Kemp Test: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
{{#ev:youtube|4wIFZmxiSTg|300}}<ref>Palmer Health Sciences Library. Kemp's Test. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=75bVhJ-sBcI [last accessed 22/10/2020]</ref> | {{#ev:youtube|4wIFZmxiSTg|300}}<ref>Palmer Health Sciences Library. Kemp's Test. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=75bVhJ-sBcI [last accessed 22/10/2020]</ref> | ||
== Evidence == | == Evidence == | ||
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
Revision as of 02:22, 23 October 2020
Original Editor - Rachael Lowe
Top Contributors - Aminat Abolade, Admin, Rachael Lowe, Kim Jackson, Lucinda hampton, WikiSysop, 127.0.0.1, Tony Lowe, Roel De Groef, Aarti Sareen, Oyemi Sillo, Kai A. Sigel, Wanda van Niekerk and Jess Bell
This article is currently under review and may not be up to date. Please come back soon to see the finished work! (23/10/2020)
Description[edit | edit source]
The Kemp test or lumbar quadrant test is used to assess the lumbar spine facet joints. It is a provocative test to detect pain, which can be local, referred or radicular.[1]
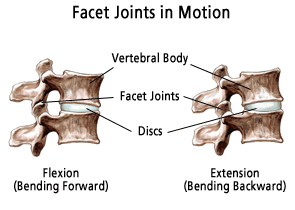
Clinically Relevant Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The facet joints (FJ) or zygapophyseal joints play an important role in load transmission. The purpose of these FJ is to stabilize the motion segment in flexion, extension and also restricting axial rotation. They also provide a posterior load-bearing helper.
The lumbar FJ are paired, true synovial joint that comprise the posterolateral articulation between vertebral levels. The orientation of the FJ in a transverse plane varies from the upper level of the lumbar spine to the lower one.
Lumbar FJ contains hyaline cartilage, synovial membrane, fibrous capsule, and a joint space with a potential capacity of 1 to 2 mL. The existence of menisci in the lumbar FJ has been emphasized in numerous publications.[2]
Purpose[edit | edit source]
The purpose of this test is to assess lumbar spine facet joints pain. It uses the patient’s trunk both as a lever to induce tension and as a compressive force. This test is used in differentiation and diagnosis of a lumbar posterior facet syndrome, though it is nonspecific.[3] It is a provocation test to detect pain. Local pain suggest a facet cause, while radiating pain into the leg is more suggestive of nerve root irritation. Especially if the pain is below the knee.[4]
Technique[edit | edit source]
The lumbar quadrant test may be performed with the patient either in the seated or standing position.
Standing position:
1. Patient is standing before the therapist.
2. The therapist fixes the opposite ilium from the side being tested with one hand.
3. The other hand grabs the shoulder from the patient and leads the patient to extension, ipsilateral side bending and psilateral rotation (3D extension movement).
4. Hold this position for three seconds.
Seated position:
1. The patient seated with arms crossed over the chest.
2. One hand of the therapist stabilize the patient’s lumbosacral region on the side to be tested.
3. The other arm controls the patient’s upper body movement.
4. The patient is passively directed into flexion, rotation, lateral flexion, and finally extension.
5. Depending on the patient’s response, axial compression may be applied in the fully extended and rotated position to increase stress on the posterior joints.
The test is positive when the patient reports pain, numbness or tingling in the area of the back or lower extremities. The pain is located on the side being tested.[1][6][3] Local pain suggests a facet cause, while radiating pain into the leg is more suggestive of nerve root irritation. Especially if the pain is below the knee.[4]
The seated position is more preferable because the therapist has more control over the patient’s positioning and there is less muscle activation.[3][4]
Evidence[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
http://videos.rehabstudents.com/lumbar-quadrant-test/
http://ptjournal.apta.org/content/85/2/120
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Steve Jensen; back pain – clinical assessment; Australian Family Physician Vol. 33, No. 6, June 2004 (level of evidence:D)
- ↑ Kalichman L, Hunter DJ. Lumbar facet joint osteoarthritis: a review. InSeminars in arthritis and rheumatism 2007 Oct 1 (Vol. 37, No. 2, pp. 69-80). WB Saunders.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Craig E. Morris; Low back syndromes; McGraw-hill professional; 2005 (Level of evidence: D)
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Souza TA. Differential diagnosis and management for the chiropractor: protocols and algorithms. Jones & Bartlett Publishers; 2009 Oct 7.
- ↑ Rocky Bains. Kemp's Test. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tBVhHpxF3ZQ [last accessed 22/10/2020]
- ↑ Lyle MA, Manes S, McGuinness M, Ziaei S, Iversen MD. Relationship of physical examination findings and self-reported symptom severity and physical function in patients with degenerative lumbar conditions. Physical therapy. 2005 Feb 1;85(2):120-33.
- ↑ Palmer Health Sciences Library. Kemp's Test. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=75bVhJ-sBcI [last accessed 22/10/2020]