Coordination Exercises: Difference between revisions
Rewan Aloush (talk | contribs) (Created page with " == '''<u>coordination Exercises</u>''' == ==== '''Definition of coordination Exercises:''' ==== It is the ability to execute smooth, accurate, controlled motor responses (op...") |
Rewan Aloush (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
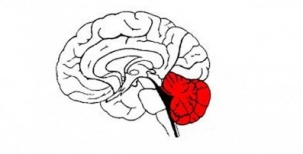
==== '''Importance of the cerebellum in coordination:''' ==== | ==== '''Importance of the cerebellum in coordination:''' ==== | ||
The cerebellum is the primary center in the brain for coordination of movement. | |||
==== '''Components of coordinated movement:''' ==== | ==== '''Components of coordinated movement:''' ==== | ||
<u>Volition:</u> is the ability to initiate,maintain or stop an activity or motion. | |||
<u>Perception:</u>in tact proprioception and subcortical centres to integrate motor impulses and the sensory feedback. When proprioception is affected it is compensated with visual feedback. | |||
<u>Engramformation:</u>is the neurologica lmuscular activity developed in the extrapyramidal system. Research proved that high repetitions of precise performance must be performed in order to develop an engram. | |||
==== '''Types of coordination:''' ==== | ==== '''Types of coordination:''' ==== | ||
Revision as of 18:52, 11 August 2017
coordination Exercises[edit | edit source]
Definition of coordination Exercises:[edit | edit source]
It is the ability to execute smooth, accurate, controlled motor responses (optimal interaction of muscle function).
Coordination is the ability to select the right muscle at the right time with proper intensity to achieve proper action.
Coordinated movement is characterized by appropriate speed, distance, direction, timing and muscular tension.
It is the process that results in activation of motor units of multiple muscles with simultaneous inhibition of all other muscles in order to carry out a desired activity.
The ability to execute smooth accurate motor response depends on:[edit | edit source]
– Deep sensations.
– Vision.
– Vestibular system and cerebellum.
– Motor system.
– Flexibility and ROM.
Importance of the cerebellum in coordination:[edit | edit source]
The cerebellum is the primary center in the brain for coordination of movement.
Components of coordinated movement:[edit | edit source]
Volition: is the ability to initiate,maintain or stop an activity or motion.
Perception:in tact proprioception and subcortical centres to integrate motor impulses and the sensory feedback. When proprioception is affected it is compensated with visual feedback.
Engramformation:is the neurologica lmuscular activity developed in the extrapyramidal system. Research proved that high repetitions of precise performance must be performed in order to develop an engram.
Types of coordination:[edit | edit source]
1) Fine motor skills:
Require coordinated movement of small muscles (hands, face).
Examples: include writing, drawing, buttoning a shirt, blowing bubbles
2) Gross motor skills:
Require coordinated movement of large muscles or groups of muscles (trunk, extremities).
Examples: include walking, running, lifting activities.
3)Hand-eye skills:
The ability of the visual system to coordinate visual information. Received and then control or direct the hands in the accomplishment of a task .
Examples : include catching a ball,sewing,computer mouse use.