrPs in teres major muscle typically refer pain into the posterior deltoid region and over the long head of the triceps brachii, as well as into the posterior shoulder joint, occasionally into the dorsal aspect of the forearm, and rarely into the scapula or elbow.<ref name="Travell" /> | |||
[[Image:Teres maj trp referral.png|center|630x350px]] | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 02:04, 13 January 2022
Original Editor - Evan Thomas
Top Contributors - Evan Thomas, Lucinda hampton, Joao Costa, Kim Jackson, WikiSysop, 127.0.0.1, Admin, Oyemi Sillo and Naomi O'Reilly
Introduction[edit | edit source]
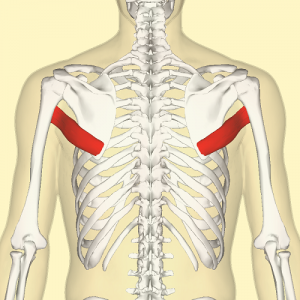
Teres major is a small muscle that runs along the lateral border of the scapula. It is one of the seven scapulohumeral muscles that act around the glenohumeral joint to facilitate shoulder movement[1].[2] It's sometimes called "lat's little helper" because of its synergistic action with the latissimus dorsi.[3]
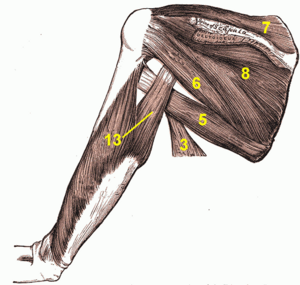
Image 1: Posterior aspect shoulder - 5 teres major; 3 latissimus dorsi; 6 teres minor; 7 supraspinatus; 8 infraspinatus; 13 triceps brachii long head.
| [4] | [5] |
|---|
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Origin: The dorsal surface of the inferior angle of the scapula
Insertion: The medial lip of the intertubercular groove of the humerus[1].
- It is related to the latissimus dorsi muscle which wraps around the lower border of teres major. The tendon of the teres major lies posterior to the tendon of the latissimus dorsi and there is a bursa between them.
Innervation: lower subscapular nerve (C5, C6)
Arterial supply: thoracodorsal branch of the subscapular artery, posterior circumflex humeral artery
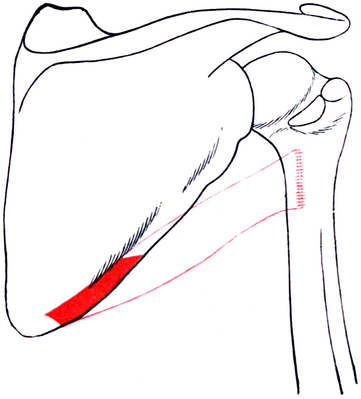
Image 2: Teres major of right side - outline and attachment-areas[1].
Function[edit | edit source]
The teres major (TM) muscle acts as a function as a unit with the latissimus dorsi (LD), where it acts in synergy to extend, adduct and internally rotate the shoulder. eg The TM and LD muscles act in the acceleration and follow through phases of the throwing motion in pitchering in baseball.[6]; assists the latissimus dorsi in eg rock climbing, tennis, wood-chopping, swimming, rowing.[7][8][1]
This 2.23 minute video is on Teres Major
Physiotherapy[edit | edit source]
Teres Major Tear
Teres major tear is common in sports with frequent shoulder movements: pitching in baseball, rowing, swimming, rock climbing, tennis, golf and water skiing [3].
The main symptom of a teres major tear is a sudden sharp pain in the shoulder, upper arm and armpit [3]. The area near the bottom of the shoulder blade can become swollen.[8]
Palpation[3][edit | edit source]
- With the patient in prone and arm off the side of the table, grasp latissimus dorsi between your fingers and thumb
- Move your fingers and thumb medially to the lateral boarder of the scapula
- Teres major muscle fibers lie medial to the latissimus and attach to the lateral boarder of the scapula
- Follow these fibers up towards the axilla where they blend with latissimus dorsi
Length Tension Testing / Stretching[9][edit | edit source]
- With the patient in supine, flex the patient's shoulder to 180deg with one hand by holding on the forearm
- Stabilize the scapula along the lateral boarder with the other hand
- With the hand holding the forearm, externally rotate the arm
- Both the moving hand and the hand stabilizing the scapula are used to sense the amount of muscle tension and barrier
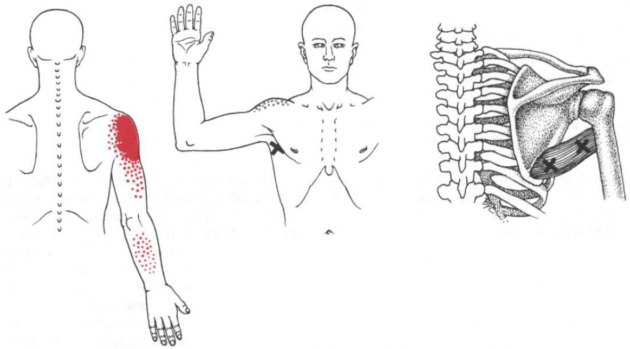
Trigger Point Referral Pattern
TrPs in teres major muscle typically refer pain into the posterior deltoid region and over the long head of the triceps brachii, as well as into the posterior shoulder joint, occasionally into the dorsal aspect of the forearm, and rarely into the scapula or elbow.[7]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Radiopedia Teres Major Available: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/teres-major-muscle(accessed 13.1.2022)
- ↑ http://www.gustrength.com/muscles:teres-major-location-actions-and-trigger-points
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Biel A (2005). Trail Guide to the Body (2nd ed). Boulder, CO: Books of Discovery.
- ↑ http://www.primalonlinelearning.com/cedaandp/muscular_system/muscles_of_the_lower_limb.aspx#bicepsfemoris
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Teres_major_muscle
- ↑ Fitzpatrick D, Cagle P, Flatow E. Isolated Teres Major Rupture: A case report with a suggested dedicated imaging protocol and review of the literature. Journal of radiology case reports. 2016 Apr;10(4):31. Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4861626/(accessed 13.1.2022)
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Travell JG, Simons DG, Simons LS (1998). Travell and Simons' Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: The Trigger Point Manual, Volume 2: The Upper Half of Body (2nd ed). Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Ehealth star Teres Major Muscle Available:https://www.ehealthstar.com/anatomy/teres-major-muscle (accessed 13.1.2022)
- ↑ Sanzo P, MacHutchon M (2015). Length Tension Testing Book 2, Upper Quadrant: A Workbook of Manual Therapy Techniques (2nd ed). Canada: Brush Education.