Moro Reflex: Difference between revisions
(added headings and info) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
[[File:Moro Reflex 1.jpg|right|frameless]] | [[File:Moro Reflex 1.jpg|right|frameless]] | ||
It was first described by Ernst Moro in 1918 and is a primitive infantile reflex. It is easily confused with startle pattern or reflex. This reflex is said to be of labyrinthine origin. | It was first described by Ernst Moro in 1918 and is a primitive infantile reflex. It is easily confused with a startle pattern or reflex. This reflex is said to be of labyrinthine origin. | ||
== Position == | == Position == | ||
'''Head Drop Method''': Supine position. Suspend the baby horizontally, in a symmetrical supine position such that the therapist's one hand behind the chest and other supports the head. The infant's head should be in midline position. | '''Head Drop Method''': Supine position. Suspend the baby horizontally, in a symmetrical supine position such that the therapist's one hand behind the chest and the other supports the head. The infant's head should be in the midline position. | ||
It is important to guarantee that both the infant's hands are open at the moment of elicitation of the reflex so as not to produce any asymmetrical response. Also ensure that the baby is not crying and awake during the procedure. | It is important to guarantee that both the infant's hands are open at the moment of elicitation of the reflex so as not to produce any asymmetrical response. Also, ensure that the baby is not crying and awake during the procedure. | ||
'''Baby Drop Method''': Same as head drop method. | '''Baby Drop Method''': Same as the head drop method. | ||
== Stimulus == | == Stimulus == | ||
'''Head Drop Method:''' Dropping of head of the baby by few | '''Head Drop Method:''' Dropping of the head of the baby by a few centimetres. | ||
'''Baby Drop Method''': | '''Baby Drop Method''': The therapist lowers their hands rapidly about 10 to 20 cm and brings them to an abrupt halt. | ||
'''Subcutaneous Stimulus''': Painful stimulus to the subcutaneous tissue of the epigastrium.( considered to be a more sensitive technique) | '''Subcutaneous Stimulus''': Painful stimulus to the subcutaneous tissue of the epigastrium.( considered to be a more sensitive technique) | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
== Duration == | == Duration == | ||
This reflex can be stimulated in all neonates during the first 12 weeks of age and disintegrates by 6 months of age. | This reflex can be stimulated in all neonates during the first 12 weeks of age and disintegrates by 6 months of age. | ||
{{#ev:youtube|PTz-iVI2mf4}} | |||
== Neural Mechanism == | == Neural Mechanism == | ||
This reflex is primarily elicited by the vestibular nuclei. It is mediated by brainstem and therefore its | This reflex is primarily elicited by the vestibular nuclei. It is mediated by the brainstem and therefore its centre seems to be in the lower region of the pons to the medulla. The efferent pathways of the response seem to originate in the vestibulospinal and/or reticulospinal neurons and the reflex movement is generated by the subcortical structures without cortical participation. | ||
== The Difference between Moro and Startle Reflex == | == The Difference between Moro and Startle Reflex == | ||
Revision as of 13:34, 30 June 2022
Introduction[edit | edit source]
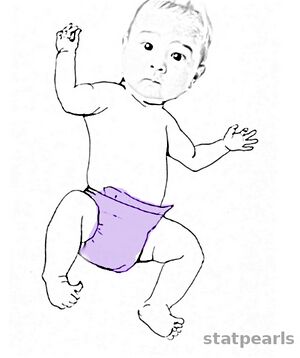
It was first described by Ernst Moro in 1918 and is a primitive infantile reflex. It is easily confused with a startle pattern or reflex. This reflex is said to be of labyrinthine origin.
Position[edit | edit source]
Head Drop Method: Supine position. Suspend the baby horizontally, in a symmetrical supine position such that the therapist's one hand behind the chest and the other supports the head. The infant's head should be in the midline position.
It is important to guarantee that both the infant's hands are open at the moment of elicitation of the reflex so as not to produce any asymmetrical response. Also, ensure that the baby is not crying and awake during the procedure.
Baby Drop Method: Same as the head drop method.
Stimulus[edit | edit source]
Head Drop Method: Dropping of the head of the baby by a few centimetres.
Baby Drop Method: The therapist lowers their hands rapidly about 10 to 20 cm and brings them to an abrupt halt.
Subcutaneous Stimulus: Painful stimulus to the subcutaneous tissue of the epigastrium.( considered to be a more sensitive technique)
Response[edit | edit source]
Normal Response[edit | edit source]
Initial Phase: Abduction of the upper extremities and extension of the arms. The fingers extend, and there is a slight extension of the neck and spine.
After Phase: Arms adduct and the hands come to the front of the body before returning to the infant's side.
Abnormal Response[edit | edit source]
Diminution of the reflex within 2 to 3 months of age.
Persistence of the response beyond 6 months of age.
Asymmetrical response.
Duration[edit | edit source]
This reflex can be stimulated in all neonates during the first 12 weeks of age and disintegrates by 6 months of age.
Neural Mechanism[edit | edit source]
This reflex is primarily elicited by the vestibular nuclei. It is mediated by the brainstem and therefore its centre seems to be in the lower region of the pons to the medulla. The efferent pathways of the response seem to originate in the vestibulospinal and/or reticulospinal neurons and the reflex movement is generated by the subcortical structures without cortical participation.