Hypermobile Meniscus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
Kamiya T, Suzuki T, Otsubo H, Kuroda M, Matsumura T, Kubota C, et al. Midterm outcomes after arthroscopic surgery for hypermobile lateral meniscus in adults: Restriction of paradoxical motion. J Orthop Sci [Internet]. 2018;23(6):1000–4. Available from: <nowiki>http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jos.2018.06.003</nowiki></ref> It is a rare, uncommon condition. <ref name=":0" /> The menisci are crescent shaped, cartilaginous discs that lie between the articular cartilage of the femur and tibia. The menisci have various functions - load transmission, shock absorption, joint lubrication, nutrition, secondary mechanical stability, and guiding of movements.<ref>Habegger A. The Knee. 2023 Mar.</ref> | Kamiya T, Suzuki T, Otsubo H, Kuroda M, Matsumura T, Kubota C, et al. Midterm outcomes after arthroscopic surgery for hypermobile lateral meniscus in adults: Restriction of paradoxical motion. J Orthop Sci [Internet]. 2018;23(6):1000–4. Available from: <nowiki>http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jos.2018.06.003</nowiki></ref> It is a rare, uncommon condition. <ref name=":0" /> The menisci are crescent shaped, cartilaginous discs that lie between the articular cartilage of the femur and tibia. The menisci have various functions - load transmission, shock absorption, joint lubrication, nutrition, secondary mechanical stability, and guiding of movements.<ref>Habegger A. The Knee. 2023 Mar.</ref> | ||
[[File:6A6AAE72-452D-49FD-BC2C-1FD4E10B9F0F.jpeg|thumb|260x260px|Posterior view of knee | [[File:6A6AAE72-452D-49FD-BC2C-1FD4E10B9F0F.jpeg|thumb|260x260px|Posterior view of knee|alt=]] | ||
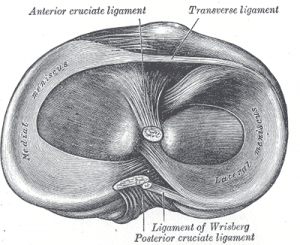
[[File:Meniscus sup view Gray349.png|center|thumb|Caudal view of right knee|alt=]] | [[File:Meniscus sup view Gray349.png|center|thumb|Caudal view of right knee|alt=]] | ||
<br>In a stable knee, the LM is smaller, thinner, and more mobile than the medial meniscus. In addition, the lateral meniscus has less stabilizers at its posterolateral aspect.<ref name=":0" /> The stabilizers of the lateral meniscus include the – popliteomeniscal fascicles (PMF), the posterior capsule, the meniscofemoral ligaments, and the posterior meniscotibial ligament. <ref name=":0" /> These attachments to the posterior knee prevent the subluxation of the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus into the knee joint. <ref name=":2">McHugh C. Hypermobile lateral Meniscus [Internet]. Orthosports. 2022 [cited 2023 Mar 28]. Available from: <nowiki>https://orthosports.com.au/hypermobile_lateral_meniscus</nowiki></ref> | <br>In a stable knee, the LM is smaller, thinner, and more mobile than the medial meniscus. In addition, the lateral meniscus has less stabilizers at its posterolateral aspect.<ref name=":0" /> The stabilizers of the lateral meniscus include the – popliteomeniscal fascicles (PMF), the posterior capsule, the meniscofemoral ligaments, and the posterior meniscotibial ligament. <ref name=":0" /> These attachments to the posterior knee prevent the subluxation of the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus into the knee joint. <ref name=":2">McHugh C. Hypermobile lateral Meniscus [Internet]. Orthosports. 2022 [cited 2023 Mar 28]. Available from: <nowiki>https://orthosports.com.au/hypermobile_lateral_meniscus</nowiki></ref> | ||
Revision as of 17:30, 28 March 2023
Top Contributors - Robert Pierce, Madisyn Melchor, Kim Jackson, Matt Huey, Cindy John-Chu and Briana Marin
Top Contributors - Robert Pierce, Madisyn Melchor, Kim Jackson, Matt Huey, Cindy John-Chu and Briana Marin
Clinically Relevant Anatomy
[edit | edit source]
Lateral meniscus hypermobility (LMH) is excess motion at the lateral meniscus (LM) that can cause lateral knee pain or tenderness, locking of the knee, or limitation of the range of motion during knee flexion. [1][2] It is a rare, uncommon condition. [1] The menisci are crescent shaped, cartilaginous discs that lie between the articular cartilage of the femur and tibia. The menisci have various functions - load transmission, shock absorption, joint lubrication, nutrition, secondary mechanical stability, and guiding of movements.[3]
In a stable knee, the LM is smaller, thinner, and more mobile than the medial meniscus. In addition, the lateral meniscus has less stabilizers at its posterolateral aspect.[1] The stabilizers of the lateral meniscus include the – popliteomeniscal fascicles (PMF), the posterior capsule, the meniscofemoral ligaments, and the posterior meniscotibial ligament. [1] These attachments to the posterior knee prevent the subluxation of the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus into the knee joint. [4]
Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process
[edit | edit source]
LMH is thought to be related to a congenital deficiency in the capsular attachments[5], or an atraumatic injury to the ligamentous attachments[4], specifically the PMF [2]. Trauma that causes rupture to the PMF can be insignificant, so patients may not recall a specific mechanism of injury.
Commonly, hypermobility is due to an overuse injury, as well as atraumatic hypermobility. An isolated incidence of LMH is rare. Studies have found that in many cases of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), and/or posterolateral injuries to the knee there is concurrent damage to the PMF, which may result in LMH.
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Symptoms include lateral knee pain, instability and painful popping or locking with the knee specifically in flexion and/or external rotation.[1] Pain can be reproduced through application of a varus force with the hip and knee placed in flexion and external rotation.[6] Case studies have shown patients can experience atraumatic, painful locking when sitting with legs crossed, however there radiographs will appear normal. [4][6]
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
Arthroscopy is considered the gold standard of diagnosing LMH. If 50% of the LM crosses anterior to the midline of the tibial plateau, an LMH diagnosis is confirmed. This is called a Gutter's Sign and is present in 95.5% of patients with LMH. To determine the level of hypermobility of the LM, an arthroscopic procedure is conducted to test for a Gutter's Sign - a probed hooked behind the posterior lateral meniscus with anterior pressure to cause translation of the LM beyond the tibial articular surface. [5]
The two main surgical techniques to stabilize the LM is to either suture the tissue to the anterior popliteomeniscal fascicle or fasten the LM to the posterior capsule of the knee.[1] According to a study that focused on suturing the LM to the posterior capsule, there was an 82% success rate and 56% of participants returned to sport at the same performance level prior to injury. [7]
An MRI will show no abnormalities, but if an MRI is taken during the “locked” phase, you may see the posterior aspect of the LM anterior to the midline of the tibial plateau. This is indicative of LMH.[2]
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
- Lower Extremity Functional Scale (LEFS)
- Psychological Readiness Return to Sport Scale
- Cincinnati Knee Rating System
- Lysholm Knee Scoring Scale
- Western Ontario Meniscal Evaluation Tool (WOMET)
- Numeric Rating Scale for pain (NES)
- Visual Analogue Scale for pain (VAS)
Management / Interventions
[edit | edit source]
Early physical therapy interventions should focus on returning to full weight-bearing status and establishing early range of motion immediately following surgery. [8] It is recommended to restrain from weight-bearing past 90 degrees of knee flexion during the first 4 weeks following surgery. Release to full activity and sport participation can occur at approximately 12 weeks post-surgery.[5] The treating clinician should consider the clinical evidence of the LM biomechanical functional capabilities during treatment to allow for full tissue healing and a safe return to activity.[8]
Goals of Rehab (0-3 weeks)[9]
- Pain management
- Promote tissue healing
- Reduce swelling
- Knee mobility
- Restore full knee extension
- Quadriceps activation
- NMES
Goals of Rehab (3-6 weeks)[9]
- Pain management
- Promote tissue healing
- Maintain full knee extension
- Strengthening exercises
- Minimal to Moderate Intensity
Goals of Rehab (6 weeks +)[9]
- Establish normal gait pattern
- Equal degrees of knee flexion compared to non-surgical limb
- Progress strengthening exercises
- Functional movement patterns
- Return to Sport Training
- Plyometrics
- Agility
- Straight-Line Running
- Return to Sport Testing
- Return to Sport Guidelines
- No report of pain
- No instability
- No popping
- No catching during deep knee flexion past 90 degrees
Differential Diagnosis
[edit | edit source]
- Bucket-handle Meniscal Lesion
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL Tear)
- Ligamentous Instabilities
- Articular Cartilage lesions
- Patellar Dislocation
- Patellar Pathology
Resources
[edit | edit source]
Meniscal Lesions Physio-Pedia Page
MassGeneral Rehabilitation Guidelines for Athroscopic Meniscal Repair
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1. Beel W, Macchiarola L, Mouton C, Laver L, Seil R. The hypermobile and unstable lateral meniscus: a narrative review of the anatomy, biomechanics, diagnosis and treatment options. Ann Jt [Internet]. 2022;7:14–14. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/aoj-21-9
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 4. Kamiya T, Suzuki T, Otsubo H, Kuroda M, Matsumura T, Kubota C, et al. Midterm outcomes after arthroscopic surgery for hypermobile lateral meniscus in adults: Restriction of paradoxical motion. J Orthop Sci [Internet]. 2018;23(6):1000–4. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jos.2018.06.003
- ↑ Habegger A. The Knee. 2023 Mar.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 McHugh C. Hypermobile lateral Meniscus [Internet]. Orthosports. 2022 [cited 2023 Mar 28]. Available from: https://orthosports.com.au/hypermobile_lateral_meniscus
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Van Steyn MO, Mariscalco MW, Pedroza AD, Smerek J, Kaeding CC, Flanigan DC. The hypermobile lateral meniscus: a retrospective review of presentation, imaging, treatment, and results. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc [Internet]. 2016;24(5):1555–9. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-3497-0
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Nakashima H, Takahara Y, Uchida Y, Kato H, Itani S, Tsujimura Y, et al. Hypermobile anterior horn of the lateral meniscus: A case report and literature review. Case Rep Orthop [Internet]. 2020;2020:8870156. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2020/8870156
- ↑ Steinbacher G, Alentorn-Geli E, Alvarado-Calderón M, Barastegui D, Álvarez-Díaz P, Cugat R. Meniscal fixation is a successful treatment for hypermobile lateral meniscus in soccer players. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc [Internet]. 2019;27(2):354–60. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00167-018-5080-6
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Spang RC III, Nasr MC, Mohamadi A, DeAngelis JP, Nazarian A, Ramappa AJ. Rehabilitation following meniscal repair: a systematic review. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med [Internet]. 2018;4(1):e000212. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmjsem-2016-000212
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Rehabilitation protocol for arthroscopic meniscal repair [Internet]. Massgeneral.org. [cited 2023 Mar 28]. Available from: https://www.massgeneral.org/assets/mgh/pdf/orthopaedics/sports-medicine/physical-therapy/rehabilitation-protocol-for-meniscus-repair.pdf