Scapular balance angle: Difference between revisions
Ruchi Desai (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Ruchi Desai (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Purpose == | == Purpose == | ||
The condition of altered scapular mechanics and motion is called ‘scapular dyskinesis’, where ‘dys’ indicates alteration and ‘kinesis’ indicates motion. it can be found in healthy individuals or be responsible for a syndrome characterised by several symptoms called SICK. (Scapular malposition, Inferior medial border prominence, Coracoid pain and malposition, and Dyskinesis of scapular motion). | The condition of altered scapular mechanics and motion is called ‘scapular dyskinesis’, where ‘dys’ indicates alteration and ‘kinesis’ indicates motion. it can be found in healthy individuals or be responsible for a syndrome characterised by several symptoms called SICK. (Scapular malposition, Inferior medial border prominence, Coracoid pain and malposition, and Dyskinesis of scapular motion)<ref>López-Vidriero E, López-Vidriero R, Rosa LF, et al. Scapular dyskinesis: related pathology. International Journal of Orthopaedics 2015;2(1):191-5.</ref>. | ||
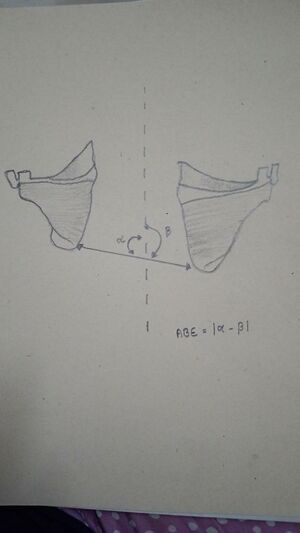
scapular balance angle (SBA) is defined as “the difference between the angles formed by the line joining the 2 inferior angles of the scapula with the vertical line passing through the spine”<ref name=":0">Contreras J, Gil D, de Dios Errázuriz J, Ruiz P, Díaz C, Águila P, et al. Valores de referencia del ángulo de balance escapular en población sana. Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol. 2014;58:24---30.</ref> | scapular balance angle (SBA) is defined as “the difference between the angles formed by the line joining the 2 inferior angles of the scapula with the vertical line passing through the spine”<ref name=":0">Contreras J, Gil D, de Dios Errázuriz J, Ruiz P, Díaz C, Águila P, et al. Valores de referencia del ángulo de balance escapular en población sana. Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol. 2014;58:24---30.</ref> | ||
Revision as of 10:47, 22 April 2023
Purpose[edit | edit source]
The condition of altered scapular mechanics and motion is called ‘scapular dyskinesis’, where ‘dys’ indicates alteration and ‘kinesis’ indicates motion. it can be found in healthy individuals or be responsible for a syndrome characterised by several symptoms called SICK. (Scapular malposition, Inferior medial border prominence, Coracoid pain and malposition, and Dyskinesis of scapular motion)[1].
scapular balance angle (SBA) is defined as “the difference between the angles formed by the line joining the 2 inferior angles of the scapula with the vertical line passing through the spine”[2]
Technique[edit | edit source]
The Scapular balance angle measurement is obtained with the patient standing on both bare feet, with arms, pelvis, and heels together. Next, the inferior angle of the scapula was marked bilaterally and the line connecting these marks and another vertical line between the C7 and T9---T10 spinous processes were drawn. Lastly, the angles formed by the line joining both inferior angles of the scapula with the vertical line running through the spine were measured with the goniometer. The SBA was defined as ‘‘the difference between the angles formed by the line joining the 2 inferior angles of the scapula with the vertical line passing through the spine. SBA greater than 7 ◦ would entail the diagnosis of scapular dyskinesia[2].
Manual measurement of the SBA is reproducible at an intra observer (ICC: 0.87) and inter observer (ICC: 0.84) level.[2]
This criterion presented a sensitivity of 72.73%, specificity of 90.91% and odds ratio of 8[2].
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ López-Vidriero E, López-Vidriero R, Rosa LF, et al. Scapular dyskinesis: related pathology. International Journal of Orthopaedics 2015;2(1):191-5.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Contreras J, Gil D, de Dios Errázuriz J, Ruiz P, Díaz C, Águila P, et al. Valores de referencia del ángulo de balance escapular en población sana. Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol. 2014;58:24---30.