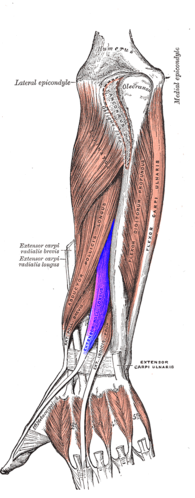
Extensor Indicis Proprius: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
Extensor Indicis Propius is a narrow elongated [[Muscle|skeletal muscle]] situated in deep layer of posterior compartment of the forearm along with Supinator, Abductor Pollicis Longus, Extensor Pollicis Longus and Brevis. It is responsible for the movement of the index finger.<ref name=":0">Drake R, Vogl AW, Mitchell AW. Gray's Anatomy for Students E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2009 Apr 4.</ref> A few variations of Extensor Indicis muscle is observed in people which are classified as<ref>Komiyama M, Nwe TM, Toyota N, Shimada Y. Variations of the extensor indicis muscle and tendon. The Journal of Hand Surgery: British & European Volume. 1999 Oct 1;24(5):575-8.</ref> - | Extensor Indicis Propius is a narrow elongated [[Muscle|skeletal muscle]] situated in deep layer of posterior compartment of the forearm along with [[Supinator]], Abductor Pollicis Longus, [[Extensor Pollicis Longus]] and [[Extensor Pollicis Brevis|Brevis]]. It is responsible for the movement of the index finger.<ref name=":0">Drake R, Vogl AW, Mitchell AW. Gray's Anatomy for Students E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2009 Apr 4.</ref> A few variations of Extensor Indicis muscle is observed in people which are classified as<ref>Komiyama M, Nwe TM, Toyota N, Shimada Y. Variations of the extensor indicis muscle and tendon. The Journal of Hand Surgery: British & European Volume. 1999 Oct 1;24(5):575-8.</ref> - | ||
* Type 1 - An additional tendon slip from the Extensor Indicis tendon | * Type 1 - An additional tendon slip from the Extensor Indicis tendon | ||
* Type 2 - An Extensor Indicis Radialis or Extensor Pollicis et Indicis Accessorius | * Type 2 - An Extensor Indicis Radialis or Extensor Pollicis et Indicis Accessorius | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
=== Origin === | === Origin === | ||
[[File:Extensor pollicis longus muscle.png|thumb|Next to the highlighted muscle (Right) is Extensor Indicis Propius|center|500x500px]] | [[File:Extensor pollicis longus muscle.png|thumb|Next to the highlighted muscle (Right) is Extensor Indicis Propius|center|500x500px]] | ||
It originates from the posterior surface of Ulna (distal to Extensor Pollicis Longus muscle) and interosseous membrane.<ref name=":0" /> | It originates from the posterior surface of [[Ulna]] (distal to Extensor Pollicis Longus muscle) and interosseous membrane.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
=== Insertion === | === Insertion === | ||
It inserts on the base of the second proximal phalange and into the tendon of Extensor Digitorum.<ref>Cael C. Functional anatomy: musculoskeletal anatomy, kinesiology, and palpation for manual therapists. Jones & Bartlett Learning; 2020 Aug 3.</ref> | It inserts on the base of the second proximal phalange and into the tendon of [[Extensor Digitorum Communis|Extensor Digitorum]].<ref>Cael C. Functional anatomy: musculoskeletal anatomy, kinesiology, and palpation for manual therapists. Jones & Bartlett Learning; 2020 Aug 3.</ref> | ||
{{#ev:youtube|QY1RMlAv6oU|300}}<ref>Kenhub - Learn Human Anatomy. Extensor Indicis Muscle - Origins & Function - Human Anatomy | Kenhub. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QY1RMlAv6oU [last accessed 19/10/2020]</ref> | {{#ev:youtube|QY1RMlAv6oU|300}}<ref>Kenhub - Learn Human Anatomy. Extensor Indicis Muscle - Origins & Function - Human Anatomy | Kenhub. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QY1RMlAv6oU [last accessed 19/10/2020]</ref> | ||
=== Nerve === | === Nerve === | ||
It is innervated by the Posterior Interosseous nerve which is a deep branch of Radial nerve ( 7th and 8th cervical nerve root).<ref name=":0" /> | It is innervated by the Posterior Interosseous nerve which is a deep branch of [[Radial nerve]] ( 7th and 8th cervical nerve root).<ref name=":0" /> | ||
=== Artery === | === Artery === | ||
Revision as of 16:28, 19 October 2020
Original Editor - Shreya Pavaskar
Top Contributors - Shreya Pavaskar and Shaimaa Eldib
Description[edit | edit source]
Extensor Indicis Propius is a narrow elongated skeletal muscle situated in deep layer of posterior compartment of the forearm along with Supinator, Abductor Pollicis Longus, Extensor Pollicis Longus and Brevis. It is responsible for the movement of the index finger.[1] A few variations of Extensor Indicis muscle is observed in people which are classified as[2] -
- Type 1 - An additional tendon slip from the Extensor Indicis tendon
- Type 2 - An Extensor Indicis Radialis or Extensor Pollicis et Indicis Accessorius
- Type 3 - An Extensor Medii Proprius with or without Extensor Medii Brevis
- Type 4 - An Extensor Indicis Radialis and Extensor Medii Proprius.
Origin[edit | edit source]
It originates from the posterior surface of Ulna (distal to Extensor Pollicis Longus muscle) and interosseous membrane.[1]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
It inserts on the base of the second proximal phalange and into the tendon of Extensor Digitorum.[3]
Nerve[edit | edit source]
It is innervated by the Posterior Interosseous nerve which is a deep branch of Radial nerve ( 7th and 8th cervical nerve root).[1]
Artery[edit | edit source]
It is supplied by the Posterior Interosseous branch of the Ulnar artery and perforating branches of the Anterior Interosseous artery.[5]
Function[edit | edit source]
- The primary function of Extensor Indicis Propius is the extension of second digit at metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints.
- It may assist in wrist extension.
- It assists in abducting the index finger.
- It may assist in slight supination of forearm.
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
Assessment[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Drake R, Vogl AW, Mitchell AW. Gray's Anatomy for Students E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2009 Apr 4.
- ↑ Komiyama M, Nwe TM, Toyota N, Shimada Y. Variations of the extensor indicis muscle and tendon. The Journal of Hand Surgery: British & European Volume. 1999 Oct 1;24(5):575-8.
- ↑ Cael C. Functional anatomy: musculoskeletal anatomy, kinesiology, and palpation for manual therapists. Jones & Bartlett Learning; 2020 Aug 3.
- ↑ Kenhub - Learn Human Anatomy. Extensor Indicis Muscle - Origins & Function - Human Anatomy | Kenhub. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QY1RMlAv6oU [last accessed 19/10/2020]
- ↑ Revol MP, Lantieri L, Loy S, Guérin-Surville H. Vascular anatomy of the forearm muscles: a study of 50 dissections. Plastic and reconstructive surgery. 1991 Dec;88(6):1026-33.
- ↑ nabil ebraheim. Conditions Affecting Dorsal Wrist Compartments - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZKGB2sFaJzA [last accessed 19/10/2020]
- ↑ Ball State Athletic Training. Extensor Digitorum, Indicis, & Minimi MMT. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SaMga26WYRg [last accessed 19/10/2020]