The Gensingen Brace: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
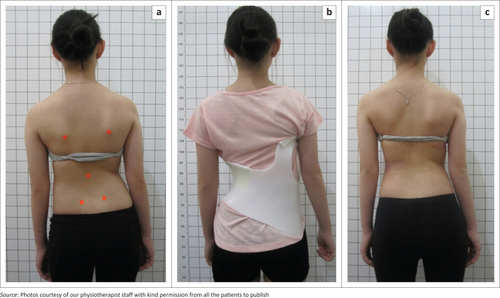
In many studies that is made on patients who used the GBW we found that there are an improvement in trunk rotation as measured in ATR and an improvement in pain symptoms. <ref>Widjaja BS, Varani R. Impact of Gensingen brace treatment on Lenke 5 curvatures and chronic low back pain in late adolescent and adult scoliosis patients. S Afr J Physiother. 2022 Mar 25;78(1):1585. doi: 10.4102/sajp.v78i1.1585. PMID: 35402746; PMCID: PMC8991184.</ref> | In many studies that is made on patients who used the GBW we found that there are an improvement in trunk rotation as measured in ATR and an improvement in pain symptoms. <ref>Widjaja BS, Varani R. Impact of Gensingen brace treatment on Lenke 5 curvatures and chronic low back pain in late adolescent and adult scoliosis patients. S Afr J Physiother. 2022 Mar 25;78(1):1585. doi: 10.4102/sajp.v78i1.1585. PMID: 35402746; PMCID: PMC8991184.</ref> | ||
[[File:GBW effects.png|thumb]] | [[File:GBW effects.png|thumb|center|500x500px]] | ||
===== References ===== | ===== References ===== | ||
Revision as of 11:25, 30 November 2023
Definition/Description[edit | edit source]
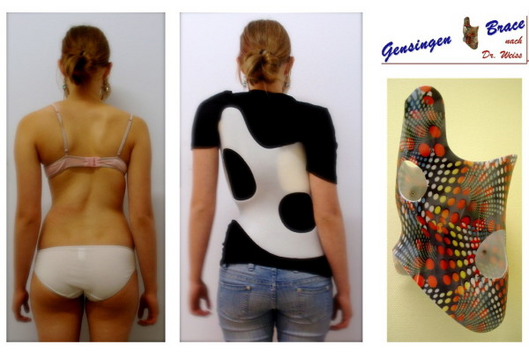
The Gensingen brace used to reduce The Cobbs angle in the treatment of Scoliosis by changing the alignment and the curvature of the vertebrae three dimensionally instead of the surgery. also used for reducing pain and improve the cosmetic appearance.
The advantage of the Gensingen brace is easily adjustable to use and comfortable to wear, it has compressive effects on sagital and frontal planes for correction
There are many different forms of brace including models for thoracolumbar curve patterns and athletic trunks plus models for small children. so we will not need more than one braces for correction.[2]
How to build the brace[edit | edit source]
the trunk of the patient is scanned with a whole trunk optical 3D-scan and the patients' data coming from the clinical measurements are added, So we can create the model of the brace and modify the trunk model of the patient 'on screen' to create an individual brace model with the CAD/CAM tools then choosing a model from the library and re-size it to the patients' models 'on screen'. rarely the Trunk correction scan is used, in curve patterns easy classified , the second procedure is usually chosen. in of the brace advantages, the patient can receive a specially developed brace.[2]
Impact of Gensingen brace treatment[edit | edit source]
The aims of treatment in our patients are to reduce of scoliosis curvature and reduce pain, and to decrease the severity of the Cobb angle
The Gensingen brace has beneficial effects during growth in reducing the progression of the growth and in the improvement of the angle of curvature also in improvement of the cosmetic appearance as well.
Scoliosis affects the sagittal profile and also leads to thoracic flattening and lumbar kyphosis. In scoliosis with high 3D spinal deviations, Chêneau style braces (Rigo brace or GBW) are used as braces to improve the sagittal plane deformity that is found in patients with idiopathic scoliosis (loss of thoracic kyphosis, loss of lumbar lordosis, flat back deformity.
The GBW is be designed in way to stabilize the lumbar segment with a 3D correction.
In many studies that is made on patients who used the GBW we found that there are an improvement in trunk rotation as measured in ATR and an improvement in pain symptoms. [3]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Weiss HR. "Brace technology" thematic series - the Gensingen brace™ in the treatment of scoliosis. Scoliosis. 2010 Oct 13;5:22. doi: 10.1186/1748-7161-5-22. PMID: 20942970; PMCID: PMC2967515.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Weiss HR. "Brace technology" thematic series - the Gensingen brace™ in the treatment of scoliosis. Scoliosis. 2010 Oct 13;5:22. doi: 10.1186/1748-7161-5-22. PMID: 20942970; PMCID: PMC2967515.
- ↑ Widjaja BS, Varani R. Impact of Gensingen brace treatment on Lenke 5 curvatures and chronic low back pain in late adolescent and adult scoliosis patients. S Afr J Physiother. 2022 Mar 25;78(1):1585. doi: 10.4102/sajp.v78i1.1585. PMID: 35402746; PMCID: PMC8991184.