Post Concussion Syndrome Case Study: Following a Fall: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
''Static Balance'' | ''Static Balance'' | ||
''Functional Gait Assessment'' | ''[[Functional Gait Assessment]]'' | ||
''The Headache Impact Test'' | ''The Headache Impact Test'' | ||
| Line 115: | Line 115: | ||
# a, b, and c | # a, b, and c | ||
[[Category:Queen's University Neuromotor Function Project]] | [[Category:Queen's University Neuromotor Function Project]] | ||
<references /> | |||
Revision as of 02:54, 12 May 2020
Abstract[edit | edit source]
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Client Characteristics[edit | edit source]
Examination Findings[edit | edit source]
Subjective[edit | edit source]
History of Present Illness
Past Medical History
Symptoms
Medications
Health Habits
Social History
Current Level of Function
Objective[edit | edit source]
Blood Pressure
Heart Rate
General Observation
Gait
Speech
Upper Limb Scan Exam
Cranial Nerve Testing
Cervical Active ROM
Palpation
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
Static Balance
The Headache Impact Test
Dizziness Handicap Inventory
Vestibular-Ocular Screening (VOMS) Test
Clinical Impression[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis: 36 year-old female presenting with post concussion syndrome two weeks after diagnosis of concussion from fall while ice skating on Jan 2, 2020. Patient has bilateral tightness in upper trapezius and levator scapulae, impaired bilateral single leg stance with eyes closed, and gait impacted by vertical and horizontal head turns. Symptoms are interfering with return to work, driving at night, getting a restful sleep, and grocery shopping. Patient is an excellent candidate for physiotherapy.
Problem List[edit | edit source]
- Disturbance in quality of sleep (unable to sleep straight through the night)
- Inability to drive at night due to light sensitivity
- Experiencing dizziness with dual tasks when walking and impacting performance in ADLs
- Unable to return to work due to symptoms from post concussion syndrome
- Tightness bilaterally in upper fibre traps and levator scapula
- Impaired single leg stance with eyes closed
- Gait impacted with vertical and horizontal head turns
- Headaches impacting health related quality of life
- Headache with all tasks on the VOMS
- Vestibular ocular reflex horizontal and vertical elicits dizziness and nausea along with headache
- Mild dizziness during visual motion sensitivity test
- Increase in pain when performing activities with head movements
Intervention[edit | edit source]
Goals[edit | edit source]
Education[edit | edit source]
Manual Therapy[edit | edit source]
Exercise[edit | edit source]
Balance
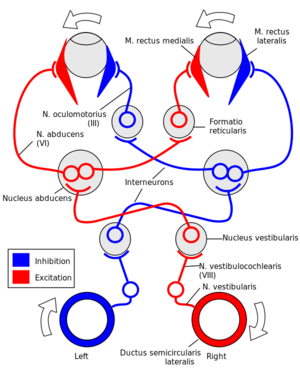 When the head moves to the right, the right semicircular canals detect this movement, sending an excitatory signal to the ipsilateral vestibular nucleus, subsequently to the left abducens nucleus which causes excitation of left lateral rectus and right medial rectus - keeping eye gaze in the same direction as the head moves to the right.[1]
When the head moves to the right, the right semicircular canals detect this movement, sending an excitatory signal to the ipsilateral vestibular nucleus, subsequently to the left abducens nucleus which causes excitation of left lateral rectus and right medial rectus - keeping eye gaze in the same direction as the head moves to the right.[1]
Stretching
Vestibular-ocular Reflex Specific Exercise
Outcome[edit | edit source]
Status Change Post Intervention[edit | edit source]
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
Discharge Plan[edit | edit source]
Discussion[edit | edit source]
Self Study Questions[edit | edit source]
The consequences of concussions can include which of the following?
- Physical
- Cognitive
- Emotional
- All of the above
Post concussion symptoms typically resolve in _________ days in adults.
- 4-6
- 7-10
- 15-20
- 10-12
The vestibular oculomotor screening test (VOMS) test the following?
- Convergence
- Smooth pursuits
- Visual motion sensitivity
- a and b
- a and c
- a, b, and c
- ↑ {{Template:The copyright holder allows this work to be used for non-commercial and/or educational purposes}}






