Navicular stress syndrome: Difference between revisions
Sazia Queyam (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
Sazia Queyam (talk | contribs) m (Added images) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
[[File:Foot accessory navicular CLINICAL ANATOMY 1 anat01.jpg|thumb|Navicular Bone]] | [[File:Foot accessory navicular CLINICAL ANATOMY 1 anat01.jpg|thumb|Navicular Bone]] | ||
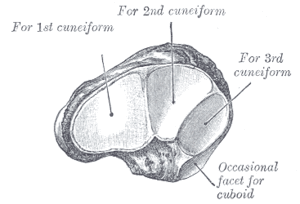
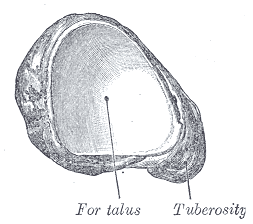
Its name derives from the human bone's resemblance to a small boat. It articulates | Its name '''(''os naviculare pedis; scaphoid bone'')''' derives from the human bone's resemblance to a small boat. It articulates with ''four'' bones: the talus and the three cuneiforms; occasionally with a fifth, the cuboid. | ||
[[File:Navicular Bone Articulation.gif|thumb|The left navicular. Antero-lateral view.]] | |||
[[File:Navicular bone articulation PM.gif|thumb|The left navicular. Postero-medial view.]] | |||
=== CLINICALLY RELEVANT ANATOMY === | |||
Revision as of 19:38, 15 December 2018
-----PAGE IS UNDER CONSTRUCTION----
INTRODUCTION[edit | edit source]
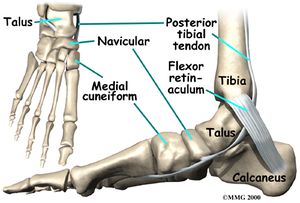
The Navicular is an intermediate tarsal bone on the medial side of the foot[1].
Its name (os naviculare pedis; scaphoid bone) derives from the human bone's resemblance to a small boat. It articulates with four bones: the talus and the three cuneiforms; occasionally with a fifth, the cuboid.
CLINICALLY RELEVANT ANATOMY[edit | edit source]
REFERENCES[edit | edit source]
- ↑ D.Richard, V.Wayne, M. Adam, Gray’s Anatomy for Students. Spain: Elsevier Publishers, 2005