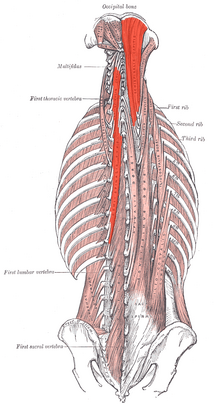
Semispinalis
Original Editor - Lucinda hampton
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton and Kim Jackson
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The semispinalis muscle belongs to the transversospinalis muscles. The transversospinalis muscle group is a very deep layer of muscles located on either side of the spine.
The semispinalis muscle is:
- The most superficial layer of this muscle group.
- The largest muscle mass in the posterior part of the neck.
- Responsible for maintaining posture and for movement of the head and the vertebral column.[1]
- Has the longest fascicles of transversospinalis group, spanning six segments.[2]
Sub Heading 2[edit | edit source]
Sub Heading 3[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
The semispinalis capitis is the largest muscle in the posterior neck.
The semispinalis cervicis and capitis lie deep to the upper trapezius. The trapezius is often blamed for muscle pain in this area that actually emanates from the deeper semispinalis musculature.
The greater occipital nerve, which innervates the posterior scalp, pierces through the semispinalis capitis (as well as the upper trapezius). A tight (overly facilitated) semispinalis capitis can compress this nerve, causing greater occipital neuralgia[3].
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Healthline Semispinalis Available: https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/semispinalis-muscle#1(accessed 2.2.2022)
- ↑ Radiopedia Transversospinalis muscle group Available: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/transversospinalis-muscle-group?lang=gb(accessed 2.2.2022)
- ↑ Learn Muscles Semispinalis Available: https://learnmuscles.com/glossary/semispinalis/(accessed 2.2.2022)