Iliopsoas Tendinopathy: Difference between revisions
Shejza Mino (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Shejza Mino (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
Other reported causes: | Other reported causes: | ||
* [[Snapping hip syndrome]] (related to iliopsoas tendinitis) has been described more commonly amongst dancers who have a decreased pelvic bone width, decreased lateral hip rotation, increased abduction as well as increased strength to the lateral rotators of the hips. | * [[Snapping hip syndrome]] (related to iliopsoas tendinitis) has been described more commonly amongst dancers who have a decreased pelvic bone width, decreased lateral hip rotation, increased abduction as well as increased strength to the lateral rotators of the hips. | ||
* One | * One potential cause of iliopsoas bursitis, which is closely associated to iliopsoas tendinitis, is [[rheumatoid arthritis]]. | ||
== Clinical Presentation == | == Clinical Presentation == | ||
=== History === | === History === | ||
A history of insidious groin or anterior hip pain is common. | |||
=== Physical Examination === | === Physical Examination === | ||
Revision as of 21:51, 20 September 2020
Original Editor - Shejza Mino
Top Contributors - Shejza Mino, Lucinda hampton, Kim Jackson, Wendy Snyders, Rishika Babburu and Leana Louw
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Iliopsoas tendinitis describes inflammation of the iliopsoas muscle tendon or inflammation of the area surrounding this tendon. Acute traumatic injury or overuse injury from repetitive hip flexion have been reported to be the two primary causes. Due to the close proximally of the Iliopsoas tendon and the related bursa, inflammation of one of these structures causes inflammation of the other. Therefore, the clinical presentation of iliopsoas tendonitis and iliopsoas bursitis is indistinguishable and both conditions are managed the same.
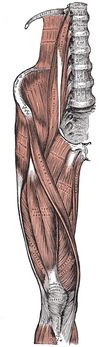
Clinically Relevant Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The origin of the psoas and iliacus muscles is at the transverse process of the T12 to L5 vertebrae and the superior anterior iliac crest of the pelvis.
The psoas major and illiacus muscles merge at the level of L5-S2, which becomes the origin of iliopsoas muscle. The iliopsoas runs from the pelvis to the thigh under the inguinal ligament to attach onto the lesser trochanter of the femur. The iliacus component of the iliopsoas muscle is innervated by the femoral nerve and the psoas component is innervated by branches of the lumbar plexus.
Vascular innervation of the iliopsoas muscle includes the iliolumbar artery as well as the medial femoral circumflex artery.
See Psoas Major.
Sport-specific Biomechanics[edit | edit source]
Epidemiology[edit | edit source]
In general, iliopsoas pathologic conditions (including tendinitis, bursitis, snapping and impingement) have been deemed to be the main cause of chronic groin pain in roughly 12-36% of athletes and in 25-30% of athletes with acute injury to the groin region
Data on the prevalence of iliopsoas tendonitis remains unknown however, it more commonly affects young adults and is mildly more prevalent in females
Etiology[edit | edit source]
Acute injury and overuse injury are the most common causes of iliopsoas tendinitis:
- Acute injury: from either eccentric contraction of the muscle or brisk flexion against an extension force. Either way, the acute injury leading to iliopsoas tendintis is not commonly due to a direct traumatic event.
- Overuse injury: may result from any activity requiring repetitive hip flexion or repetitive external rotation of the hip.
Other reported causes:
- Snapping hip syndrome (related to iliopsoas tendinitis) has been described more commonly amongst dancers who have a decreased pelvic bone width, decreased lateral hip rotation, increased abduction as well as increased strength to the lateral rotators of the hips.
- One potential cause of iliopsoas bursitis, which is closely associated to iliopsoas tendinitis, is rheumatoid arthritis.
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
History[edit | edit source]
A history of insidious groin or anterior hip pain is common.
Physical Examination[edit | edit source]
Differential Diagnoses[edit | edit source]
Workup[edit | edit source]
Laboratory Analysis[edit | edit source]
Medical Imaging[edit | edit source]
- Radiography
- Ultrasonography
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Lidocaine Injection[edit | edit source]
Management[edit | edit source]
Physical Therapy[edit | edit source]
- Acute Phase
- Recovery Phase
- Maintenance Phase
- Return to Play
Surgical Intervention[edit | edit source]
Medications[edit | edit source]
Other[edit | edit source]
Complications[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x