Supinator
Original Editor - Kate Sampson,
Top Contributors - Kate Sampson, Kim Jackson, Nina Myburg, 127.0.0.1 and Joao Costa;
Description [edit | edit source]
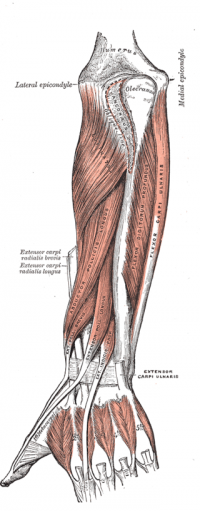
Spinator is located in the posterior compartment of the forearm. It is the prime supinator of the forearm and has a broad origin from the ulna and humerus and extends down to the posterior surface of the proximal third of the radius. [1]
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Origin[edit | edit source]
- Lateral epicondyle of the humerus
- Annular ligament
- Supinator Cest fossa of the ulna [2]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
- Proximal third of the radius on the anterolateral surface, distal to the radial tuberosity. [2]
Nerve supply[edit | edit source]
Supinator is supplied by the posterior interosseous brach of the radial nerve (C5, C6) [3]
Function[edit | edit source]
Supinator supinates the forearm. It causes the distal end of the radius to move anterolaterally around the ulna, causing them to lie paralell
Supinator works with biceps brachii if powerful supination is required. However biceps brachii is unable to function to supinate when the elbow is extended[3]
Assessment[edit | edit source]
Palpation[edit | edit source]
Place the patients arm in extension at the elbow and the forearm in midposition. Actively resist supination and palpate along the posterior part of the proximal third of the radius. [3]
Resources[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Drake RL, Vogl W, Mitchell AWM. Gray's anatomy for students. London: Churchill livingstone. 2005
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Martini FH. Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology. Seventh Edition. Pearson Education Inc, 2006.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Palastanga N, Field D, Soames R. Anatomy and human movement. Structure and function. 5th ed. London: Butterworth Heinemann Elsevier, 2006