Pisiform: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(citations added, reference added and info updated) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
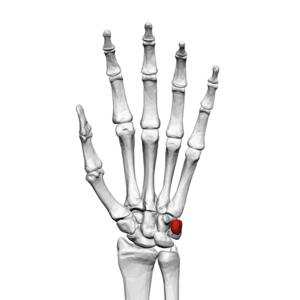
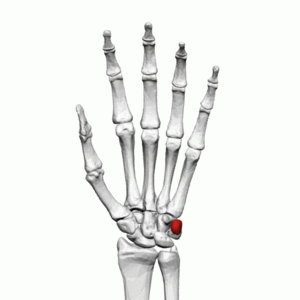
[[File:Pisiform bone (left hand) palmar view.png|thumb|Pisiform bone (Left Hand)]]The pisiform is one of eight | [[File:Pisiform bone (left hand) palmar view.png|thumb|Pisiform bone (Left Hand)]]The pisiform is one of eight carpal bones that forms part of the wrist joint. The name pisiform is derived from the Latin word ''pisum'' which means "pea". It can be felt on the anteromedial side of the [[Wrist and Hand|wrist]]. | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
It is the smallest carpal bone and is a pea-shaped bone<ref name=":0">Tang A. Varacallo M. [https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Matthew_Varacallo/publication/329861188_Anatomy_Shoulder_and_Upper_Limb_Hand_Carpal_Bones/links/5c1d9a11299bf12be391373b/Anatomy-Shoulder-and-Upper-Limb-Hand-Carpal-Bones.pdf Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Hand Carpal Bones]. StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. 2018</ref><ref name=":1">Wadsworth CT. [https://www.jospt.org/doi/pdfplus/10.2519/jospt.1983.4.4.206 Clinical anatomy and mechanics of the wrist and hand]. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy. 1983 Apr 1;4(4):206-16.</ref>. It is considered a sesamoid bone and contributes to wrist stability<ref name=":2">Petrou IG, Savioz-Leissing C, Gray A. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5919795/pdf/10-1055-s-0037-1606206.pdf Traumatic dislocation of the pisiform bone]. Journal of Hand and Microsurgery. 2018 Apr;10(01):037-40.</ref>. The pisiform can be found in the proximal row of carpal bones<ref name=":1" />. | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
The pisiform serves as an attachment for tendons and ligaments.<ref> | The pisiform serves as an attachment for tendons and ligaments<ref name=":0" />. The flexor carpi ulnaris covers the volar surface and the other connections onto the pisiform include the pisohamate ligament, extensor retinaculum, origin of the abductor digiti minimi, pisometacarpal ligament and anterior annular ligament<ref name=":2" />. | ||
The pisiform also forms part of the ulnar canal or Guyon canal<ref name=":3">Ramage JL, Varacallo M. [https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Matthew_Varacallo/publication/329717458_Anatomy_Shoulder_and_Upper_Limb_Hand_Guyon_Canal/links/5c17e48d299bf139c760571c/Anatomy-Shoulder-and-Upper-Limb-Hand-Guyon-Canal.pdf Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Hand Guyon Canal]. StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. 2018</ref>. The Guyon canal is a fibro-osseous tunnel of which the pisiform forms part of the ulnar border<ref name=":3" />. The [[Ulnar Nerve|ulnar nerve]] and ulnar artery pass through this canal<ref name=":3" />. | |||
== Articulations == | == Articulations == | ||
Revision as of 16:21, 26 July 2023
Original Editor - Nina Myburg
Top Contributors - Nina Myburg, Kim Jackson, Nikhil Benhur Abburi, Wendy Snyders and Leana Louw
Description[edit | edit source]
The pisiform is one of eight carpal bones that forms part of the wrist joint. The name pisiform is derived from the Latin word pisum which means "pea". It can be felt on the anteromedial side of the wrist.
Structure[edit | edit source]
It is the smallest carpal bone and is a pea-shaped bone[1][2]. It is considered a sesamoid bone and contributes to wrist stability[3]. The pisiform can be found in the proximal row of carpal bones[2].
Function[edit | edit source]
The pisiform serves as an attachment for tendons and ligaments[1]. The flexor carpi ulnaris covers the volar surface and the other connections onto the pisiform include the pisohamate ligament, extensor retinaculum, origin of the abductor digiti minimi, pisometacarpal ligament and anterior annular ligament[3].
The pisiform also forms part of the ulnar canal or Guyon canal[4]. The Guyon canal is a fibro-osseous tunnel of which the pisiform forms part of the ulnar border[4]. The ulnar nerve and ulnar artery pass through this canal[4].
Articulations[edit | edit source]
The pisiform does not form part of the wrist joint movement, unlike all other carpal bones. It is situated where the ulna and the wrist meet but articulates with the triquetrum only. It lies in a plane anterior and superficially to all other carpal bones.
Muscle attachments[edit | edit source]
- Flexor carpi ulnaris – This is an extrinsic muscle that attaches to the pisiform, hook of hamate and 5th metacarpal. It allows wrist flexion and adduction.
- Abductor digiti minimi – This is a hypothenar muscle. It allows abduction of the 5th finger and flexion of its proximal phalanx.
See Also[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Tang A. Varacallo M. Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Hand Carpal Bones. StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. 2018
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Wadsworth CT. Clinical anatomy and mechanics of the wrist and hand. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy. 1983 Apr 1;4(4):206-16.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Petrou IG, Savioz-Leissing C, Gray A. Traumatic dislocation of the pisiform bone. Journal of Hand and Microsurgery. 2018 Apr;10(01):037-40.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Ramage JL, Varacallo M. Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Hand Guyon Canal. StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. 2018