Benediction Hand (aka Benediction Sign or Preacher's Hand): Difference between revisions
Rachael Lowe (talk | contribs) m (Text replace - 'Physiopedia.com' to 'Physiopedia') |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (58 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | |||
'''Original Editor '''-[[User:Pamela Gonzalez|Pamela Gonzalez]] | |||
Original Editor - | |||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | |||
</div> | |||
| | == Description == | ||
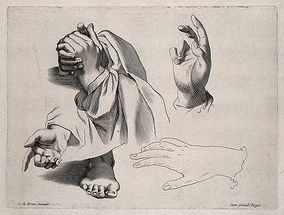
[[File:Benediction hand.jpg|thumb|284x284px]]The Benediction Sign is commonly associated with a [[Median Nerve|median nerve]] pathology. It is seen when the patient attempts to make a fist but is unable to flex the index and middle fingers at the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) and [[Interphalangeal Joints of the Hand|interphalangeal]] (IP) joints, causing these fingers to remain extended while the other fingers flex normally. This distinct clinical presentation is a result of damage to the median nerve, which impairs the function of the lateral lumbricals that flex these joints. | |||
== | == Historical and Cultural Context == | ||
Historically, the Benediction Sign has been linked to cultural representations of blessings and greetings, which typically involved an open hand with extended fingers. It was noted in some historical and cultural analyses, such as the research by Futterman <ref name="Futterman">Futterman B. Analysis of the Papal Benediction Sign: the ulnar neuropathy of St. Peter. Clinical Anatomy. 2015 Sep;28(6):696-701.</ref>, that figures like Peter, the first Pope, might have had an ulnar neuropathy, which influenced the traditional hand blessing posture. However, this specific condition affects the ability to abduct and flex the fourth and fifth digits and is distinct from the Benediction Sign associated with median nerve pathology. | |||
==Clinically Relevant Anatomy== | |||
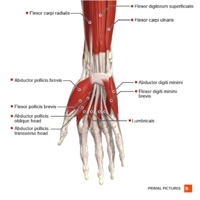
[[File:Muscles_of_the_hand_anterior_aspect_Primal.png|thumb|200x200px]] | |||
== | The [[Median Nerve|median nerve]] originates from the [[Brachial Plexus|brachial plexus]] and primarily innervates the first and second lumbricals of the hand, among other structures. In the case of Benediction Sign, the inability to flex the second and third digits arises from damage to this nerve. However, [https://physio-pedia.com/Ulnar_Nerve?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=search&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal ulnar nerve] pathology affects the fourth and fifth digits, leading to what is often termed as "[[Claw Hand]]," where these digits may exhibit hyperextension at the MCP joints and flexion at the IP joints. | ||
== Clinical Presentation == | == Clinical Presentation == | ||
Patients with Benediction Sign may experience numbness and muscle weakness primarily in the second and third digits. The presentation involves these fingers remaining extended during an attempt to make a fist. This should not be confused with ulnar nerve symptoms, which affect the outer digits of the hand. | |||
<ref>Floranda EE, Jacobs BC. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24209726 Evaluation and treatment of upper extremity nerve entrapment syndromes]. Primary care. 2013 Dec;40(4):925.</ref>[[Image:Benediction hand ulnar claw.JPG|center|300px]] | |||
== | == Differential Diagnosis == | ||
The differential diagnosis should consider other conditions that mimic the posture of Benediction Sign but are due to different underlying causes, such as [[Rheumatoid Arthritis|rheumatoid arthritis]] or other forms of peripheral neuropathy. | |||
== Management and Treatment == | |||
The treatment of Benediction Hand involves the management and treatment of the underlying median nerve pathology. Treatment options may include: <ref>Hand of Benediction. What Is It, Causes, and More. Available from: <nowiki>https://www.osmosis.org/answers/hand-of-benediction</nowiki> ( Accessed, 19/07/2021).</ref> | |||
* Non-steroidal inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to control pain and prevent symptoms to get worse. | |||
* Use of hand or wrist brace to minimise further nerve compression and excessive bending. | |||
* [[Hand Exercises|Hand stretching and strengthening exercises]] with a Physiotherapist or Occupational Therapist if needed. | |||
* Nerve decompression surgery to reduce pressure and relieve pain if the median nerve is affected because of the [[Carpal Tunnel Syndrome]].<br /> | |||
{{#ev:youtube|0AAligXLJ1A |300}}<ref>FSUMedMedia. Claw Hand, Ape Hand, and the Sign of Benediction: Animated Review. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0AAligXLJ1A [Accessed, 19/07/2021]</ref> | |||
== Summary == | |||
It is important to distinguish the Benediction Sign, primarily a median nerve issue, from conditions affecting the ulnar nerve. Understanding the specific nerve involvements helps in accurate diagnosis and effective management of the condition. | |||
== | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
<br> | |||
[[Category:Conditions]] | |||
[[Category:Hand - Conditions]] | |||
[[Category:Hand - Conditions]] | |||
[[Category:Neurological - Conditions]] | |||
[[Category:Musculoskeletal/Orthopaedics]] | |||
[[Category:Neuropathy]] | |||
[[Category:Hand]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:34, 6 May 2024
Original Editor -Pamela Gonzalez
Top Contributors - Laura Ritchie, Aminat Abolade, Kirenga Bamurange Liliane, Admin, Kim Jackson, Pamela Gonzalez, Rachael Lowe, David Adamson, WikiSysop, Lauren Kwant, Evan Thomas and Richard Benes
Description[edit | edit source]
The Benediction Sign is commonly associated with a median nerve pathology. It is seen when the patient attempts to make a fist but is unable to flex the index and middle fingers at the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) and interphalangeal (IP) joints, causing these fingers to remain extended while the other fingers flex normally. This distinct clinical presentation is a result of damage to the median nerve, which impairs the function of the lateral lumbricals that flex these joints.
Historical and Cultural Context[edit | edit source]
Historically, the Benediction Sign has been linked to cultural representations of blessings and greetings, which typically involved an open hand with extended fingers. It was noted in some historical and cultural analyses, such as the research by Futterman [1], that figures like Peter, the first Pope, might have had an ulnar neuropathy, which influenced the traditional hand blessing posture. However, this specific condition affects the ability to abduct and flex the fourth and fifth digits and is distinct from the Benediction Sign associated with median nerve pathology.
Clinically Relevant Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The median nerve originates from the brachial plexus and primarily innervates the first and second lumbricals of the hand, among other structures. In the case of Benediction Sign, the inability to flex the second and third digits arises from damage to this nerve. However, ulnar nerve pathology affects the fourth and fifth digits, leading to what is often termed as "Claw Hand," where these digits may exhibit hyperextension at the MCP joints and flexion at the IP joints.
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Patients with Benediction Sign may experience numbness and muscle weakness primarily in the second and third digits. The presentation involves these fingers remaining extended during an attempt to make a fist. This should not be confused with ulnar nerve symptoms, which affect the outer digits of the hand.
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
The differential diagnosis should consider other conditions that mimic the posture of Benediction Sign but are due to different underlying causes, such as rheumatoid arthritis or other forms of peripheral neuropathy.
Management and Treatment[edit | edit source]
The treatment of Benediction Hand involves the management and treatment of the underlying median nerve pathology. Treatment options may include: [3]
- Non-steroidal inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to control pain and prevent symptoms to get worse.
- Use of hand or wrist brace to minimise further nerve compression and excessive bending.
- Hand stretching and strengthening exercises with a Physiotherapist or Occupational Therapist if needed.
- Nerve decompression surgery to reduce pressure and relieve pain if the median nerve is affected because of the Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
Summary[edit | edit source]
It is important to distinguish the Benediction Sign, primarily a median nerve issue, from conditions affecting the ulnar nerve. Understanding the specific nerve involvements helps in accurate diagnosis and effective management of the condition.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Futterman B. Analysis of the Papal Benediction Sign: the ulnar neuropathy of St. Peter. Clinical Anatomy. 2015 Sep;28(6):696-701.
- ↑ Floranda EE, Jacobs BC. Evaluation and treatment of upper extremity nerve entrapment syndromes. Primary care. 2013 Dec;40(4):925.
- ↑ Hand of Benediction. What Is It, Causes, and More. Available from: https://www.osmosis.org/answers/hand-of-benediction ( Accessed, 19/07/2021).
- ↑ FSUMedMedia. Claw Hand, Ape Hand, and the Sign of Benediction: Animated Review. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0AAligXLJ1A [Accessed, 19/07/2021]