Brachial Plexus Injury: Difference between revisions
Aarti Sareen (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Aarti Sareen (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Clinical Anatomy == | == Clinical Anatomy == | ||
The plexus consists of roots, trunks, divisions,cords and branches. | The plexus consists of roots, trunks, divisions,cords and branches. | ||
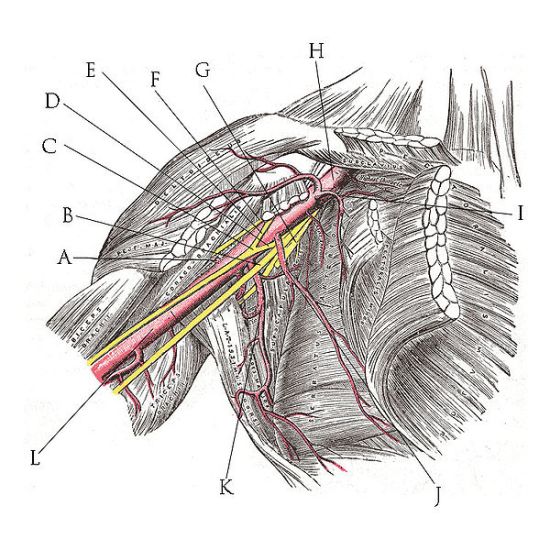
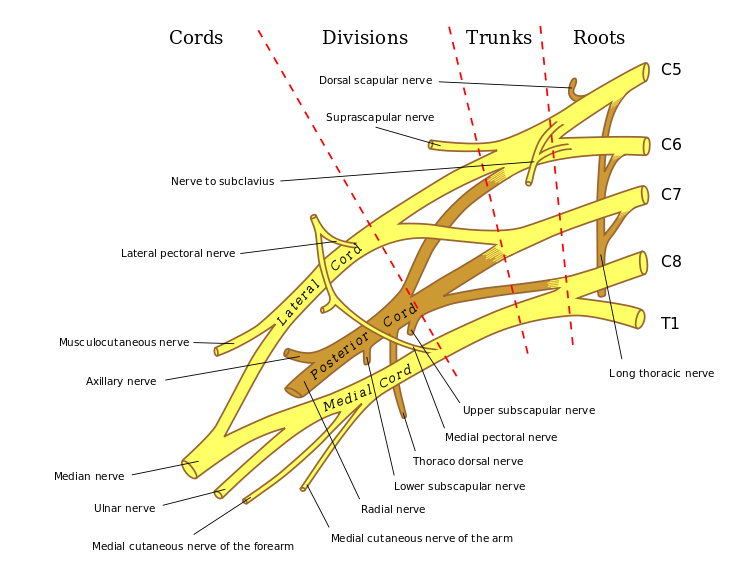
ROOTS: These are consititued by the anterior primary rami of spinal nerves C5,6,7,8 and T1 with contributions from the anterior primary rami of C4 and T2. The origin of the plexus may shift one segment either upward or downward resulting in a PRE FIXED PLEUS or POST FIXED PLEXUS respectively. Ina prefixed plexus, the contribution by C4 is large and in that from T2 is often absent. In a post fixed plexus, the contribution by T1 is large, T2 is always present, C4 is absent, and C5 is reduced in size. The roots join to form trunks as follows: | ROOTS: These are consititued by the anterior primary rami of spinal nerves C5,6,7,8 and T1 with contributions from the anterior primary rami of C4 and T2. The origin of the plexus may shift one segment either upward or downward resulting in a PRE FIXED PLEUS or POST FIXED PLEXUS respectively. Ina prefixed plexus, the contribution by C4 is large and in that from T2 is often absent. In a post fixed plexus, the contribution by T1 is large, T2 is always present, C4 is absent, and C5 is reduced in size. The roots join to form trunks as follows: | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:Brachial-plexus-2.png]]<br> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 13:34, 22 December 2013
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Brachial plexus is the network of nerves which runs through the cervical spine, neck,axilla and then into arm or it is a network of nerves passing through the cervico-axillary canal to reach axilla and innervates brachium (upper arm), antebrachium (forearm) and hand.It is a somatic nerve plexus formed by intercommunications among the ventral rami (roots) of the lower 4 cervical nerves (C5-C8) and the first thoracic nerve (T1).
Clinical Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The plexus consists of roots, trunks, divisions,cords and branches.
ROOTS: These are consititued by the anterior primary rami of spinal nerves C5,6,7,8 and T1 with contributions from the anterior primary rami of C4 and T2. The origin of the plexus may shift one segment either upward or downward resulting in a PRE FIXED PLEUS or POST FIXED PLEXUS respectively. Ina prefixed plexus, the contribution by C4 is large and in that from T2 is often absent. In a post fixed plexus, the contribution by T1 is large, T2 is always present, C4 is absent, and C5 is reduced in size. The roots join to form trunks as follows: