Coronary Artery Bypass Graft: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
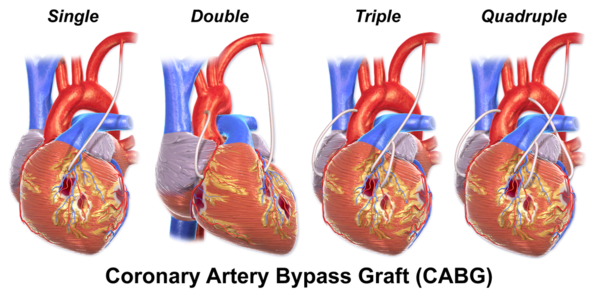
[[File:CABG All.png|right|frameless|598x598px]] | |||
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is a common surgical procedure for the treatment of myocardial ischemia. The surgeon uses an artery or vein of the patient to anastomose from the aorta to the distal end of the stenosis, so that blood flow can directly supply the distal myocardium through the graft, thereby achieving the purpose of treating myocardial ischemia<ref>Li B, Mao B, Feng Y, Liu J, Zhao Z, Duan M, Liu Y. The Hemodynamic [https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphys.2021.503687/full Mechanism of FFR-Guided Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting.] Frontiers in Physiology. 2021;12.Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphys.2021.503687/full (accessed 20.5.2021)</ref>. | Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is a common surgical procedure for the treatment of myocardial ischemia. The surgeon uses an artery or vein of the patient to anastomose from the aorta to the distal end of the stenosis, so that blood flow can directly supply the distal myocardium through the graft, thereby achieving the purpose of treating myocardial ischemia<ref>Li B, Mao B, Feng Y, Liu J, Zhao Z, Duan M, Liu Y. The Hemodynamic [https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphys.2021.503687/full Mechanism of FFR-Guided Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting.] Frontiers in Physiology. 2021;12.Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphys.2021.503687/full (accessed 20.5.2021)</ref>. | ||
Image 1: 4 types of CABGs | |||
* Coronary artery bypass grafting remains one of the most commonly performed major surgeries, with well-established symptomatic and prognostic benefits in patients with multivessel and left main coronary artery disease. | * Coronary artery bypass grafting remains one of the most commonly performed major surgeries, with well-established symptomatic and prognostic benefits in patients with multivessel and left main coronary artery disease. | ||
Revision as of 08:09, 20 May 2021
Original Editor - Lucinda hampton
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Tahreem Tarique, Kim Jackson and Rucha Gadgil
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is a common surgical procedure for the treatment of myocardial ischemia. The surgeon uses an artery or vein of the patient to anastomose from the aorta to the distal end of the stenosis, so that blood flow can directly supply the distal myocardium through the graft, thereby achieving the purpose of treating myocardial ischemia[1].
Image 1: 4 types of CABGs
- Coronary artery bypass grafting remains one of the most commonly performed major surgeries, with well-established symptomatic and prognostic benefits in patients with multivessel and left main coronary artery disease.
- Despite an increasingly higher-risk profile of patients, outcomes have significantly improved over time, with significant reductions in operative mortality and perioperative complications. Five- and 10-year survival rates are ≈85% to 95% and 75%, respectively.
- A number of technical advances could further improve short- and long-term outcomes after coronary artery bypass grafting[2].
Sub Heading 2[edit | edit source]
Sub Heading 3[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Li B, Mao B, Feng Y, Liu J, Zhao Z, Duan M, Liu Y. The Hemodynamic Mechanism of FFR-Guided Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting. Frontiers in Physiology. 2021;12.Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphys.2021.503687/full (accessed 20.5.2021)
- ↑ Head SJ, Milojevic M, Taggart DP, Puskas JD. Current practice of state-of-the-art surgical coronary revascularization. Circulation. 2017 Oct 3;136(14):1331-45.Available from:https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/pdf/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.022572 (accessed 20.5.2021)
Original Editor - User Name
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Tahreem Tarique, Kim Jackson and Rucha Gadgil
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Sub Heading 2[edit | edit source]
Sub Heading 3[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x