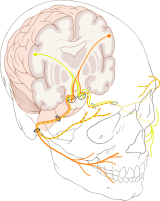
Facial Nerve
Original Editor - Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page.
Lead Editors
Description[edit | edit source]
The Facial Nerve is the seventh Cranial Nerve.
It is composed of approximately 10,000 neurons, 7,000 of which are myelinated and innervate the nerves of facial expression.
The remaining 3,000 fibres are somatosensory and secretomotor, and are known as the Nervus Intermedius.
Movements Produced[edit | edit source]
All movements of facial expression, including:
Smile, close eyes, pucker lips, wrinkle nose, raise eyebrows, frown.
Muscles[edit | edit source]
General Course[edit | edit source]
The facial nerve has six named segments:
- intracranial (cisternal) segment
- meatal segment (internal auditory canal) - 8mm - zero branches
- labyrinthine segment (IAC to geniculate ganglion) - 3-4mm - 3 branches (from geniculate ganglion)
- tympanic segment (from geniculate ganglion to pyramidal eminence) - 8-11mm - zero branches
- mastoid segment (from pyramidal eminence to stylomastoid foramen) - 8-14mm - 3 branches
- extratemporal segment (from stylomastoid foramen to division into major branches) 15-20mm - 9 branches
Intracranial (cisternal) segment
The nerve emerges immediately beneath the pons, lateral to the abducens nerve and medial to the vestibulocochlear nerve and is joined by the nervus intermedius, which has emerged lateral to the main trunk. Together the two travel through the cerebellopontine angle to the internal acoustic meatus
Meatal segment
Having been joined by the nervus intermedius, they are located in the superior upper quadrant, above the falciform crest and anterior to Bill's bar.
Labyrinthine segment
As the facial nerve and nervus intermedius pass through the anterior superior quadrant of theinternal acoustic meatus it enters the Fallopian canal, passing anterolaterally between and superior to the cochlea (anterior) and vestibule (posterior), and then runs back posteriorly at thegeniculate ganglion (where the nervus intermedius joins the facial nerve and where fibers for taste synapse). It is here that three branches originate:
- greater superficial petrosal nerve
- lesser petrosal nerve
- external petrosal nerve
The labyrinthine segment is the shortest only measuring 3-4 mm. It is also the narrowest and the most susceptible to vascular compromise.
Tympanic segment
As the nerve passes posteriorly from the geniculate ganglion it becomes the tympanic segment (8-11 mm in length) and is immediately beneath the lateral semicircular canal in the medial wall of the middle ear cavity. The nerve passes posterior to the cochleariform process, tensor tympani and oval window. Just distal to the pyramidal eminence the nerve makes a second turn (second genu) passing vertically downwards as the mastoid segment.
The tympanic segment has no branches.
Mastoid segment
The mastoid segment, measuring 8-14mm in length, extends from the second genu to the stylomastoid foramen, through what is confusingly referred to as the fallopian canal. It gives off three branches:
- nerve to stapedius
- chorda tympani - terminal branch of the nervus intermedius carrying both secretomotor fibres to the submandibular gland and sublingual gland and taste to the anterior two thirds of the tongue
- nerve from the auricular branch of the vagus nerve (CN X) - pain fibers to the posterior part of the external acoustic meatus
Extratemporal segment
As the nerve exits the stylomastoid foramen, it gives off a sensory branch that supplies part of the external acoustic meatus and tympanic membrane.
It then passes between the posterior belly of the digastric muscle and the stylohyoid muscle and enters the parotid gland. Lying between the deep and superficial lobes of the gland the nerve divides into to main branches at the pes anserinus (Latin = "duck foot") - a superior temporofacial and and inferior cervicofacial branches.
From the anterior border of the gland, five branches emerge: temporal, zygomatic, buccal, mandibular (marginal) and cervical.
Open Packed Position[edit | edit source]
Other Important Information[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Extension:RSS -- Error: Not a valid URL: Feed goes here!!|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.
= Facial Nerve =