Extensor Digitorum Communis: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | <div class="editorbox"> | ||
'''Original Editor '''- [[User:Simisola Ajeyalemi |Simisola Ajeyalemi]] | '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Simisola Ajeyalemi |Simisola Ajeyalemi]] | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
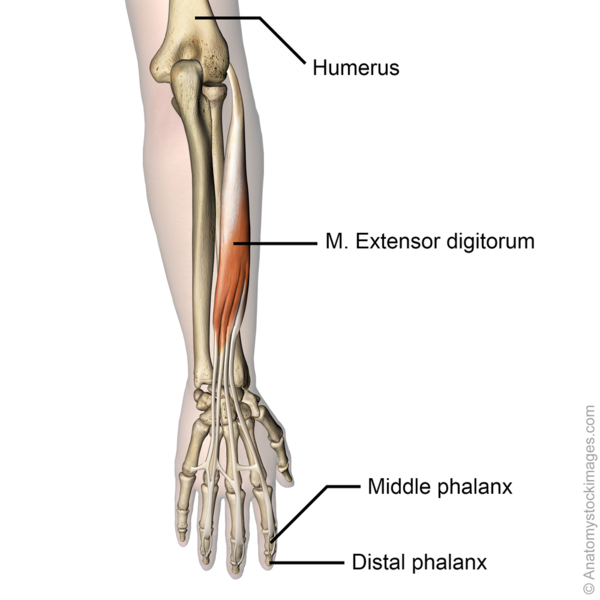
The extensor digitorum communis is a superficial extensor muscle located in the posterior compartment of the forearm. <ref name=":0">Moore, KL, Dalley, AF, Agur, AM. Clinically oriented anatomy. 7th ed. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2014</ref> It shares a common synovial tendon sheaths along with other extensor muscles which helps to reduce friction between the tendon and the surrounding structures. As it courses the dorsum of the hand, the extensor digitorum communis muscle spreads out into four (4) flat tendons deep to the extensor retinaculum to the medial four fingers. | The extensor digitorum communis is a superficial extensor [[muscle]] located in the posterior compartment of the forearm. <ref name=":0">Moore, KL, Dalley, AF, Agur, AM. Clinically oriented anatomy. 7th ed. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2014</ref> It shares a common synovial tendon sheaths along with other extensor muscles which helps to reduce friction between the tendon and the surrounding structures. As it courses the dorsum of the hand, the extensor digitorum communis muscle spreads out into four (4) flat [[Tendon Anatomy|tendons]] deep to the extensor retinaculum to the medial four fingers. | ||
[[Image:Extensor Digitorum Communis Muscle.png|right|600px]] | [[Image:Extensor Digitorum Communis Muscle.png|right|600px]] | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
Primarily, the extensor digitorum communis extends medial four digits at the metacarpophalangeal joints and secondarily at the interphalangeal joints. <ref name=":0" /> It also acts to extend the [[Wrist and Hand|wrist]] joint. | Primarily, the extensor digitorum communis extends medial four digits at the metacarpophalangeal joints and secondarily at the interphalangeal joints. <ref name=":0" /> It also acts to extend the [[Wrist and Hand|wrist]] joint. | ||
{{#ev:youtube|aylgUWAuYBk}}<ref>Extensor Digitorum Communis - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim. Available from: | {{#ev:youtube|aylgUWAuYBk}}<ref>Extensor Digitorum Communis - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aylgUWAuYBk [last accessed 02/10/2020]</ref> | ||
== Clinical relevance == | == Clinical relevance == | ||
The extensor digitorum communis has been found to play a role in the pathology of [[Lateral Epicondylitis|lateral epicondylitis]]<ref>Fairbank SM, Corlett RJ. The role of the extensor digitorum communis muscle in lateral epicondylitis. J Hand Surg Br. 2002 Oct;27(5):405-9. doi: 10.1054/jhsb.2002.0761. PMID: 12367535.</ref> | The extensor digitorum communis has been found to play a role in the pathology of [[Lateral Epicondylitis|lateral epicondylitis]]<ref>Fairbank SM, Corlett RJ. The role of the extensor digitorum communis muscle in lateral epicondylitis. J Hand Surg Br. 2002 Oct;27(5):405-9. doi: 10.1054/jhsb.2002.0761. PMID: 12367535.</ref> because of its role in the extension of the middle finger which reproduces pain on resisted extension. It has been suggested that pathology in the extensor digitorum communis may be the basis of a positive [[Maudsley's test]]. | ||
== Assessment == | == Assessment == | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
<div class="col-md-6"> {{#ev:youtube|Qs7h8Lk1aKg|250}} </div> | <div class="col-md-6"> {{#ev:youtube|Qs7h8Lk1aKg|250}}<ref>Manual Muscle Test for Extensor Digitorum Communis. Available from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qs7h8Lk1aKg [last accessed 20/10/2020]</ref> | ||
<div class="col-md-6"> {{#ev:youtube|BaxgmHT_2eQ|250}} </div> | </div> | ||
<div class="col-md-6"> {{#ev:youtube|BaxgmHT_2eQ|250}}<ref>Physio Tutors- Maudsley's Lateral Epicondylitis Test⎟Lateral Epicondylitis or Tennis Elbow. Available from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BaxgmHT_2eQ [last accessed 20/10/2020] | |||
</ref> | |||
</div> | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
== | See [[Extensor Tendon Injuries of the Hand]] for more information on injury to the extensor digitorum communis tendon. | ||
== References == | |||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
| Line 43: | Line 47: | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] | [[Category:Anatomy]] | ||
[[Category:Muscles]] | [[Category:Muscles]] | ||
[[Category:Hand - Muscles]] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:13, 18 December 2020
Original Editor - Simisola Ajeyalemi
Top Contributors - Simisola Ajeyalemi and Manisha Shrestha
Description[edit | edit source]
The extensor digitorum communis is a superficial extensor muscle located in the posterior compartment of the forearm. [1] It shares a common synovial tendon sheaths along with other extensor muscles which helps to reduce friction between the tendon and the surrounding structures. As it courses the dorsum of the hand, the extensor digitorum communis muscle spreads out into four (4) flat tendons deep to the extensor retinaculum to the medial four fingers.
Origin[edit | edit source]
Lateral epicondyle of the humerus at the common extensor tendon.
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Inserts into the extensor expansion of the medial four digits.
Nerve[edit | edit source]
Deep branch of radial nerve
Artery[edit | edit source]
The extensor digitorum communis is supplied by the posterior interosseous artery and the radial recurrent artery.
Function[edit | edit source]
Primarily, the extensor digitorum communis extends medial four digits at the metacarpophalangeal joints and secondarily at the interphalangeal joints. [1] It also acts to extend the wrist joint.
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
The extensor digitorum communis has been found to play a role in the pathology of lateral epicondylitis[3] because of its role in the extension of the middle finger which reproduces pain on resisted extension. It has been suggested that pathology in the extensor digitorum communis may be the basis of a positive Maudsley's test.
Assessment[edit | edit source]
See Extensor Tendon Injuries of the Hand for more information on injury to the extensor digitorum communis tendon.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Moore, KL, Dalley, AF, Agur, AM. Clinically oriented anatomy. 7th ed. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2014
- ↑ Extensor Digitorum Communis - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aylgUWAuYBk [last accessed 02/10/2020]
- ↑ Fairbank SM, Corlett RJ. The role of the extensor digitorum communis muscle in lateral epicondylitis. J Hand Surg Br. 2002 Oct;27(5):405-9. doi: 10.1054/jhsb.2002.0761. PMID: 12367535.
- ↑ Manual Muscle Test for Extensor Digitorum Communis. Available from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qs7h8Lk1aKg [last accessed 20/10/2020]
- ↑ Physio Tutors- Maudsley's Lateral Epicondylitis Test⎟Lateral Epicondylitis or Tennis Elbow. Available from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BaxgmHT_2eQ [last accessed 20/10/2020]