Back Muscles: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
There are three major groups of back muscles: | There are three major groups of back muscles: | ||
# Superficial: attached to the shoulder girdle | # Superficial: attached to the [[shoulder]] girdle | ||
# Intermediate: attached to the posterior thorax | # Intermediate: attached to the posterior [[Thoracic Anatomy|thorax]] | ||
# Deep: attached to the vertebral column, also known as the intrinsic muscle group<ref>Geeky Medics back Muscles Available: https://geekymedics.com/superficial-back-muscles/<nowiki/>(accessed 24.1.2022)</ref> | # Deep: attached to the vertebral column, also known as the intrinsic muscle group<ref>Geeky Medics back Muscles Available: https://geekymedics.com/superficial-back-muscles/<nowiki/>(accessed 24.1.2022)</ref> | ||
These groups serve to allow: flexion/extension, rotation, and side bending of the back; movement of the limbs; locomotor function; and assistance in the respiratory effort<ref name=":0">Modes RJ, Fahrioglu SL. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539746/ Anatomy, Back]. StatPearls [Internet]. 2021 Mar 27. Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539746/ (accessed 24.1.2022)</ref>. | These groups serve to allow: flexion/extension, rotation, and side bending of the back; movement of the limbs; locomotor function; and assistance in the respiratory effort<ref name=":0">Modes RJ, Fahrioglu SL. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539746/ Anatomy, Back]. StatPearls [Internet]. 2021 Mar 27. Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539746/ (accessed 24.1.2022)</ref>. | ||
Additional terminology | Additional terminology | ||
| Line 19: | Line 17: | ||
# The superficial and intermediate muscle groups (or extrinsic muscles) are also called immigrant muscles, since they actually represent muscles of the upper limb that have migrated to the back during fetal development. | # The superficial and intermediate muscle groups (or extrinsic muscles) are also called immigrant muscles, since they actually represent muscles of the upper limb that have migrated to the back during fetal development. | ||
# The deep/intrinsic back muscles, are also called true back muscles. They are located deep to the extrinsic muscles, being separated from them by the thoracolumbar fascia<ref name=":1">Ken Hub [https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/overview-of-back-muscles Over view of Back Muscles] Available: https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/overview-of-back-muscles<nowiki/>(accessed 24.1.2022)</ref>. | # The deep/intrinsic back muscles, are also called true back muscles. They are located deep to the extrinsic muscles, being separated from them by the thoracolumbar fascia<ref name=":1">Ken Hub [https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/overview-of-back-muscles Over view of Back Muscles] Available: https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/overview-of-back-muscles<nowiki/>(accessed 24.1.2022)</ref>. | ||
Generalized back pain is a common presenting symptom for patients, the etiology of the pain commonly traces to a strain of the skeletal muscle. | |||
== Superficial Group == | == Superficial Group == | ||
| Line 37: | Line 36: | ||
* [[Serratus posterior|Serratus posterior inferior]] | * [[Serratus posterior|Serratus posterior inferior]] | ||
These muscles run from the vertebral column to the ribcage, and assist with elevating and depressing the ribs. | These muscles run from the vertebral column to the ribcage, and assist with elevating and depressing the ribs. | ||
Both serratus posterior superior and inferior are thought to have a role as accessory [[Muscles of Respiration|muscles for respiration]]<ref>teach me anatomy [https://teachmeanatomy.info/back/muscles/intermediate/ The intermediate back Muscles] Available:https://teachmeanatomy.info/back/muscles/intermediate/ (accessed 24,1,2022)</ref>. | |||
== Deep/Intrinsic Muscles == | == Deep/Intrinsic Muscles == | ||
[[File:Muscles of the back erector spinae group Primal.png|thumb|200x200px|Erector spinae group]] | [[File:Muscles of the back erector spinae group Primal.png|thumb|200x200px|Erector spinae group]] | ||
[[File:Muscles of the back transversospinales group and segmental muscles Primal.png|thumb|200x200px|Transversospinales group and segmental muscles]] | [[File:Muscles of the back transversospinales group and segmental muscles Primal.png|thumb|200x200px|Transversospinales group and segmental muscles]] | ||
These muscles are responsible for the motion of the axial skeleton. The main movements are flexion/extension, side bending, and rotation. This group further subdivides into several categories in the back and neck. The main muscle groups in the intrinsic muscle group are the erector spinae group and the transversospinalis group. | These muscles are responsible for the motion of the axial skeleton. The main movements are flexion/extension, side bending, and rotation. These muscles collectively work to help movements of the vertebral column (flexion/extension, side bending, and rotation) and to also control posture. | ||
This group further subdivides into several categories in the back and neck. The main muscle groups in the intrinsic muscle group are the | |||
The erector spinae group (medially to laterally) consisting of: | |||
Iliocostalis | |||
Longissimus | |||
Spinalis | |||
The muscle group is bilateral on either side of the vertebral column and when both sides are engaged function as the primary extensor of the back.[3] Unilaterally they assist with lateral bending and rotation of the spine.[3] | |||
Transversospinalis group (deep to the erector spinae group) consisting of, from superficial to deep: | |||
Semispinalis | |||
Multifidus | |||
Rotatores | |||
Like the erector spinae group, the transversospinalis group is located bilaterally on the vertebral column between the transverse processes and the spinous processes. These muscles assist in bending the back posteriorly when contracted bilaterally. When unilateral contraction occurs, they are responsible for assisting with lateral bending and rotation<ref name=":0" />. | |||
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
Revision as of 04:13, 24 January 2022
Original Editor - Lucinda hampton
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton and Kim Jackson
Introduction[edit | edit source]
There are three major groups of back muscles:
- Superficial: attached to the shoulder girdle
- Intermediate: attached to the posterior thorax
- Deep: attached to the vertebral column, also known as the intrinsic muscle group[1]
These groups serve to allow: flexion/extension, rotation, and side bending of the back; movement of the limbs; locomotor function; and assistance in the respiratory effort[2].
Additional terminology
- The superficial and intermediate muscle groups (or extrinsic muscles) are also called immigrant muscles, since they actually represent muscles of the upper limb that have migrated to the back during fetal development.
- The deep/intrinsic back muscles, are also called true back muscles. They are located deep to the extrinsic muscles, being separated from them by the thoracolumbar fascia[3].
Generalized back pain is a common presenting symptom for patients, the etiology of the pain commonly traces to a strain of the skeletal muscle.
Superficial Group[edit | edit source]
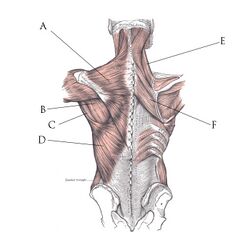
The first category is the superficial back muscles. These muscles are located posteriorly on the back, whose function is to move the scapula.. The superficial muscles include[2]:
- Trapezius
- Latissimus dorsi
- Levator scapulae
- Rhomboids
Each of the muscles in this group are fairly large and superficial and correctly locating any one of them by palpation is easily accomplished[4].
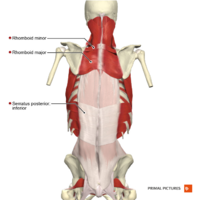
Intermediate Muscles[edit | edit source]
The intermediate group contains two muscles:
These muscles run from the vertebral column to the ribcage, and assist with elevating and depressing the ribs.
Both serratus posterior superior and inferior are thought to have a role as accessory muscles for respiration[5].
Deep/Intrinsic Muscles[edit | edit source]
These muscles are responsible for the motion of the axial skeleton. The main movements are flexion/extension, side bending, and rotation. These muscles collectively work to help movements of the vertebral column (flexion/extension, side bending, and rotation) and to also control posture.
This group further subdivides into several categories in the back and neck. The main muscle groups in the intrinsic muscle group are the
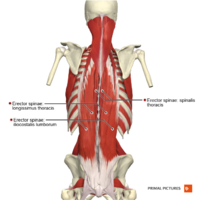
The erector spinae group (medially to laterally) consisting of:
Iliocostalis
Longissimus
Spinalis
The muscle group is bilateral on either side of the vertebral column and when both sides are engaged function as the primary extensor of the back.[3] Unilaterally they assist with lateral bending and rotation of the spine.[3]
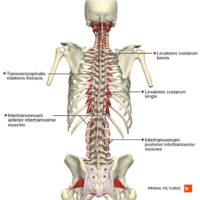
Transversospinalis group (deep to the erector spinae group) consisting of, from superficial to deep:
Semispinalis
Multifidus
Rotatores
Like the erector spinae group, the transversospinalis group is located bilaterally on the vertebral column between the transverse processes and the spinous processes. These muscles assist in bending the back posteriorly when contracted bilaterally. When unilateral contraction occurs, they are responsible for assisting with lateral bending and rotation[2].
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Geeky Medics back Muscles Available: https://geekymedics.com/superficial-back-muscles/(accessed 24.1.2022)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Modes RJ, Fahrioglu SL. Anatomy, Back. StatPearls [Internet]. 2021 Mar 27. Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539746/ (accessed 24.1.2022)
- ↑ Ken Hub Over view of Back Muscles Available: https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/overview-of-back-muscles(accessed 24.1.2022)
- ↑ Very well health Superficial Anatomy of the Back and Core Available:https://www.verywellhealth.com/superficial-definition-anatomy-297236 (accessed 24.11.2022)
- ↑ teach me anatomy The intermediate back Muscles Available:https://teachmeanatomy.info/back/muscles/intermediate/ (accessed 24,1,2022)