Leptospirosis: Difference between revisions
Shelby Adams (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| | ||
'''Original Editors '''- [[Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems| | '''Original Editors '''- [[Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems|Shelby Adams & Sarah Huttonfrom Bellarmine University's Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems project.]] | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
[[Image:Leptospirosis cycle.jpg|400x400px]]<ref name="15">Villarreal MR. File:Indian6.jpg [Internet]. File:Indian6.jpg. Unknown; [cited 2016Apr4]. Retrieved from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:indian6.jpg)</ref> | [[Image:Leptospirosis cycle.jpg|400x400px]]<ref name="15">Villarreal MR. File:Indian6.jpg [Internet]. File:Indian6.jpg. Unknown; [cited 2016Apr4]. Retrieved from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:indian6.jpg)</ref> | ||
== Prevalence<br> == | == Prevalence<br> == | ||
It is estimated that 100-200 of human Leptospirosis cases are identified annually in the United States. About 50% of these cases occur in Hawaii. Leptospirosis survives well in warm climates, fresh water, and muddy areas.<ref name="17" /> The largest recorded U.S. outbreak occurred in 1998, where 775 people were exposed to this disease, with 110 becoming infected. Incidence in the United States is relatively low, however, leptospirosis is considered to be the most widespread zoonotic disease in the world. Significant increases in incidence have been reported from Peru and Ecuador following heavy rainfall and flooding in the spring of 1998. Thailand has also reported a rapid increase in incidence between 1995 and 2000.<ref name="8" /><br> | It is estimated that 100-200 of human Leptospirosis cases are identified annually in the United States. About 50% of these cases occur in Hawaii. Leptospirosis survives well in warm climates, fresh water, and muddy areas.<ref name="17" /> The largest recorded U.S. outbreak occurred in 1998, where 775 people were exposed to this disease, with 110 becoming infected. Incidence in the United States is relatively low, however, leptospirosis is considered to be the most widespread zoonotic disease in the world. Significant increases in incidence have been reported from Peru and Ecuador following heavy rainfall and flooding in the spring of 1998. Thailand has also reported a rapid increase in incidence between 1995 and 2000.<ref name="8" /><br> | ||
== Characteristics/Clinical Presentation/Examination == | == Characteristics/Clinical Presentation/Examination == | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Pathogenic leptospires are divided in two stages. The first stage of leptospirosis is septicemia or the acute stage. This stage lasts from 3 days to 10 days and presents mostly as headache and myalgia. During this stage leptospires are found in blood in a decreasing number until 15 days after onset of symptoms. Samples must be collected up to 2 days after initiating antibiotherapy to detect leptospires. The second stage or immune stage, usually occurs during the second week after onset of symptoms and lasts 4-30 days. During this stage, the increased antibody titer is correlated to elimination of leptospires from blood.<ref name="2">Cruz LS. Leptospirosis: A Worldwide Resurgent Zoonosis and Important Cause of Acute Renal Failure and Death in Developing Nations. Ethnicity &amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp; Disease. Spring 2009: Volume 19: Pages 37-41.</ref> | Pathogenic leptospires are divided in two stages. The first stage of leptospirosis is septicemia or the acute stage. This stage lasts from 3 days to 10 days and presents mostly as headache and myalgia. During this stage leptospires are found in blood in a decreasing number until 15 days after onset of symptoms. Samples must be collected up to 2 days after initiating antibiotherapy to detect leptospires. The second stage or immune stage, usually occurs during the second week after onset of symptoms and lasts 4-30 days. During this stage, the increased antibody titer is correlated to elimination of leptospires from blood.<ref name="2">Cruz LS. Leptospirosis: A Worldwide Resurgent Zoonosis and Important Cause of Acute Renal Failure and Death in Developing Nations. Ethnicity &amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp; Disease. Spring 2009: Volume 19: Pages 37-41.</ref> | ||
== Prognosis/Associated Co-morbidities == | == Prognosis/Associated Co-morbidities == | ||
The majority of Leptospirosis cases (over 90%) are considered mild.<ref name="5" /> Early diagnosis leads to a faster onset of treatment, which can prevent the patient from developing a more severe level of Leptospirosis. If the patient does reach severe levels, it is considered a medical emergency. Patients most often succumb to this disease because of renal failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome, or a massive hemorrhage; pulmonary involvement is the most common.<ref name="5" /> Patients do survive severe Leptospirosis, especially when there is a quick initiation of supportive therapy and antibiotics.<ref name="7">Haake DA & Levett PN. NCBI [Internet]. [Place unknown]: [Publisher unknown]; 2015 May 25 [cited 2016 March 31]. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4442676/</ref> | The majority of Leptospirosis cases (over 90%) are considered mild.<ref name="5" /> Early diagnosis leads to a faster onset of treatment, which can prevent the patient from developing a more severe level of Leptospirosis. If the patient does reach severe levels, it is considered a medical emergency. Patients most often succumb to this disease because of renal failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome, or a massive hemorrhage; pulmonary involvement is the most common.<ref name="5" /> Patients do survive severe Leptospirosis, especially when there is a quick initiation of supportive therapy and antibiotics.<ref name="7">Haake DA &amp; Levett PN. NCBI [Internet]. [Place unknown]: [Publisher unknown]; 2015 May 25 [cited 2016 March 31]. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4442676/</ref> | ||
<br> | |||
Currently, there are no known documented comorbidities that were found in the research. However, it would seem reasonable to suspect those with a compromised or suppressed immune system would be more susceptible to contracting Leptospirosis. There is also a higher risk based on environment and occupation. For example, farmers, pet shop owners, and survivors of natural disasters are at an increased risk to be exposed to leptospirosis.<ref name="18">World Health Organization [Internet]. [Place unknown]: WPRO; 2012 August 13 [cited 2016 March 31]. Available from: http://www.wpro.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs_13082012_leptospirosis/en/</ref><br> | |||
Currently, there are no known documented comorbidities that were found in the research. However, it would seem reasonable to suspect those with a compromised or suppressed immune system would be more susceptible to contracting Leptospirosis. There is also a higher risk based on environment and occupation. For example, farmers, pet shop owners, and survivors of natural disasters are at an increased risk to be exposed to leptospirosis.<ref name="18">World Health Organization [Internet]. [Place unknown]: WPRO; 2012 August 13 [cited 2016 March 31]. Available from: http://www.wpro.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs_13082012_leptospirosis/en/</ref><br> | |||
== Medications == | == Medications == | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
*Intravenous erythromycin (in penicillin-allergic pregnant women)<ref name="5" /> | *Intravenous erythromycin (in penicillin-allergic pregnant women)<ref name="5" /> | ||
<br> | |||
[[Image:Medicine.png|400x300px]]<ref>epS. File:Medical Drugs for Pharmacy Health Shop of Medicine.png [Internet]. WikiMedia Commons. 2012 [cited 2016Apr10]. Retrieved from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:medical_drugs_for_pharmacy_health_shop_of_medicine.png#filelinks</ref> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
== Diagnostic Tests/Lab Tests/Lab Values == | == Diagnostic Tests/Lab Tests/Lab Values == | ||
| Line 83: | Line 83: | ||
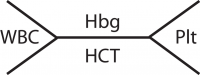
*Complete blood cell (CBC) count | *Complete blood cell (CBC) count | ||
[[Image:Cbc.png|200x150px]]<ref>E. File:Complete blood count CBC diagram.png [Internet]. Wikimedia Commons. 2012 [cited 2016Apr10]. Retrieved from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:complete_blood_count_cbc_diagram.png</ref> | [[Image:Cbc.png|200x150px]]<ref>E. File:Complete blood count CBC diagram.png [Internet]. Wikimedia Commons. 2012 [cited 2016Apr10]. Retrieved from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:complete_blood_count_cbc_diagram.png</ref> | ||
*Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rates and peripheral leukocytosis with left shift noted | *Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rates and peripheral leukocytosis with left shift noted | ||
| Line 122: | Line 122: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
== Etiology/Causes == | == Etiology/Causes == | ||
| Line 132: | Line 132: | ||
<span style="line-height: 1.5em; font-size: 13.28px;">[[Image:Mico lepto.jpg|350x300px]] <ref name="4">Ewing DEP. Public Domain Images [Internet]. Public Domain Images. Unknown; [cited 2016Apr4]. Retrieved from: http://www.public-domain-image.com/free-images/science/microscopy-images/leptospirosis-leptospira-spp/leptospira-bacteria-are-visible-at-right-dieterle-silver-stain</ref></span> | <span style="line-height: 1.5em; font-size: 13.28px;">[[Image:Mico lepto.jpg|350x300px]] <ref name="4">Ewing DEP. Public Domain Images [Internet]. Public Domain Images. Unknown; [cited 2016Apr4]. Retrieved from: http://www.public-domain-image.com/free-images/science/microscopy-images/leptospirosis-leptospira-spp/leptospira-bacteria-are-visible-at-right-dieterle-silver-stain</ref></span> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
== Systemic Involvement == | == Systemic Involvement == | ||
After infection, common systems affected by Leptospirosis are: kidney, nervous, hepatic, musculoskeletal, visual, cardiopulmonary, and integumentary. Common systemic issues that are associated with Leptospirosis in early stages include: myalgia, red eye, abdominal pain, and in some cases skin rash. In later stages it has systemic issues such as: liver damage, causing jaundice, kidney failure, meningitis, encephalitis, and bleeding in the lungs.<ref name="8" /> | After infection, common systems affected by Leptospirosis are: kidney, nervous, hepatic, musculoskeletal, visual, cardiopulmonary, and integumentary. Common systemic issues that are associated with Leptospirosis in early stages include: myalgia, red eye, abdominal pain, and in some cases skin rash. In later stages it has systemic issues such as: liver damage, causing jaundice, kidney failure, meningitis, encephalitis, and bleeding in the lungs.<ref name="8" /> | ||
== Medical Management (current best evidence) == | == Medical Management (current best evidence) == | ||
Antibiotic therapy should be given early in the course of disease.<ref name="8" /> Some sources state that in mild cases, it is typically unnecessary to treat with antibiotics since it is self-limited and can resolve without medical attention. However oral antibiotics can shorten the course of illness and can reduce and shorten urinary excretion of leptospirosis thereby decreasing chance of further spreading the infection.<ref name="5" /> In persons with more severe symptoms IV antibiotics may be needed. There is an incubation period of 7 days, with a range of 2-29 days.<ref name="8" /> In cases of widespread epidemics Prophylaxis can be used.<ref name="5" /> Patients with severe cases of leptospirosis also require additional therapy and careful management of renal, hepatic, hematologic, and central nervous system complications. If renal failure begins, starting early hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis may reduce mortality by nearly two-thirds. Other supportive care can include inotropic agents, diuretics, or ophthalmic drops.<ref name="5" /><br> | Antibiotic therapy should be given early in the course of disease.<ref name="8" /> Some sources state that in mild cases, it is typically unnecessary to treat with antibiotics since it is self-limited and can resolve without medical attention. However oral antibiotics can shorten the course of illness and can reduce and shorten urinary excretion of leptospirosis thereby decreasing chance of further spreading the infection.<ref name="5" /> In persons with more severe symptoms IV antibiotics may be needed. There is an incubation period of 7 days, with a range of 2-29 days.<ref name="8" /> In cases of widespread epidemics Prophylaxis can be used.<ref name="5" /> Patients with severe cases of leptospirosis also require additional therapy and careful management of renal, hepatic, hematologic, and central nervous system complications. If renal failure begins, starting early hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis may reduce mortality by nearly two-thirds. Other supportive care can include inotropic agents, diuretics, or ophthalmic drops.<ref name="5" /><br> | ||
== Physical Therapy Management (current best evidence) == | == Physical Therapy Management (current best evidence) == | ||
At this time there is no physical therapy management for Leptospirosis. If a Physical Therapist suspects signs and symptoms of Leptospirosis refer to a physician immediately for testing. However, once the patient gets proper treatment/medication, and they are in the recovery phases, a physical therapist can help with the associated sequelae. For example, common complications of Leptospirosis include kidney damage/failure, meningitis, liver failure, and respiratory distress.<ref name="13">Right Diagnosis [Internet]. [Place unknown]: HealthGrades Inc.; [last updated 2015 August 13: cited 2016 April 04]. Available from: http://www.rightdiagnosis.com/l/leptospirosis/complic.htm</ref><sup> </sup>These conditions come with complications that physical therapists can help treat. For instance, meningitis can cause stiffness of the trunk and neck. Physical therapists can intervene to help maintain mobility in the neck/trunk. It is important to understand that while physical therapists cannot affect the bacteria infection itself, they can affect the associated sequelae.<br><br> | At this time there is no physical therapy management for Leptospirosis. If a Physical Therapist suspects signs and symptoms of Leptospirosis refer to a physician immediately for testing. However, once the patient gets proper treatment/medication, and they are in the recovery phases, a physical therapist can help with the associated sequelae. For example, common complications of Leptospirosis include kidney damage/failure, meningitis, liver failure, and respiratory distress.<ref name="13">Right Diagnosis [Internet]. [Place unknown]: HealthGrades Inc.; [last updated 2015 August 13: cited 2016 April 04]. Available from: http://www.rightdiagnosis.com/l/leptospirosis/complic.htm</ref><sup> </sup>These conditions come with complications that physical therapists can help treat. For instance, meningitis can cause stiffness of the trunk and neck. Physical therapists can intervene to help maintain mobility in the neck/trunk. It is important to understand that while physical therapists cannot affect the bacteria infection itself, they can affect the associated sequelae.<br><br> | ||
== Differential Diagnosis<br> == | == Differential Diagnosis<br> == | ||
| Line 170: | Line 170: | ||
<sup></sup> | <sup></sup> | ||
<sup></sup><sup></sup><sup>[http://search.proquest.com/docview/1178911054/21B15BB1F3314C12PQ/6?accountid=6741 Combined involvement of muscle, nerve, and myoneural junction following Leptospira infection<ref name="12">Pradhan, S. Tandon, R. Kiskshore, J. Proquest [Internet]. Mumbai: [Publisher unknown]; 2012 September-October [last updated 2014 March 08: cited 2016 April 04]. Available from: http://search.proquest.com.libproxy.bellarmine.edu/docview/1178911054/21B15BB1F3314C12PQ/6?accountid=6741</ref>]</sup> | <sup></sup><sup></sup><sup>[http://search.proquest.com/docview/1178911054/21B15BB1F3314C12PQ/6?accountid=6741 Combined involvement of muscle, nerve, and myoneural junction following Leptospira infection<ref name="12">Pradhan, S. Tandon, R. Kiskshore, J. Proquest [Internet]. Mumbai: [Publisher unknown]; 2012 September-October [last updated 2014 March 08: cited 2016 April 04]. Available from: http://search.proquest.com.libproxy.bellarmine.edu/docview/1178911054/21B15BB1F3314C12PQ/6?accountid=6741</ref>]</sup> | ||
== Resources <br> == | == Resources <br> == | ||
| Line 176: | Line 176: | ||
[http://www.cdc.gov/leptospirosis/resources/ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention]<br> | [http://www.cdc.gov/leptospirosis/resources/ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention]<br> | ||
[http://www.who.int/topics/leptospirosis/en/ World Health Organization] | [http://www.who.int/topics/leptospirosis/en/ World Health Organization] | ||
== Recent Related Research (from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ Pubmed]) == | == Recent Related Research (from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ Pubmed]) == | ||
<div class="researchbox"> | <div class="researchbox"> | ||
<rss>http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=1pcFRJI0caoDrdgCYH28m_fYxs01IF7wxNFmky6dMjRlMb_gUD|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10</rss> | <rss>http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=1pcFRJI0caoDrdgCYH28m_fYxs01IF7wxNFmky6dMjRlMb_gUD|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10</rss> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 16:50, 13 April 2016
Original Editors - Shelby Adams & Sarah Huttonfrom Bellarmine University's Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems project.
Top Contributors - Shelby Adams, Sarah Hutton, 127.0.0.1, Elaine Lonnemann, Evan Thomas, WikiSysop, Kim Jackson and Nupur Smit Shah
Definition[edit | edit source]
Definition/DescriptioLeptospirosis is a bacterial disease that affects humans & animals. It is caused by the bacteria genus Leptospira. This bacteria is spread through urine of infected animals, which can get into water or soil and can survive for weeks to months. The most common method of transmission is through direct contact with infected urine or other bodily fluids such as saliva, or contaminated water, soil, or food.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title This bacteria can enter the body through skin or mucous membranes (eyes, nose, mouth) especially if skin is broken with cut or scratch.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title Outbreaks are most commonly associated with contaminated water such as flood waters. Person to person transmission of this bacteria is rareCite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title. Both wild and domestic animals can be carriers of this bacteria, this includes but is not limited to: cattle, pigs, horses, dogs, rodents, and wild animals. Animals may show no signs or symptoms of the disease. In humans it can cause a wide range of symptoms, which can easily be mistaken for others diseases. Some infected individuals may be asymptomatic. Without treatment, Leptospirosis can lead to serious problems such as: kidney damage, meningitis, liver failure, respiratory distress, or even death. Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
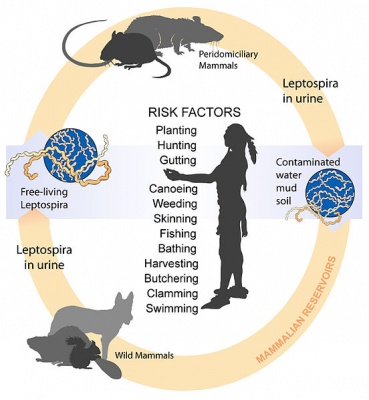 Cite error: Invalid
Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Prevalence
[edit | edit source]
It is estimated that 100-200 of human Leptospirosis cases are identified annually in the United States. About 50% of these cases occur in Hawaii. Leptospirosis survives well in warm climates, fresh water, and muddy areas.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title The largest recorded U.S. outbreak occurred in 1998, where 775 people were exposed to this disease, with 110 becoming infected. Incidence in the United States is relatively low, however, leptospirosis is considered to be the most widespread zoonotic disease in the world. Significant increases in incidence have been reported from Peru and Ecuador following heavy rainfall and flooding in the spring of 1998. Thailand has also reported a rapid increase in incidence between 1995 and 2000.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Characteristics/Clinical Presentation/Examination[edit | edit source]
Clinical presentation of leptospirosis is variable depending on the stage of the disease. Time between a person’s exposure to the source and showing these signs and symptoms can be 2 days to 4 weeks. Early state signs and symptoms include high fever, headache, chills, muscle aches, vomiting, jaundice, red eyes, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and rash. The second stage presents with more severe symptoms such as kidney or liver failure, meningitis, hemorrhage, hepatomegaly, pulmonary hemorrhage, and ARDS. This phase is also known as Weil’s disease. Case fatality for leptospirosis is 1-5%.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
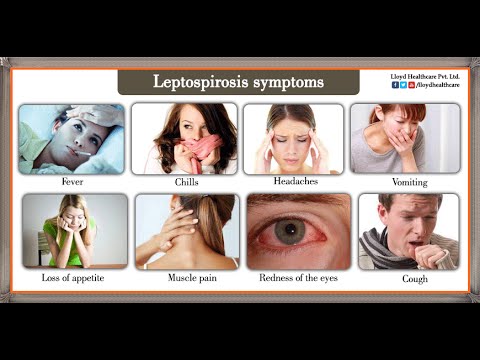 Cite error: Invalid
Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Pathogenic leptospires are divided in two stages. The first stage of leptospirosis is septicemia or the acute stage. This stage lasts from 3 days to 10 days and presents mostly as headache and myalgia. During this stage leptospires are found in blood in a decreasing number until 15 days after onset of symptoms. Samples must be collected up to 2 days after initiating antibiotherapy to detect leptospires. The second stage or immune stage, usually occurs during the second week after onset of symptoms and lasts 4-30 days. During this stage, the increased antibody titer is correlated to elimination of leptospires from blood.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Prognosis/Associated Co-morbidities[edit | edit source]
The majority of Leptospirosis cases (over 90%) are considered mild.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title Early diagnosis leads to a faster onset of treatment, which can prevent the patient from developing a more severe level of Leptospirosis. If the patient does reach severe levels, it is considered a medical emergency. Patients most often succumb to this disease because of renal failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome, or a massive hemorrhage; pulmonary involvement is the most common.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title Patients do survive severe Leptospirosis, especially when there is a quick initiation of supportive therapy and antibiotics.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Currently, there are no known documented comorbidities that were found in the research. However, it would seem reasonable to suspect those with a compromised or suppressed immune system would be more susceptible to contracting Leptospirosis. There is also a higher risk based on environment and occupation. For example, farmers, pet shop owners, and survivors of natural disasters are at an increased risk to be exposed to leptospirosis.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Medications[edit | edit source]
If antibiotic treatment is needed it may include the following:
- Doxycycline
- Ampicillin or amoxicillin
- Azithromycin or clarithromycin
- Fluoroquinolone such as ciprofloxacin or levofloxacinCite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Antibiotics for leptospirosis requiring hospitalization include the following:
- Intravenous penicillin G
- Intravenous third-generation cephalosporins (cefotaxime and ceftriaxone)
- Intravenous ampicillin or amoxicillin (second-line agents)
- Intravenous erythromycin (in penicillin-allergic pregnant women)Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Diagnostic Tests/Lab Tests/Lab Values[edit | edit source]
Laboratory studies used to screen for the diagnosis of leptospirosis include the following:
- Leptospira immunoglobulin M (IgM) ELISA or IgM/immunoglobulin G (IgG) enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay (ELISA), including rapid diagnostic kits usable in the field
- Real-time DNA polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of blood, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleCite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Laboratory studies used to confirm the diagnosis of leptospirosis include the following:
- Microscopic agglutination testing (MAT; criterion standard for serologic identification of leptospires, available at reference laboratories)
- Single titer ≥1:200 or 4-fold rise in serum drawn between the first and fourth week of illness is considered diagnostic
- DNA PCR of blood, urine, CSF, tissue
- Culture of leptospires from body fluids or tissue (criterion standard, but requires specific media and several weeks’ incubation, thus usually limited to reference laboratory)Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleCite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Studies to determine the extent of organ involvement and severity of complications may include the following, depending on the clinical presentation:
- Complete blood cell (CBC) count
- Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rates and peripheral leukocytosis with left shift noted
- Anemia due to hemorrhages
- Lowered platelet count
- Blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine may be elevated
- Serum Creatine Kinase levels elevated in patients with muscular involvement
- Increased coagulation times
- Increased Serum bilirubin levels due to obstructive disease due to capillaritis in liver
- CSF analysis:
- To exclude causes of bacterial meningitis
-Polymorphonuclear leukocytes in early leptospirosis
-Monocytes in later
-Protein may be normal or elevated
- Chest radiography
- Biliary tract ultrasonography
- Electrocardiography (ECG)
-Congestive Heart Failure
-Cardiogenic Shock
- Urinalysis may show:
-Protein
-Erythrocytes
-Hyaline casts
-Granular castsCite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive titleCite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Etiology/Causes[edit | edit source]
Leptospires are from a group of bacteria called spirochetes. There are two families of leptospiraceae: leptospira and leptonema. Leptospira have over 200 known pathogenic serologic variants, and 21 species of identified.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title 13 of these 21 species have been detected in human cases. The appearance and motility of leptospires varies with the nature of the medium in which they are grown.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title Certain geographic regions contain specific leptospiral serovars and species, the serologic characterization of an isolate is not an absolute predictor of its species designation. Leptospires are long, thin, motile spirochetes. They may be free-living or associated with animal hosts and survive well in fresh water, soil, and mud in tropical areas.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title Despite the different types of leptospires, there is no documentation of different presentations.
Once the leptospire enters the host, the pathogen reproduces. The survival rate of the leptospires depend on the immune system of the host, a suppressed immune system means the leptospires are more likely to survive and infect the host.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title Once they survive initial contact, they need to spread throughout the body. So, they migrate to the bloodstream and lymphatic system to spread quickly.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title Once in the bloodstream and lymphatic system, the bacteria continues to spread and affect the other systems of the body.
 Cite error: Invalid
Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Systemic Involvement[edit | edit source]
After infection, common systems affected by Leptospirosis are: kidney, nervous, hepatic, musculoskeletal, visual, cardiopulmonary, and integumentary. Common systemic issues that are associated with Leptospirosis in early stages include: myalgia, red eye, abdominal pain, and in some cases skin rash. In later stages it has systemic issues such as: liver damage, causing jaundice, kidney failure, meningitis, encephalitis, and bleeding in the lungs.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Medical Management (current best evidence)[edit | edit source]
Antibiotic therapy should be given early in the course of disease.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title Some sources state that in mild cases, it is typically unnecessary to treat with antibiotics since it is self-limited and can resolve without medical attention. However oral antibiotics can shorten the course of illness and can reduce and shorten urinary excretion of leptospirosis thereby decreasing chance of further spreading the infection.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title In persons with more severe symptoms IV antibiotics may be needed. There is an incubation period of 7 days, with a range of 2-29 days.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title In cases of widespread epidemics Prophylaxis can be used.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title Patients with severe cases of leptospirosis also require additional therapy and careful management of renal, hepatic, hematologic, and central nervous system complications. If renal failure begins, starting early hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis may reduce mortality by nearly two-thirds. Other supportive care can include inotropic agents, diuretics, or ophthalmic drops.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Physical Therapy Management (current best evidence)[edit | edit source]
At this time there is no physical therapy management for Leptospirosis. If a Physical Therapist suspects signs and symptoms of Leptospirosis refer to a physician immediately for testing. However, once the patient gets proper treatment/medication, and they are in the recovery phases, a physical therapist can help with the associated sequelae. For example, common complications of Leptospirosis include kidney damage/failure, meningitis, liver failure, and respiratory distress.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title These conditions come with complications that physical therapists can help treat. For instance, meningitis can cause stiffness of the trunk and neck. Physical therapists can intervene to help maintain mobility in the neck/trunk. It is important to understand that while physical therapists cannot affect the bacteria infection itself, they can affect the associated sequelae.
Differential Diagnosis
[edit | edit source]
There are many other diagnoses that present in a similar manner to Leptospirosis, especially in the early phases. The early phases present with flu-like symptoms; such as muscle aches, fever, and chills. In more severe cases, Leptospirosis may be misdiagnosed as meningitis, sepsis, or dengue.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title This is why patient history is crucial; as a clinician, it is important to ask about travel history and exposure to animals. These two points can provide information needed to get Leptospirosis on the radar.
The following conditions may also present like LeptospirosisCite error: Invalid <ref> tag; name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title:
- Brucellosis
- Chikungunya
- Enteroviral Infections
- Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome
- Hepatitis A
- Malaria
- Q Fever
- Rickettsial Infection
- Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers
- Measles
- Rubella
Case Reports/ Case Studies[edit | edit source]
Resources
[edit | edit source]
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Failed to load RSS feed from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=1pcFRJI0caoDrdgCYH28m_fYxs01IF7wxNFmky6dMjRlMb_gUD|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10: Error parsing XML for RSS
References[edit | edit source]
see adding references tutorial.
- ↑ epS. File:Medical Drugs for Pharmacy Health Shop of Medicine.png [Internet]. WikiMedia Commons. 2012 [cited 2016Apr10]. Retrieved from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:medical_drugs_for_pharmacy_health_shop_of_medicine.png#filelinks
- ↑ E. File:Complete blood count CBC diagram.png [Internet]. Wikimedia Commons. 2012 [cited 2016Apr10]. Retrieved from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:complete_blood_count_cbc_diagram.png