Lateral Plantar Nerve: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User: Elena Ferrero Vila|User Name]] '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | <div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User: Elena Ferrero Vila|User Name]] '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | ||
{{Template:Nerves}} | {{Template:Nerves}} | ||
__INDEX__ | |||
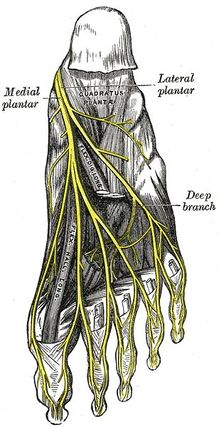
[[File:Gray833 (1).jpg|thumb|427x427px]]The lateral plantar nerve or the external plantar nerve ''(latin: nervus plantaris lateralis)'' is a terminal branch of the [[Tibial Nerve|tibial nerve]]. The lateral plantar nerve enters the sole of the [[Foot Anatomy|foot]] by passing deep to the proximal insertion of the abductor hallucis muscle. It continues across the sole anteriorly and laterally, between the digitorum brevis and quadratus plantae muscles inervating both of this muscles. Then, close to the 5th metatarsal head it will divide into the deep and superficial branches: | [[File:Gray833 (1).jpg|thumb|427x427px]]The lateral plantar nerve or the external plantar nerve ''(latin: nervus plantaris lateralis)'' is a terminal branch of the [[Tibial Nerve|tibial nerve]]. The lateral plantar nerve enters the sole of the [[Foot Anatomy|foot]] by passing deep to the proximal insertion of the abductor hallucis muscle. It continues across the sole anteriorly and laterally, between the digitorum brevis and quadratus plantae muscles inervating both of this muscles. Then, close to the 5th metatarsal head it will divide into the deep and superficial branches: | ||
* Superficial branch of the lateral plantar nerve splits into: | * Superficial branch of the lateral plantar nerve splits into: | ||
Revision as of 19:12, 20 September 2020
Original Editor - name here
Top Contributors - Elena Ferrero Vila, Leana Louw and Wendy Snyders
Description[edit source]
Root[edit source]
Branches[edit source]
Function[edit source]
Motor[edit source]
Sensory[edit source]
Clinical relevance[edit source]
Assessment[edit source]
Treatment[edit source]
Resources[edit source]
References[edit source]
The lateral plantar nerve or the external plantar nerve (latin: nervus plantaris lateralis) is a terminal branch of the tibial nerve. The lateral plantar nerve enters the sole of the foot by passing deep to the proximal insertion of the abductor hallucis muscle. It continues across the sole anteriorly and laterally, between the digitorum brevis and quadratus plantae muscles inervating both of this muscles. Then, close to the 5th metatarsal head it will divide into the deep and superficial branches:
- Superficial branch of the lateral plantar nerve splits into:
- The lateral proper plantar digital nerve, which inervates the skin of the lateral aspects of the 5th toe and a branch for inervating the flexor digiti quinti brevis.
- The common plantar digital nerve which communicates with the 3rd common branch of the medial plantar nerve and divides into the two proper digital nerves of the 4th and 5th toe.
- Deep branch of the lateral plantar nerve; is a motor branch and it inervates from the second to the fourth lumbricales, the adductor hallucis, and supplies all the interossei (appart from the ones on the 4th metatarsal space inervated by the superficial branch)
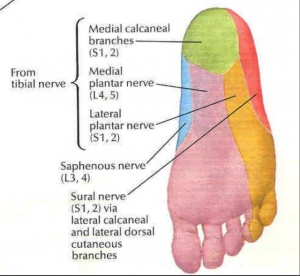
It provides sensory information from the two anterior thirds of the lateral sole of the foot, as well as the plantar surfaces for the 5th and half of the 4th toe.
It is also a motor nerve which inervates all the intrinsic muscles from the sole with the exception of abductor hallucis, flexor digitorum brevis, the flexor hallucis brevis and the first lumbrical muscle inervated by the medial plantar nerve.
The clinical relevance, the entrapement of the lateral plantar nerve is usually due to the compression of nerve branches at the inner heel. It has symptoms similar to plantar fasciitis and tarsal tunnel syndrome including pain at the inside of the ankle and heel. The lateral plantar nerve can become trapped, or compressed between the abductor hallucis muscle and the quadratus planus muscle along the inside of the foot.
It can also be a Baxter's Neuropathy, the first branch of the lateral plantar nerve (Baxter's nerve) travesses laterally ro inervate the abductor digiti quinti muscle. Baxter's nerve can be entrapped at the abductor hallucis muscle.The Baxter's Neuropatht is a painful condition that can lead to chronic heel pain. The symptoms are usually pain at the medial aspect of the heel that exponentially increases with loadberaing. The discomfort could feel as an ache, as burning pain or numbness
Assessment: