Acute Neck Pain: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
[[File:Neck_Pain_Diagram.png|thumb | [[File:Neck_Pain_Diagram.png|thumb|left]] | ||
Acute neck pain is characterised by its sudden onset, typically lasting less than three months. This discomfort can manifest as localised pain or radiate to the head, shoulders, and arms. According to NICE guidelines, the prevalence of condition-specific acute neck pain ranges from 40 to 70%. Various factors such as injury, disease, wear and tear, or poor biomechanics can stress the spine and lead to this type of pain. However, pinpointing the exact source of discomfort can be challenging. Potential contributing factors may include nerve damage, tissue scarring, arthritis, and the emotional effects of pain. | Acute neck pain is characterised by its sudden onset, typically lasting less than three months. This discomfort can manifest as localised pain or radiate to the head, shoulders, and arms. According to NICE guidelines, the prevalence of condition-specific acute neck pain ranges from 40 to 70%. Various factors such as injury, disease, wear and tear, or poor biomechanics can stress the spine and lead to this type of pain. However, pinpointing the exact source of discomfort can be challenging. Potential contributing factors may include nerve damage, tissue scarring, arthritis, and the emotional effects of pain. | ||
== Functional Anatomy == | == Functional Anatomy == | ||
[[File:Cervical_spine_anatomical_drawing.jpg|right|frameless | [[File:Cervical_spine_anatomical_drawing.jpg|right|frameless]] | ||
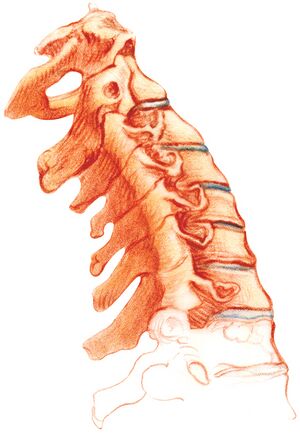
The cervical spine consists of several structural group to support the weight of the head and enable head and neck movements. | The cervical spine consists of several structural group to support the weight of the head and enable head and neck movements. | ||
Revision as of 22:02, 15 March 2024
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Acute neck pain is characterised by its sudden onset, typically lasting less than three months. This discomfort can manifest as localised pain or radiate to the head, shoulders, and arms. According to NICE guidelines, the prevalence of condition-specific acute neck pain ranges from 40 to 70%. Various factors such as injury, disease, wear and tear, or poor biomechanics can stress the spine and lead to this type of pain. However, pinpointing the exact source of discomfort can be challenging. Potential contributing factors may include nerve damage, tissue scarring, arthritis, and the emotional effects of pain.
Functional Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The cervical spine consists of several structural group to support the weight of the head and enable head and neck movements.
- Muscles - anterior muscles, posterior muscles, lateral muscles, muscles that feed into the neck?
- Ligaments
- Neurological structures - arteries, nerves, glands, and passageways