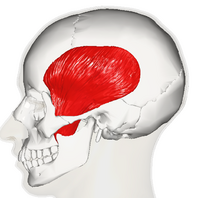
Temporalis
This article or area is currently under construction and may only be partially complete. Please come back soon to see the finished work! (9/01/2024)
Original Editor - Carina Therese Magtibay
Top Contributors - Carina Therese Magtibay
Description[edit | edit source]
The temporalis muscle is one of the four primary muscles of mastication. It is a fan-shaped muscle with anterior fibres that have a vertical orientation, mid fibres have an oblique orientation, and posterior fibres have a more of horizontal orientation. [1]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Temporal bone, specifically the floor of the temporal fossa
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Coronoid process of the mandible
Nerve[edit | edit source]
Central part: deep temporal nerves of the mandibular nerve
Anterior part: branches of the buccal nerve
Posterior part: branches of the masseteric nerve
Artery[edit | edit source]
Function[edit | edit source]
Anterior fibres: Elevates mandible
Posterior fibres: Retracts the mandible
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
Temporalis is used for:[2]
- Direct temporalis tendon injections
- As a landmark for inferior alveolar nerve block anesthesia, third molar extraction, and determining posterior denture flange
- Temporalis tendon transfers in plastic surgery
Assessment[edit | edit source]
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Basit H, Tariq MA, Siccardi MA. Anatomy, head and neck, mastication muscles.
- ↑ Yu SK, Kim TH, Yang KY, Bae CJ, Kim HJ. Morphology of the temporalis muscle focusing on the tendinous attachment onto the coronoid process. Anatomy & Cell Biology. 2021 Sep 1;54(3):308-14.