Tracheobronchial Tree
Original Editor - User Name
Top Contributors - Stella Constantinides and Kim Jackson
Introduction[edit | edit source]
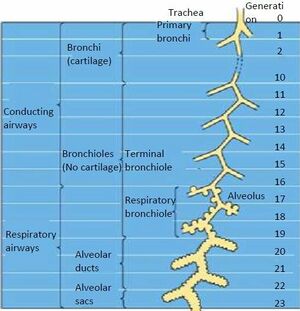
The tracheobronchial tree is a branching tree of airways composed of:
- the trachea
- the bronchi
- the bronchioles.
Main function of the tracheobronchial tree is to allow the transport of air to from the environment to the lungs for gas exchange.
In all, there are approximately 23 generations (divisions) of airway in the human lung extending from trachea (generation 0) to the last order of terminal bronchioles (generation 23).
Trachea[edit | edit source]
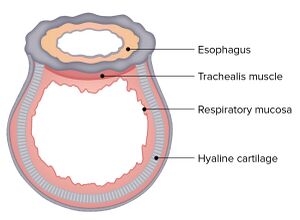
The trachea, or windpipe, descends from the larynx into the thorax and is situated anterior to the oesophagus. (biblio).Extends from cricoid cartilage to carina 10-12 cm long /2.0-2.5 cm in diameter.
The trachea is a U-shaped structure that is composed of hyaline cartilage on the anterior and lateral walls, with the trachealis smooth muscle forming the posterior border of the trachea , and the trachea is composed of several primary structural annular ligament.https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/trachealis-muscle
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448070/
Bronchi[edit | edit source]
Right main bronchi
- 3cm
- Wider
- More vertical.
- Left main bronchi
- 5cm
- Narrower
- More horizontal
Bronchioles[edit | edit source]
Alveoli
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x