Sporting Hand and Wrist - What to Consider When Measuring Range of Motion: Difference between revisions
Carin Hunter (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Carin Hunter (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
not directly because it's pertained to the wrist, although you can see with external forces, you are going to get that additional 10% or additional movement and torsion happening over there. But it is important because pathology is like, your TFCCs. Pathologies, which involve these sort of pronation supination movements, which is very big in sports, you know, think about golf. Think about, you know, your rugby's, your movements. Think about your tennis. So what other movements you're doing and whether they have obviously that external force or not, you need that movement and if that is obviously limited, it can require more movements to occur, more distally | not directly because it's pertained to the wrist, although you can see with external forces, you are going to get that additional 10% or additional movement and torsion happening over there. But it is important because pathology is like, your TFCCs. Pathologies, which involve these sort of pronation supination movements, which is very big in sports, you know, think about golf. Think about, you know, your rugby's, your movements. Think about your tennis. So what other movements you're doing and whether they have obviously that external force or not, you need that movement and if that is obviously limited, it can require more movements to occur, more distally | ||
Supination | Supination | ||
== Tools used to measure range of motion in the wrist and hand == | == Tools used to measure range of motion in the wrist and hand == | ||
<gallery widths=“250px” heights=“350px”> | <gallery widths="“250px”" heights="“350px”"> | ||
File:Wrist flexion and extension ROM.jpg|Goniometer position for wrist flexion and extension | File:Wrist flexion and extension ROM.jpg|Goniometer position for wrist flexion and extension | ||
File:Inclinomter1.jpg|Inclinometer | File:Inclinomter1.jpg|Inclinometer | ||
File:Cellphone Inclinometer.png|Cellphone Inclinometer </gallery> | File:Cellphone Inclinometer.png|Cellphone Inclinometer </gallery> | ||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! | |||
!Goniometer | |||
!Inclinometer | |||
!Cellphone Inclinometer | |||
|- | |||
|Pros | |||
|Compact, easy to use and portable | |||
|Accurate and measures multiple planes | |||
|Accurate, measures multiple planes, free downloadable appconvenient | |||
|- | |||
|Limitations | |||
|Only one plane of movement | |||
|Bulky and expensive | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
== Considerations when measuring wrist flexion and extension == | |||
<gallery widths="“250px”" heights="“350px”"> | |||
File:E RD.png|Extension/radial deviation | |||
File:Neutral.png|Neutral | |||
File:F UD.png|Flexion/Ulnar deviation </gallery> | |||
Coupling | |||
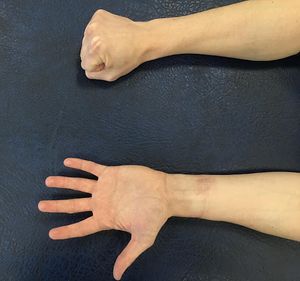
Open versus closed hand | Open versus closed hand | ||
[[File:Open vs closed hand.jpg|left|thumb|Open vs closed hand]] | |||
Flexion | Flexion | ||
* Open hand = joint | |||
* Closed hand = soft tissue | |||
Extension | |||
* Open hand = soft tissue | |||
* Closed hand = joint | |||
== Reason to measure == | == Reason to measure == | ||
Baseline | Baseline | ||
Gupta and Moosawy 2005, talking about that free movement and external forces and the difference about those, how the impact on the radiocarpal joint | Gupta and Moosawy 2005, talking about that free movement and external forces and the difference about those, how the impact on the radiocarpal joint | ||
Revision as of 11:47, 17 March 2021
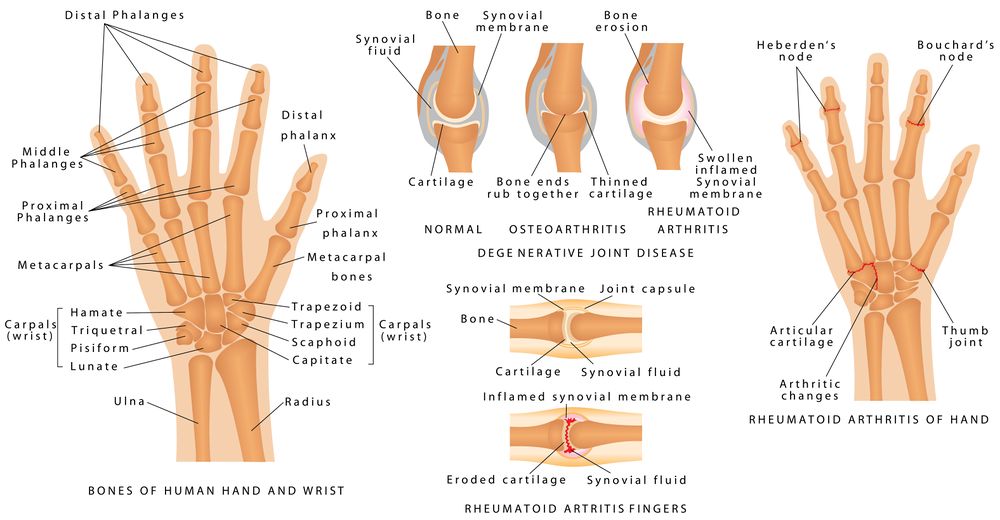
Joints in the wrist and hand[edit | edit source]
Radiocarpal joint
Midcarpal joint
Distal interphalangeal
Proximal Interphalangeal
Metacarpal phalangeal
Range of motion in the wrist and hand[edit | edit source]
Flexion
When looking at flexion, roughly about 90 degrees. 60% of it is coming from that midcarpal joint that we discussed, the more distal joint versus 40% coming from the radiocarpal joint. So you can see if there's more movement happening from the midcarpal joint, or even not to get confused, that there's a big percentage, you know, almost half, but more than half happening from that midcarpal joint, we need to know how to measure it. And so that's where it comes when we talk about the how, to try and make sure we incorporate that.
Extension
Extension tends to be a bit less. Depends obviously, what type of sport you do? You always have these exceptions, but tends to be a bit less, 80 degrees. But now it's reversed. So you have more movement that tends to occur at your radiocarpal joint than your midcarpal joint. And that's really is occurring because of the mechanics of the scaphoid, which I'm not going to dwell into detail over here because we're trying to keep it uncomplicated rather than complicated, but just an understanding that obviously, if you're doing flexion and extension, you have a component of radiocarpal and midcarpal joint.
Radial deviation
The same can be said then for your radial deviation and also your ulnar deviation. So to go back to radial deviation, you can see like flexion, you have a bit more of that midcarpal joint occurring versus radial and the movements are about up to 20 degrees. Ulnar deviation tends to be more. It tends to be double. So almost a ratio of twos to one, ulnar deviation versus radial deviation. But again, that's if it's from a normative population, you have to see the type of athletes they are, what are they doing? You tend to have compensations, but obviously, it's good understanding of knowing you're left to right. So again, you can see like flexion and radial deviation, a bit more midcarpal joint. So really what we need to take away from here to try to keep it simple, movements are happening from both the midcarpal joint and the radiocarpal joint. So it's an understanding that when we're measuring, we need to measure that.
Ulnar deviation
Distal interphalangeal
Proximal Interphalangeal
Pronation
not directly because it's pertained to the wrist, although you can see with external forces, you are going to get that additional 10% or additional movement and torsion happening over there. But it is important because pathology is like, your TFCCs. Pathologies, which involve these sort of pronation supination movements, which is very big in sports, you know, think about golf. Think about, you know, your rugby's, your movements. Think about your tennis. So what other movements you're doing and whether they have obviously that external force or not, you need that movement and if that is obviously limited, it can require more movements to occur, more distally
Supination
Tools used to measure range of motion in the wrist and hand[edit | edit source]
| Goniometer | Inclinometer | Cellphone Inclinometer | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pros | Compact, easy to use and portable | Accurate and measures multiple planes | Accurate, measures multiple planes, free downloadable appconvenient |
| Limitations | Only one plane of movement | Bulky and expensive |
Considerations when measuring wrist flexion and extension[edit | edit source]
Coupling
Open versus closed hand
Flexion
- Open hand = joint
- Closed hand = soft tissue
Extension
- Open hand = soft tissue
- Closed hand = joint
Reason to measure[edit | edit source]
Baseline
Gupta and Moosawy 2005, talking about that free movement and external forces and the difference about those, how the impact on the radiocarpal joint