Anatomical snuff box: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "'''Description''' The anatomical snuffbox (also known as the radial fossa), is a triangular depression found on the lateral aspect of the dorsum of the hand. It is located a...") |
(Added 3 illustrative pictures,see also,references and resources) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Description''' | '''Description:''' | ||
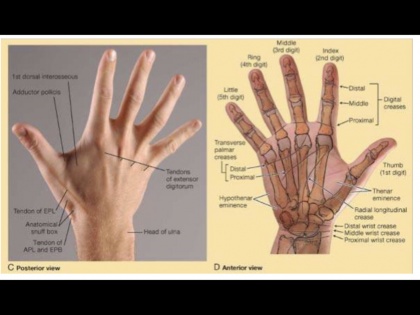
The anatomical snuffbox (also known as the radial fossa), is a triangular depression found on the lateral aspect of the dorsum of the hand. It is located at the level of the carpal bones and best seen when the thumb is abducted. | The anatomical snuffbox (also known as the radial fossa), is a triangular depression found on the lateral aspect of the dorsum of the hand. It is located at the level of the carpal bones and best seen when the thumb is abducted. | ||
In the past, this depression was used to hold snuff (ground tobacco) before inhaling via the nose – hence it was given the name ‘snuffbox’. | In the past, this depression was used to hold snuff (ground tobacco) before inhaling via the nose – hence it was given the name ‘snuffbox’. | ||
[[File:Snuff box3.jpg|left|thumb|420x420px]] | |||
'''Structure/Borders''': | '''Structure/Borders''': | ||
The tendons of the APL and EPB indicate the lateral (anterior) boundary of the anatomical snuff box, and the tendon of the EPL indicates the medial (posterior) boundary of the box. The radial artery crosses the floor of the snuff box, where its pulsations may be felt. The scaphoid and, less distinctly, the trapezium are palpable in the floor of the snuff box. | The tendons of the APL and EPB indicate the lateral (anterior) boundary of the anatomical snuff box, and the tendon of the EPL indicates the medial (posterior) boundary of the box. The radial artery crosses the floor of the snuff box, where its pulsations may be felt. The scaphoid and, less distinctly, the trapezium are palpable in the floor of the snuff box. | ||
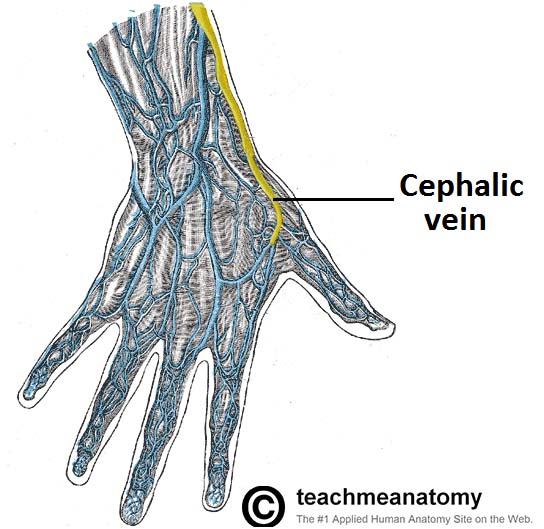
'''Contents''' | '''Contents''' | ||
| Line 21: | Line 23: | ||
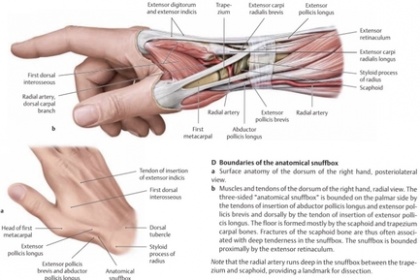
The three muscles acting on the thumb (APL, EPB, and EPL) are deep to the superficial extensors and emerge (“crop out”) from a furrow in the lateral part of the forearm that divides the extensors. Because of this characteristic, they are referred to as outcropping muscles. The tendons of the APL and EPB bound the triangular anatomical snuff box laterally, and the tendon of the EPL bounds it medially. The snuff box is visible as a hollow on the lateral aspect of the wrist when the thumb is extended fully; this draws the APL, EPB, and EPL tendons up and produces a concavity between them. Observe that the: | The three muscles acting on the thumb (APL, EPB, and EPL) are deep to the superficial extensors and emerge (“crop out”) from a furrow in the lateral part of the forearm that divides the extensors. Because of this characteristic, they are referred to as outcropping muscles. The tendons of the APL and EPB bound the triangular anatomical snuff box laterally, and the tendon of the EPL bounds it medially. The snuff box is visible as a hollow on the lateral aspect of the wrist when the thumb is extended fully; this draws the APL, EPB, and EPL tendons up and produces a concavity between them. Observe that the: | ||
Radial artery lies on the floor of the snuff box.
Radial styloid process can be palpated proximally and the base of the first metacarpal can be palpated distally in the snuff box. Scaphoid and trapezium can be felt in the floor of the snuff box between the radial styloid process and the first metacarpal. | Radial artery lies on the floor of the snuff box.
Radial styloid process can be palpated proximally and the base of the first metacarpal can be palpated distally in the snuff box. Scaphoid and trapezium can be felt in the floor of the snuff box between the radial styloid process and the first metacarpal. | ||
[[File:Snuff box2.jpg|alt=Muscles around snuff box|left|frameless|420x420px]] | |||
'''Clinical relevance''' | '''Clinical relevance''' | ||
| Line 32: | Line 35: | ||
'''Idiopathic Radial artery aneurysm in the anatomical snuff box''' | '''Idiopathic Radial artery aneurysm in the anatomical snuff box''' | ||
Radial artery aneurysms are extremely rare. They are usually associated with trauma, usually penetrating or iatrogenic. They are less common than aneuryms of the ulnar artery although this discrepancy is unexplained . Incidents following blunt trauma have been described . | Radial artery aneurysms are extremely rare. They are usually associated with trauma, usually penetrating or iatrogenic. They are less common than aneuryms of the ulnar artery although this discrepancy is unexplained . Incidents following blunt trauma have been described .<gallery> | ||
File:Radial_artery_aneurysm.JPG | |||
</gallery> | |||
'''Resources''' | |||
http://teachmeanatomy.info/upper-limb/areas/anatomical-snuffbox/ | |||
http://www.actaorthopaedica.be/acta/download/2002-3/12-walton-choudhary.pdf | |||
===== Keith L. Moore, Anne M.R. Agur, and Arthur F. Dalley, “Essential Clinical Anatomy,4 ed” ===== | |||
===== General Anatomy and Musculoskeletal System (THIEME Atlas of Anatomy)Paperback – March 1, 2010by [/www.amazon.com/s/ref%3Ddp%20byline%20sr%20book%201%3Fie%3DUTF8%26text%3DMichael%2BSchuenke%26search-alias%3Dbooks%26field-author%3DMichael%2BSchuenke%26sort%3Drelevancerank Michael Schuenke] (Author), [/www.amazon.com/s/ref%3Ddp%20byline%20sr%20book%202%3Fie%3DUTF8%26text%3DErik%2BSchulte%26search-alias%3Dbooks%26field-author%3DErik%2BSchulte%26sort%3Drelevancerank Erik Schulte] (Author), [/www.amazon.com/s/ref%3Ddp%20byline%20sr%20book%203%3Fie%3DUTF8%26text%3DUdo%2BSchumacher%26search-alias%3Dbooks%26field-author%3DUdo%2BSchumacher%26sort%3Drelevancerank Udo Schumacher] (Author), [/www.amazon.com/s/ref%3Ddp%20byline%20sr%20book%204%3Fie%3DUTF8%26text%3DLawrence%2BM%2BRoss%26search-alias%3Dbooks%26field-author%3DLawrence%2BM%2BRoss%26sort%3Drelevancerank Lawrence M Ross] (Author), [/www.amazon.com/s/ref%3Ddp%20byline%20sr%20book%205%3Fie%3DUTF8%26text%3DEdward%2BD%2BLamperti%26search-alias%3Dbooks%26field-author%3DEdward%2BD%2BLamperti%26sort%3Drelevancerank Edward D Lamperti] (Author), [/www.amazon.com/s/ref%3Ddp%20byline%20sr%20book%206%3Fie%3DUTF8%26text%3DMarkus%2BVoll%26search-alias%3Dbooks%26field-author%3DMarkus%2BVoll%26sort%3Drelevancerank Markus Voll] (Author) ===== | |||
See also | See also | ||
[[Scaphoid Fracture]] | |||
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed) | Recent Related Research (from Pubmed) | ||
References | |||
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27541059 | |||
References | |||
===== Teachmeanatomy.info ===== | |||
===== Essential clinical anatomy ===== | |||
===== Thieme atlas of anatomy ===== | |||
===== Idiopathic radial artery aneurism in the anatomical snuff box By N. P. WAlton F. CHoudhary ===== | |||
Revision as of 00:19, 27 August 2017
Description:
The anatomical snuffbox (also known as the radial fossa), is a triangular depression found on the lateral aspect of the dorsum of the hand. It is located at the level of the carpal bones and best seen when the thumb is abducted. In the past, this depression was used to hold snuff (ground tobacco) before inhaling via the nose – hence it was given the name ‘snuffbox’.
Structure/Borders:
The tendons of the APL and EPB indicate the lateral (anterior) boundary of the anatomical snuff box, and the tendon of the EPL indicates the medial (posterior) boundary of the box. The radial artery crosses the floor of the snuff box, where its pulsations may be felt. The scaphoid and, less distinctly, the trapezium are palpable in the floor of the snuff box.
Contents
The main contents of the anatomical snuffbox are the radial artery, a branch of the radial nerve, and the cephalic vein. The radial artery crosses the floor of the anatomical snuffbox in an oblique manner. It runs deep to the extensor tendons. The radial pulse can be palpated in some individuals by placing two fingers on the proximal portion of the anatomical snuffbox. Subcutaneously, terminal branches of the superficial branch of the radial nerve run across the roof of the anatomical snuffbox, providing innervation to the skin of the lateral 3 1/2 digits on the dorsum of the hand, and the associated palm area. Also subcutaneously, the cephalic vein crosses the anatomical snuffbox, having just arisen from the dorsal venous network of the hand.
Function:
The three muscles acting on the thumb (APL, EPB, and EPL) are deep to the superficial extensors and emerge (“crop out”) from a furrow in the lateral part of the forearm that divides the extensors. Because of this characteristic, they are referred to as outcropping muscles. The tendons of the APL and EPB bound the triangular anatomical snuff box laterally, and the tendon of the EPL bounds it medially. The snuff box is visible as a hollow on the lateral aspect of the wrist when the thumb is extended fully; this draws the APL, EPB, and EPL tendons up and produces a concavity between them. Observe that the: Radial artery lies on the floor of the snuff box. Radial styloid process can be palpated proximally and the base of the first metacarpal can be palpated distally in the snuff box. Scaphoid and trapezium can be felt in the floor of the snuff box between the radial styloid process and the first metacarpal.
Clinical relevance
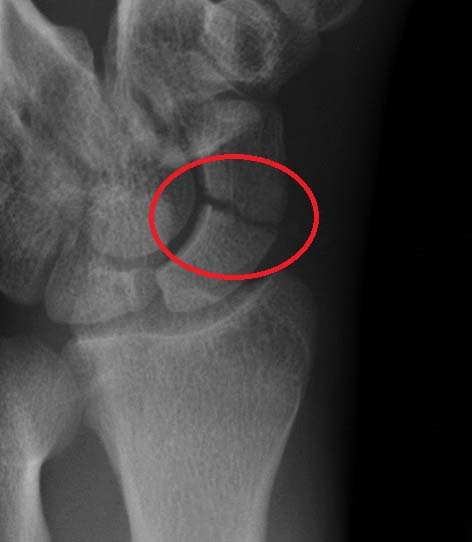
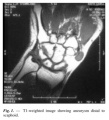
Fractures of the Scaphoid In the anatomical snuffbox, the scaphoid and the radius articulate to form part of the wrist joint. In the event of a blow to the wrist (e.g falling on an outstretched hand), the scaphoid takes most of the force. If localized pain is reported in the anatomical snuffbox, a fracture of the scaphoid is the most likely cause. The scaphoid has a unique blood supply, which runs distal to proximal. A fracture of the scaphoid can disrupt the blood supply to the proximal portion – this is an emergency. Failure to revascularise the scaphoid can lead to avascular necrosis, and future arthritis for the patient.
Idiopathic Radial artery aneurysm in the anatomical snuff box
Radial artery aneurysms are extremely rare. They are usually associated with trauma, usually penetrating or iatrogenic. They are less common than aneuryms of the ulnar artery although this discrepancy is unexplained . Incidents following blunt trauma have been described .
Resources
http://teachmeanatomy.info/upper-limb/areas/anatomical-snuffbox/
http://www.actaorthopaedica.be/acta/download/2002-3/12-walton-choudhary.pdf
Keith L. Moore, Anne M.R. Agur, and Arthur F. Dalley, “Essential Clinical Anatomy,4 ed”[edit | edit source]
General Anatomy and Musculoskeletal System (THIEME Atlas of Anatomy)Paperback – March 1, 2010by [/www.amazon.com/s/ref%3Ddp%20byline%20sr%20book%201%3Fie%3DUTF8%26text%3DMichael%2BSchuenke%26search-alias%3Dbooks%26field-author%3DMichael%2BSchuenke%26sort%3Drelevancerank Michael Schuenke] (Author), [/www.amazon.com/s/ref%3Ddp%20byline%20sr%20book%202%3Fie%3DUTF8%26text%3DErik%2BSchulte%26search-alias%3Dbooks%26field-author%3DErik%2BSchulte%26sort%3Drelevancerank Erik Schulte] (Author), [/www.amazon.com/s/ref%3Ddp%20byline%20sr%20book%203%3Fie%3DUTF8%26text%3DUdo%2BSchumacher%26search-alias%3Dbooks%26field-author%3DUdo%2BSchumacher%26sort%3Drelevancerank Udo Schumacher] (Author), [/www.amazon.com/s/ref%3Ddp%20byline%20sr%20book%204%3Fie%3DUTF8%26text%3DLawrence%2BM%2BRoss%26search-alias%3Dbooks%26field-author%3DLawrence%2BM%2BRoss%26sort%3Drelevancerank Lawrence M Ross] (Author), [/www.amazon.com/s/ref%3Ddp%20byline%20sr%20book%205%3Fie%3DUTF8%26text%3DEdward%2BD%2BLamperti%26search-alias%3Dbooks%26field-author%3DEdward%2BD%2BLamperti%26sort%3Drelevancerank Edward D Lamperti] (Author), [/www.amazon.com/s/ref%3Ddp%20byline%20sr%20book%206%3Fie%3DUTF8%26text%3DMarkus%2BVoll%26search-alias%3Dbooks%26field-author%3DMarkus%2BVoll%26sort%3Drelevancerank Markus Voll] (Author)[edit | edit source]
See also
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27541059
References