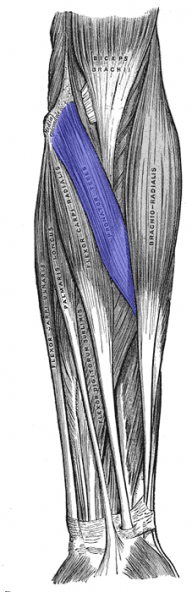
Pronator Teres
Top Contributors - Peter Zatezalo, Ilona Malkauskaite, Joao Costa, Evan Thomas, Kirenga Bamurange Liliane and Ewa Jaraczewska
Description[edit | edit source]
The pronator teres muscle is a long, thin muscle that is located on the underside of the forearm. This muscle has two different muscle heads (otherwise known as places of origins), the humeral head and the ulnar head. [1]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Origin of Humeral Head: Immediately above the medial epicondyle of the humerus, common flexor tendon and deep antibrachial fascia.
Origin of Ulnar Head: Medial side of the coronoid process of the ulna[2].
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Middle of the lateral surface of the radius.[2]
Nerve[edit | edit source]
Median nerve, C6 and C7.[2]
Artery[edit | edit source]
Ulnar artery, anterior recurrent ulnar artery.[3]
Function[edit | edit source]
Pronator teres pronates the forearm and assists in flexion of the elbow joint.[2]
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
Weakness[edit | edit source]
Allows a supinated position of the forearm, and interferes with many everyday functions, such as using a knife or turning the hand downwad in picking up a cup or other object.[2]
Contracture[edit | edit source]
With the forearm held in a position of pronation, interferes markedly with many normal functions of the hand and forearm that require moving from pronation to supination.
Trigger points[edit | edit source]
Assessment[edit | edit source]
Palpation[edit | edit source]
Power[edit | edit source]
Patient is supine or sitting. The elbow should be held against the patients side or be stabilized by the examiner to avoid any shoulder abduction movement.
Test: Pronation of the forearm with the elbow partially flexed. Pressure: At the lower forearm , above the wrist (to avoid twisting the wrist), in the direction of supinating the forearm. [2]
Length[edit | edit source]
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Strengthening[edit | edit source]
Stretching[edit | edit source]
Manual therapy[edit | edit source]
See also[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ https://study.com/academy/lesson/pronator-teres-definition-function-nerve-supply.html (accessed 20 July 2018).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Kendall F, McCreary E, Provance P,Rodgers M,Romani W. Muscles:Testing and function with posture and pain. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2005.
- ↑ https://rad.washington.edu/muscle-atlas/pronator-teres/ (accessed 20 July 2018).