Pelvic Floor Anatomy
The Pelvic Floor - Overview and Function[edit | edit source]
The pelvic floor is an area of muscle and connective tissue that spans the area underneath the pelvis, separating the pelvic cavity above from the perineal region below. It provides support to the pelvic viscera including the bladder, intestines and uterus (in females). It also assists with continence through control of the urinary and anal sphincters. It facilitates birth by resisting the descent of the presenting part, causing the fetus to rotate forwards to navigate through the pelvic girdle. Finally , it helps to maintain optimal intraabdominal pressure.
Osteology and Ligaments[edit | edit source]
Pelvic Floor Myology[edit | edit source]
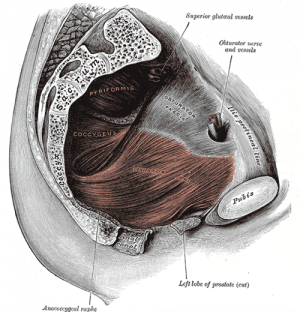
Pelvic diaphragm
- Levator ani - pubococcygeus, puborectalis, iliococcygeus
- Ischiococcygeus (Coccygeus)
Sphincter urethrae
Perineal membrane
Superficial genital muscles;
- Bulbocavernosus (bulbospongiosus in men)
- Ischiocavernosus
- Superficial transverse perineal
Associated muscles;
- Piriformis
- Obturator internus
- Adductors
- Gluteals
- Transverse abdominus
- Multifidus
- Respiratory diaphragm
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Action | Innervation |
| Levator Ani (Pubococcygeus) | Posterior aspect of body of pubis and anterior part of arcus tendineus | Coccyx and anococcygeal ligament | Helps to support pelvic viscera and resists increase in intra-abdominal pressure | Nerve to levator ani (branches of S4), inferior rectal nerve (from pudendal nerve - S3, S4), coccygeal plexus
|
| Levator Ani (Iliococcygeus) | Posterior aspect of arcus tendineus and the ischial spine | Anococcygeal raphe and the coccyx | Helps to support pelvic viscera and resists increase in intra-abdominal pressure | Nerve to levator ani (branches of S4), inferior rectal nerve (from pudendal nerve - S3, S4), coccygeal plexus
|
| Levator Ani (Puborectalis) | Lower part of pubic symphysis and superior fascia of urogenital diaphragm | Unites with its partner to make a U-shaped sling around the rectum | Controls defecation by pulling anorectal junction forward | Nerve to levator ani (branches of S4), branch of pudendal nerve (S2-4)
|
| Ischiococcygeus (Coccygeus) | Ischial Spine | Lower two sacral and upper two coccygeal spinal segments, blends with sacrospinous ligament on its external surface | Supports pelvic viscera, flexion of coccyx | Anterior rami of S4 and S5 |
| Sphincter urethrae | Controls flow of urine through urethra | |||