Deep Brain Stimulation: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
[[File:Deep brain stimulation.jpeg|right|frameless|354x354px]] | |||
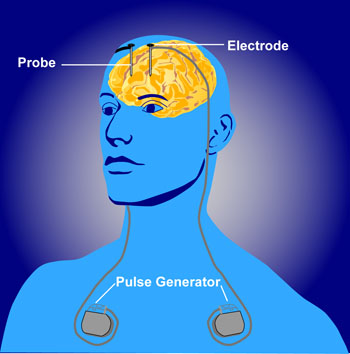
DBS involves the placement of electrodes into deep brain structures. Current is administered through these electrodes by an implanted power pack, which can be remotely controlled by the subject and adjusted by physicians. In essence, DBS is like a pacemaker for the brain<ref>The Conversation Do brain interventions to treat disease change the essence of who we are? Available from: https://theconversation.com/do-brain-interventions-to-treat-disease-change-the-essence-of-who-we-are-45943 (accessed 19.5.2021)</ref>. | |||
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is used in a variety of clinical settings, predominantly in patients with poorly controlled movement disorders. Although effective, its exact mode of function continues to be poorly understood<ref name=":0">Radiopedia Deep Brain Stimulation Available from: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/deep-brain-stimulation<nowiki/>(accessed 19.5.2021)</ref> . | Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is used in a variety of clinical settings, predominantly in patients with poorly controlled movement disorders. Although effective, its exact mode of function continues to be poorly understood<ref name=":0">Radiopedia Deep Brain Stimulation Available from: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/deep-brain-stimulation<nowiki/>(accessed 19.5.2021)</ref> . | ||
DBS is designed to alter the function of circuits in the brain brain. It has been used with varying degrees of success in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, dystonia, epilepsy, obsessive-compulsive disorder and even depression. | DBS is designed to alter the function of circuits in the brain brain. It has been used with varying degrees of success in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, dystonia, epilepsy, obsessive-compulsive disorder and even depression. | ||
DBS | Careful patient selection and target selection are essential if the procedure is to have good efficacy<ref name=":0" />. | ||
== Anatomy == | |||
The DBS apparatus consists of electrodes implanted adjacent to specific deep brain structures, which are then connected to a pacemaker-like machine (pulse generator) that is implanted on the chest wall, via a subcutaneous wire. Stimulation parameters are then relayed by a computer to the pulse generator, appropriating proper amplitudes, frequencies, and pulse width. Common structures targeted by DBS include the subthalamic nucleus (STN), globus pallidus interna (GPi), and the ventral intermediate nucleus of the thalamus (VIM). | |||
The precise mechanism of the resultant therapeutic effects of deep brain stimulation remains unclear. Imaging and physiologic studies corroborate the hypothesis that the ultimate effect of deep brain stimulation is the increase of the firing of the targeted neurons.<ref>Fariba K, Gupta V. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557847/ Deep Brain Stimulation.] StatPearls [Internet]. 2020 May 17.Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557847/ (accessed 19.5.2021)</ref> | |||
== Indications == | |||
1.Parkinson disease | |||
* subthalamic nucleus | |||
* pedunculopontine nucleus | |||
* globus pallidus (pars interna) | |||
* Severe essential tremor | |||
** ventral intermediate nucleus | |||
2. Dystonia (cervical dystonia and tardive dystonia) | |||
* globus pallidus (pars interna) | |||
* Cluster headaches | |||
** hypothalamus | |||
3. Chronic pain | |||
* thalamus | |||
* periaqueductal grey matter | |||
= | 4. Neuropsychiatric disorders: largely experimental<ref name=":0" /> | ||
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
Revision as of 07:52, 19 May 2021
Original Editor - Lucinda hampton
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Joseph Ayotunde Aderonmu and Pacifique Dusabeyezu
Introduction[edit | edit source]
DBS involves the placement of electrodes into deep brain structures. Current is administered through these electrodes by an implanted power pack, which can be remotely controlled by the subject and adjusted by physicians. In essence, DBS is like a pacemaker for the brain[1].
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is used in a variety of clinical settings, predominantly in patients with poorly controlled movement disorders. Although effective, its exact mode of function continues to be poorly understood[2] .
DBS is designed to alter the function of circuits in the brain brain. It has been used with varying degrees of success in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, dystonia, epilepsy, obsessive-compulsive disorder and even depression.
Careful patient selection and target selection are essential if the procedure is to have good efficacy[2].
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The DBS apparatus consists of electrodes implanted adjacent to specific deep brain structures, which are then connected to a pacemaker-like machine (pulse generator) that is implanted on the chest wall, via a subcutaneous wire. Stimulation parameters are then relayed by a computer to the pulse generator, appropriating proper amplitudes, frequencies, and pulse width. Common structures targeted by DBS include the subthalamic nucleus (STN), globus pallidus interna (GPi), and the ventral intermediate nucleus of the thalamus (VIM).
The precise mechanism of the resultant therapeutic effects of deep brain stimulation remains unclear. Imaging and physiologic studies corroborate the hypothesis that the ultimate effect of deep brain stimulation is the increase of the firing of the targeted neurons.[3]
Indications[edit | edit source]
1.Parkinson disease
- subthalamic nucleus
- pedunculopontine nucleus
- globus pallidus (pars interna)
- Severe essential tremor
- ventral intermediate nucleus
2. Dystonia (cervical dystonia and tardive dystonia)
- globus pallidus (pars interna)
- Cluster headaches
- hypothalamus
3. Chronic pain
- thalamus
- periaqueductal grey matter
4. Neuropsychiatric disorders: largely experimental[2]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ The Conversation Do brain interventions to treat disease change the essence of who we are? Available from: https://theconversation.com/do-brain-interventions-to-treat-disease-change-the-essence-of-who-we-are-45943 (accessed 19.5.2021)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Radiopedia Deep Brain Stimulation Available from: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/deep-brain-stimulation(accessed 19.5.2021)
- ↑ Fariba K, Gupta V. Deep Brain Stimulation. StatPearls [Internet]. 2020 May 17.Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557847/ (accessed 19.5.2021)