Parotid Gland: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
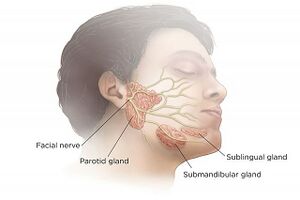
[[File:Parotid.png|right|frameless]]The parotid gland is the largest of three paired major salivary glands. The salivary glands' primary function is to secrete saliva, which plays an important role in lubrication, digestion, immunity, and the overall maintenance of homeostasis within the human body.<ref name=":0">Kochhar A, Larian B, Azizzadeh B. Facial nerve and parotid gland anatomy. Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America. 2016 Apr 1;49(2):273-84.</ref> | [[File:Parotid.png|right|frameless]]The parotid gland is the largest of three paired major salivary glands. The salivary glands' primary function is to secrete saliva, which plays an important role in lubrication, digestion, immunity, and the overall maintenance of homeostasis within the human body.<ref name=":0">Kochhar A, Larian B, Azizzadeh B. Facial nerve and parotid gland anatomy. Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America. 2016 Apr 1;49(2):273-84.</ref> | ||
== Anatomy == | == Anatomy == | ||
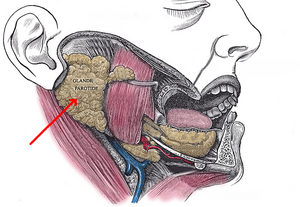
[[File:Parotid Gland.jpg| | The paired parotid glands are situated in the preauricular region and span from the masseter to the posterior surface of the mandible. It is within the [[Triangles of the Neck|submandibular/digastric triangle of the neck]].[[File:Parotid Gland.jpg|frameless|left]] | ||
The | The gland is divided into superficial and deep lobes by the [[Facial Nerve|facial nerve]]: <ref name=":0" /> | ||
* '''Superficial lobe''' - the part of the gland lateral to the nerve and overlies the lateral surface of the [[masseter]] muscle. | |||
* '''Superficial lobe''' - the part of the gland lateral to the nerve and overlies the lateral surface of the masseter muscle. | |||
* '''Deep lobe''' - located medial to the facial nerve and lies between the mastoid process of the temporal bone and the mandibular ramus with deep margins resting in the prestyloid compartment of the parapharyngeal space.<br /> | * '''Deep lobe''' - located medial to the facial nerve and lies between the mastoid process of the temporal bone and the mandibular ramus with deep margins resting in the prestyloid compartment of the parapharyngeal space.<br /> | ||
== Physiology == | == Physiology == | ||
== Vascular Supply == | == Vascular Supply & Lymphatic Drainage == | ||
Vascular supply of parotid gland:<ref name=":0" /> | |||
* Arterial blood supply: External carotid artery | |||
* Venous outflow: retromandibular vein, which is formed by the maxillary and superficial temporal veins. | |||
= | There is a high density of lymph nodes within and around the parotid gland. The parotid is the only salivary gland with 2 nodal layers, both drains into the superficial and deep cervical lymph systems. <ref name=":0" /> | ||
== | == Autonomic Innervation == | ||
Revision as of 11:32, 10 January 2024
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The parotid gland is the largest of three paired major salivary glands. The salivary glands' primary function is to secrete saliva, which plays an important role in lubrication, digestion, immunity, and the overall maintenance of homeostasis within the human body.[1]
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The paired parotid glands are situated in the preauricular region and span from the masseter to the posterior surface of the mandible. It is within the submandibular/digastric triangle of the neck.
The gland is divided into superficial and deep lobes by the facial nerve: [1]
- Superficial lobe - the part of the gland lateral to the nerve and overlies the lateral surface of the masseter muscle.
- Deep lobe - located medial to the facial nerve and lies between the mastoid process of the temporal bone and the mandibular ramus with deep margins resting in the prestyloid compartment of the parapharyngeal space.
Physiology[edit | edit source]
Vascular Supply & Lymphatic Drainage[edit | edit source]
Vascular supply of parotid gland:[1]
- Arterial blood supply: External carotid artery
- Venous outflow: retromandibular vein, which is formed by the maxillary and superficial temporal veins.
There is a high density of lymph nodes within and around the parotid gland. The parotid is the only salivary gland with 2 nodal layers, both drains into the superficial and deep cervical lymph systems. [1]