Critical Illness Polyneuropathy (CIP)
Original Editor - Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page.
Lead Editors
Definition
[edit | edit source]
Critical Illness Polyneuropathy (CIP) is one of three classifications of Intensive care -unit acquired weakness (ICUAW), the others being Critical Illness Myopathy (CIM) and Critical Illness Neuromyopathy (CINM)[1]. ICUAW is defined as 'a clinically detected weakness in critically ill patients in whom there is no plausable aetiology other than critical illness' [2]
Clinically Relevant Anatomy
[edit | edit source]
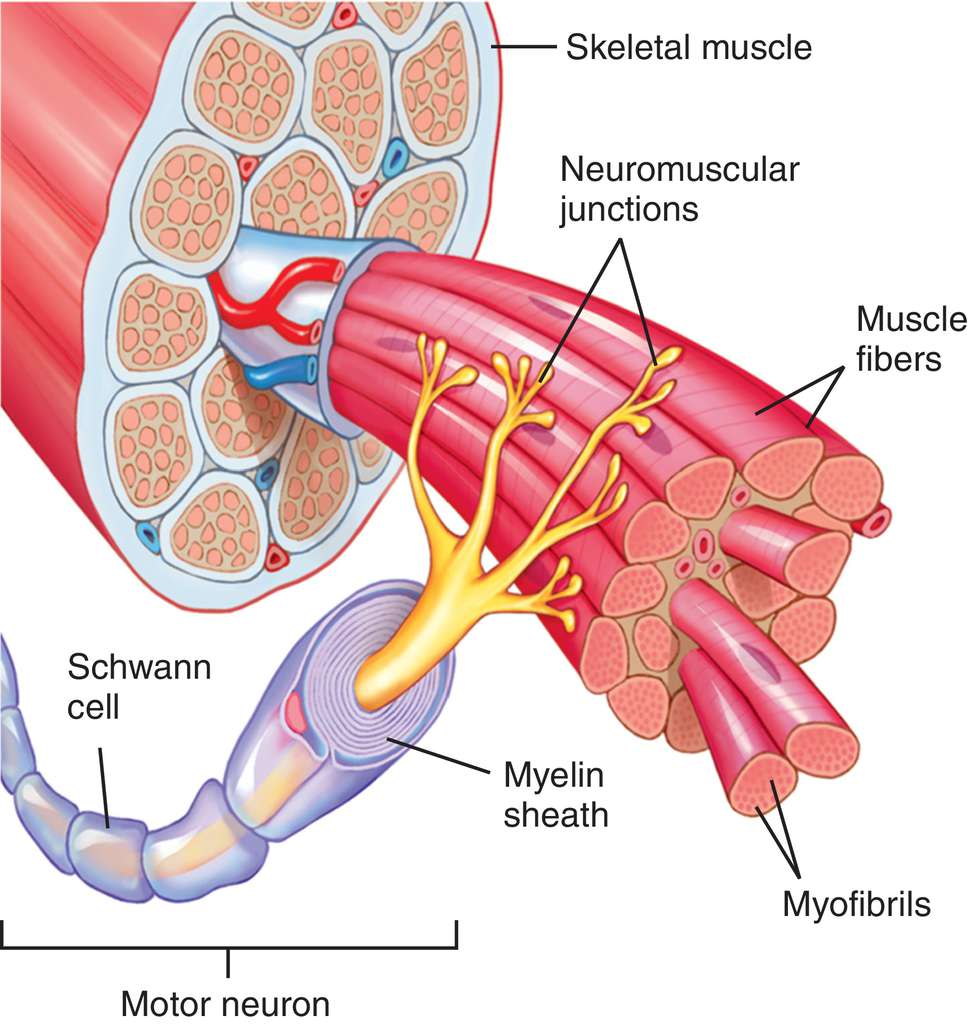
The peripheral nervous systems describe the nerves that reside outside of the brain and the spinal cord. There are two main types of peripheral nerves; sensory and motor that arise from the dorsal and ventral aspects of the spinal cord respectively.
Extrafusual muscle fibres are innervated by a single alpha motor neurone and as there are more muscle fibres than there are neurones, a single alpha motor neurone will synapse onto many fibres across a wide area - this is known as a motor unit. Not only does this ensure an even contractile force across the muscle, it also ensures that should one or more alpha motor neurones be damaged the effect upon the contractile function of the muscle is reduced [3]
When an action potential passes down the axonal branches, all the muscle fibres are stimulated at virtually the same moment and a twitch of force is produced. Within a single muscle there are a wide range of motor unit sizes, the number and type of the muscle fibres are determined by the size and the function of the motoneuron that innervates them. Muscles that require fine motor control usually have a large number of small motor units while muscles that need to create significant force, such as the gastrocnemius, has a small number of large motor units that innervate many muscle fibre
Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process
[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the mechanism of injury and/or pathology of the condition
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the clinical presentation of the condition
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to diagnostic tests for the condition
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
add links to outcome measures here (see Outcome Measures Database)
Management / Interventions
[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to management approaches to the condition
Differential Diagnosis
[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the differential diagnosis of this condition
Resources
[edit | edit source]
add appropriate resources here
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Appleton, R. and Kinsella, J., 2012. Intensive care unit-acquired weakness. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia, Critical Care and Pain, 12(2), pp.62-66.
- ↑ Stevens, R.D., Marshall, S.A., Cornblath, D.R., Hoke, A., Needham, D.M., de Jonghe, B., Ali, N.A. and Sharshar, T., 2009. A framework for diagnosing and classifying intensive care unit-acquired weakness. Critical care medicine, 37(10), pp.S299-S308.
- ↑ Purves D, Augustine GJ, Fitzpatrick D, et al., editors. Neuroscience. 2nd edition. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates; 2001. The Motor Unit.Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK10874/