Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) is a condition in which injury to the brain of neonate occur following deprivation of oxygen supply to brain. <ref>Greco P, Nencini G, Piva I, Scioscia M, Volta CA, Spadaro S, Neri M, Bonaccorsi G, Greco F, Cocco I, Sorrentino F. [https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13760-020-01308-3 Pathophysiology of hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy: a review of the past and a view on the future.] Acta Neurologica Belgica. 2020 Apr;120(2):277-88.</ref>It is the common cause of neonate mortality and developmental psychomotor disorders in the pediatric worldwide.<ref name=":0">Kleuskens DG, Goncalves Costa F, Annink KV, van den Hoogen A, Alderliesten T, Groenendaal F, Benders MJ, Dudink J. [https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fped.2021.631258/full Pathophysiology of cerebral hyperperfusion in term neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: A systematic review for future research.] Frontiers in pediatrics. 2021:17.</ref> | Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) is a condition in which injury to the brain of neonate occur following deprivation of oxygen supply to brain. <ref>Greco P, Nencini G, Piva I, Scioscia M, Volta CA, Spadaro S, Neri M, Bonaccorsi G, Greco F, Cocco I, Sorrentino F. [https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13760-020-01308-3 Pathophysiology of hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy: a review of the past and a view on the future.] Acta Neurologica Belgica. 2020 Apr;120(2):277-88.</ref>It is the common cause of neonate mortality and developmental psychomotor disorders in the pediatric worldwide.<ref name=":0">Kleuskens DG, Goncalves Costa F, Annink KV, van den Hoogen A, Alderliesten T, Groenendaal F, Benders MJ, Dudink J. [https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fped.2021.631258/full Pathophysiology of cerebral hyperperfusion in term neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: A systematic review for future research.] Frontiers in pediatrics. 2021:17.</ref> | ||
Attributing neonatal encephalopathy to perinatal hypoxic–ischemic injury requires combinations of parameters indicative of metabolic acidosis in the first postnatal hours with low cord pH (<7.0), base deficit of over 12, and evidence of a need for respiratory support also starting in the first minutes, with low Apgar scores at and beyond 5 min. | |||
== Epidemiology == | == Epidemiology == | ||
| Line 12: | Line 14: | ||
* The incidence of HIE is ~1–8 per 1,000 live births in technically advanced countries and is up to 26 per 1,000 live births in less developed countries.<ref name=":0" /> | * The incidence of HIE is ~1–8 per 1,000 live births in technically advanced countries and is up to 26 per 1,000 live births in less developed countries.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
* | * | ||
== Etiology == | |||
Maternal factor | |||
Fetal factor | |||
Delivery condition | |||
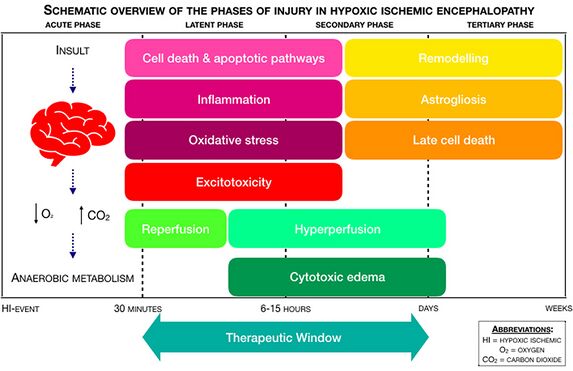
== Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process == | == Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process == | ||
| Line 17: | Line 26: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
== Clinical Presentation | == Clinical Presentation/manifestation == | ||
Fetal asphysia: | |||
Meconium stained liquor: | |||
APGAR score | |||
Seizure | |||
tone | |||
<br> | |||
== Classification of HIE == | |||
There are three classification system of HIE | |||
* Levene | |||
* Sarnat and Sarnat staging | |||
* Thompson scoring | |||
== Complication == | |||
== Outcome measures == | |||
== Investigations == | |||
* EEG | |||
* Cranial ultrasound | |||
* CT scan | |||
* MRI | |||
* | |||
== Management / Interventions == | |||
=== Medical Management === | |||
* Therapeutic Cerebral Hypothermia | |||
** Hypothermia is a proven effective treatment of HIE and can improve survival and long-term prognosis of children. It has been suggested that hypothermia treatment of HIE should start within 6 hours after hypoxia ischemia. | |||
* Medications | |||
=== Physiotherapy Management === | |||
== Prognosis == | |||
Depending upon the severity of brain damage and medical treatment, usally: | |||
Mild or moderate cases could be cured completely, but severe cases represent poor prognosis with high mortality or cerebral complications such as mental retardation and cerebral palsy. | |||
Overall mortality: 20% | |||
Overall incidence of sequel: 30% | |||
Mild: 100% good prognosis | |||
Moderate: 80% normal | |||
Severe: 50 5 death , 50% sequel | |||
Presence of seizure increases chance of cerebral palsy by 50-70 times | |||
== | == Prevention == | ||
* Better obstetric care | |||
* Skilled resuscitation teams and neonatal facilities | |||
== Differential Diagnosis | == Differential Diagnosis == | ||
<br> | |||
== Resources <br> == | == Resources <br> == | ||
Revision as of 05:51, 17 February 2022
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) is a condition in which injury to the brain of neonate occur following deprivation of oxygen supply to brain. [1]It is the common cause of neonate mortality and developmental psychomotor disorders in the pediatric worldwide.[2]
Attributing neonatal encephalopathy to perinatal hypoxic–ischemic injury requires combinations of parameters indicative of metabolic acidosis in the first postnatal hours with low cord pH (<7.0), base deficit of over 12, and evidence of a need for respiratory support also starting in the first minutes, with low Apgar scores at and beyond 5 min.
Epidemiology[edit | edit source]
- The incidence of HIE is ~1–8 per 1,000 live births in technically advanced countries and is up to 26 per 1,000 live births in less developed countries.[2]
Etiology[edit | edit source]
Maternal factor
Fetal factor
Delivery condition
Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process[edit | edit source]
Clinical Presentation/manifestation[edit | edit source]
Fetal asphysia:
Meconium stained liquor:
APGAR score
Seizure
tone
Classification of HIE[edit | edit source]
There are three classification system of HIE
- Levene
- Sarnat and Sarnat staging
- Thompson scoring
Complication[edit | edit source]
Outcome measures[edit | edit source]
Investigations[edit | edit source]
- EEG
- Cranial ultrasound
- CT scan
- MRI
Management / Interventions[edit | edit source]
Medical Management[edit | edit source]
- Therapeutic Cerebral Hypothermia
- Hypothermia is a proven effective treatment of HIE and can improve survival and long-term prognosis of children. It has been suggested that hypothermia treatment of HIE should start within 6 hours after hypoxia ischemia.
- Medications
Physiotherapy Management[edit | edit source]
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
Depending upon the severity of brain damage and medical treatment, usally:
Mild or moderate cases could be cured completely, but severe cases represent poor prognosis with high mortality or cerebral complications such as mental retardation and cerebral palsy.
Overall mortality: 20%
Overall incidence of sequel: 30%
Mild: 100% good prognosis
Moderate: 80% normal
Severe: 50 5 death , 50% sequel
Presence of seizure increases chance of cerebral palsy by 50-70 times
Prevention[edit | edit source]
- Better obstetric care
- Skilled resuscitation teams and neonatal facilities
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Resources
[edit | edit source]
add appropriate resources here
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Greco P, Nencini G, Piva I, Scioscia M, Volta CA, Spadaro S, Neri M, Bonaccorsi G, Greco F, Cocco I, Sorrentino F. Pathophysiology of hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy: a review of the past and a view on the future. Acta Neurologica Belgica. 2020 Apr;120(2):277-88.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Kleuskens DG, Goncalves Costa F, Annink KV, van den Hoogen A, Alderliesten T, Groenendaal F, Benders MJ, Dudink J. Pathophysiology of cerebral hyperperfusion in term neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: A systematic review for future research. Frontiers in pediatrics. 2021:17.